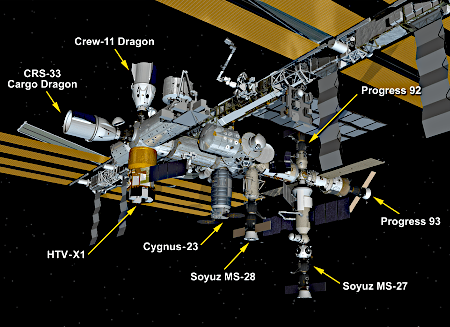
Link here. In announcing last week the European Space Agency’s (ESA) budget for the next three years, along with its general overall goals, the European council (dubbed CM-25) also apparently committed about $1.45 billion to its “European Launcher Challenge”, a program created in 2023 and designed to encourage the development of new European rockets, owned and operated by independent competing startups.
The article at the link provides a good overall summary of major increase in funding for this program, including which ESA countries are contributing the most and why. The key quote however is this:
In July 2025, ESA shortlisted Isar Aerospace, Rocket Factory Augsburg, PLD Space, MaiaSpace, and Orbex to proceed to the initiative’s next phase. It then began discussions with the host country of each company to assess its willingness to contribute to that company’s participation in the European Launcher Challenge.
During his post-CM25 address, ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher revealed that Member States had committed double the anticipated amount for the European Launcher Challenge, with the final figure exceeding €900 million. While the funding model’s structure suggests that only the UK, Spain, France, and Germany contributed, post-CM25 disclosures have indicated that a few additional countries also committed funds to the programme.
Germany appears to be the biggest contributor, supplying more than a third of the total fund ($422 million). This isn’t surprising, since Germany also has the most rocket startups, three, two of which are on that shortlist (Rocket Factory and Isar). Spain is next with a contribution of $196 million, aimed helping the rocket startup PLD. The UK is next, also contributing $196 million, likely to be used to support its Orbex startup that wants to launch from its Saxavord spaceport in the Shetland Islands.
A variety of other ESA nations, the Czech Republic, the Netherlands, and Norway, have also outlined their contributions, for a variety of space-related startups unrelated to rockets.
France also appears to have donated a significant amount, but has not made that number public. Its MaiaSpace startup is one on that shortlist above, but France also has one or two other rocket startups that might eventually qualify for aid.
The bottom line is that ESA here is committing funding to aid the development of rockets and space infrastructure that it won’t own or control, a major shift from its past policy of owning and controlling everything through its Arianespace pseudo-commercial company, what I call the Soviet- or government-run model. Instead, these ESA nations are going to help fund a range of competing private rockets, which will own the rockets and operate them for profit. ESA will simply become one of their customers, following the capitalism model that the U.S. switched to in the previous decade.
This increased commitment to capitalism in the ESA suggests that we should see some real progress by these startups in the next three years.
If you think the launch records being set this year are breath-taking, you ain’t seen nothin’ yet.