What might be the weirdest crater on Mars
Cool image time! The picture to the right is taken from a global mosaic created from images taken by the wide-view context camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The original source image was probably a photograph taken on February 15, 2020.
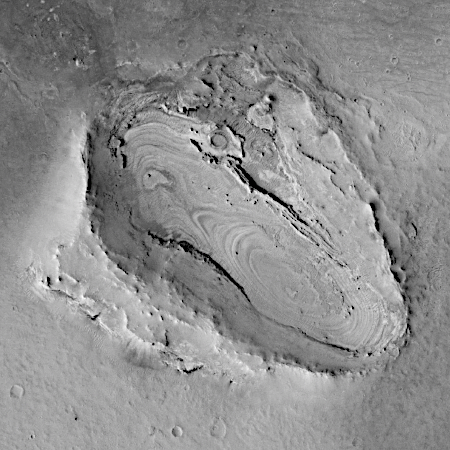
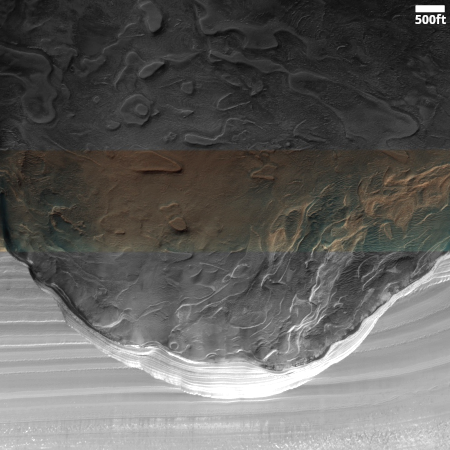
I normally begin with an image from MRO’s high resolution camera, but the only images that camera took of this crater did not show it entirely. This context camera shows it in all its glory, what to my eye appears to be one of the weirdest craters I’ve seen on Mars.
First, note its oblong shape — 5.5 miles long and 3.7 miles wide — which appears to narrow to the southeast. It certainly appears that if this crater was caused by an impact, the bolide came in at a very low angle from the northwest, plowing this 700-foot-deep divot as it drove itself into the ground. Research has shown that an impact has to come in almost sideways to do this. Even at slightly higher angles the resulting craters will still appear round.
But wait, there’s more!
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right is taken from a global mosaic created from images taken by the wide-view context camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The original source image was probably a photograph taken on February 15, 2020.
I normally begin with an image from MRO’s high resolution camera, but the only images that camera took of this crater did not show it entirely. This context camera shows it in all its glory, what to my eye appears to be one of the weirdest craters I’ve seen on Mars.
First, note its oblong shape — 5.5 miles long and 3.7 miles wide — which appears to narrow to the southeast. It certainly appears that if this crater was caused by an impact, the bolide came in at a very low angle from the northwest, plowing this 700-foot-deep divot as it drove itself into the ground. Research has shown that an impact has to come in almost sideways to do this. Even at slightly higher angles the resulting craters will still appear round.
But wait, there’s more!
» Read more