InSight shut down temporarily because of lack of power
Because a dust storm has caused a further decline in the power being generated by InSight’s solar panels, the science team has decided to put the lander into safe mode for the next two weeks in the hope that the air will then clear, allowing its power levels to rise.
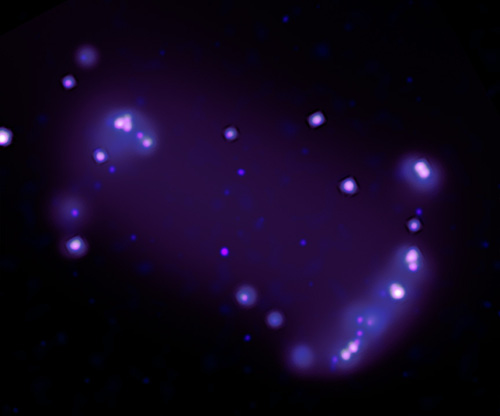
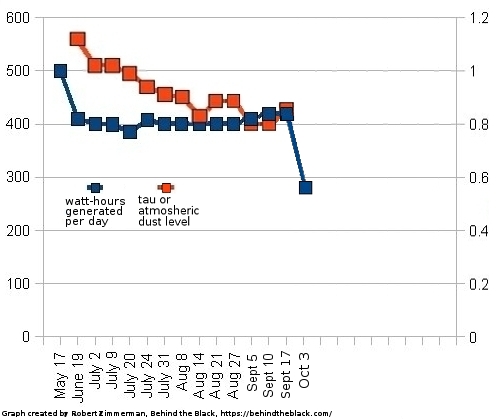
The graph to the right shows that drop. From the press release:
By Monday, Oct. 3, the storm had grown large enough and was lofting so much dust that the thickness of the dusty haze in the Martian atmosphere had increased by nearly 40% around InSight. With less sunlight reaching the lander’s panels, its energy fell from 425 watt-hours per Martian day, or sol, to just 275 watt-hours per sol.
InSight’s seismometer has been operating for about 24 hours every other Martian day. But the drop in solar power does not leave enough energy to completely charge the batteries every sol. At the current rate of discharge, the lander would be able to operate only for several weeks. So to conserve energy, the mission will turn off InSight’s seismometer for the next two weeks.
The real problem however is the dust covering the solar panels. If that dust gets thicker due to this storm, the lander will not recover when they power it up in two weeks. It will still generate electricity at this low number, making future operations likely impossible.

Because a dust storm has caused a further decline in the power being generated by InSight’s solar panels, the science team has decided to put the lander into safe mode for the next two weeks in the hope that the air will then clear, allowing its power levels to rise.
The graph to the right shows that drop. From the press release:
By Monday, Oct. 3, the storm had grown large enough and was lofting so much dust that the thickness of the dusty haze in the Martian atmosphere had increased by nearly 40% around InSight. With less sunlight reaching the lander’s panels, its energy fell from 425 watt-hours per Martian day, or sol, to just 275 watt-hours per sol.
InSight’s seismometer has been operating for about 24 hours every other Martian day. But the drop in solar power does not leave enough energy to completely charge the batteries every sol. At the current rate of discharge, the lander would be able to operate only for several weeks. So to conserve energy, the mission will turn off InSight’s seismometer for the next two weeks.
The real problem however is the dust covering the solar panels. If that dust gets thicker due to this storm, the lander will not recover when they power it up in two weeks. It will still generate electricity at this low number, making future operations likely impossible.