Click for original.
Click for interactive map
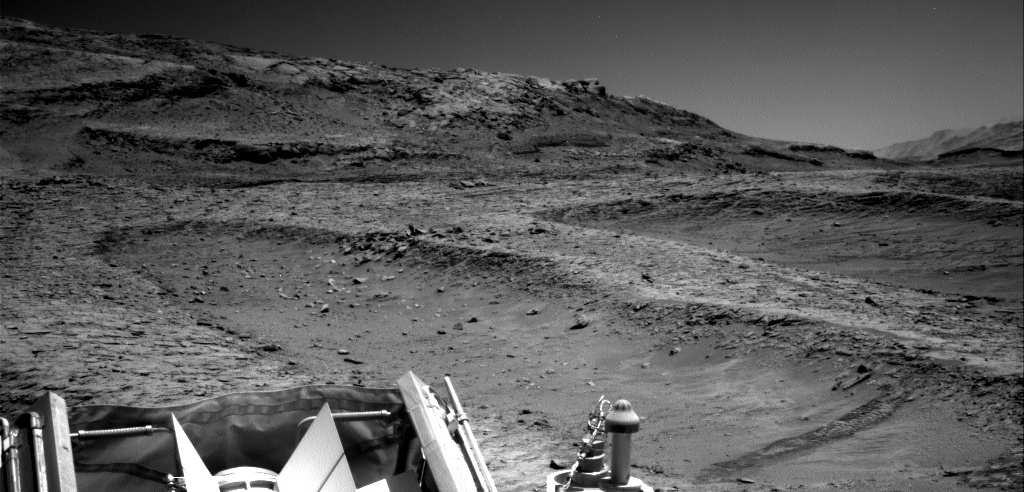
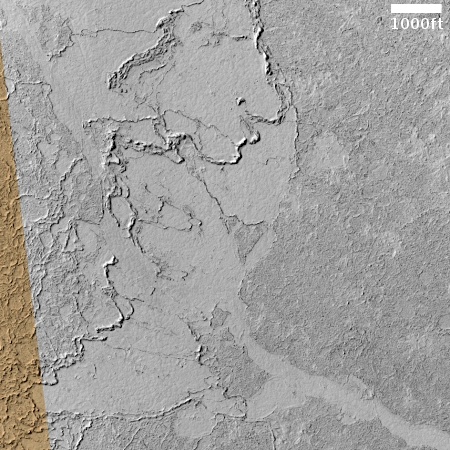
In reviewing the pictures downloaded today by the Mars rover Curiosity, I noticed something very intriguing in the pictures taken by rover’s two navigation cameras. One such picture is above, taken by the right navigation camera and looking west across the boxwork ridges that Curiosity has been traversing for the past two months. You can see two such ridges in the right foreground, cutting diagonally from left to right.
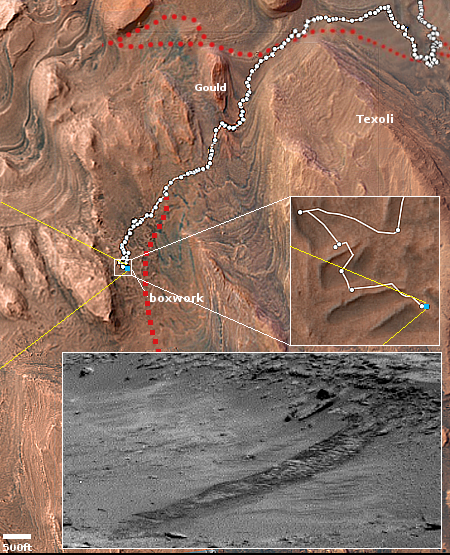
The overview map to the right gives the context, with the blue dot marking Curiosity’s position. The white and red dotted lines indicate its actual and planned routes respectively, with the top inset zooming in to show the recent travels more clearly. The yellow lines show the approximate area covered by the picture above.
Note the dark streak in the lower right of the picture. The bottom inset on the overview map shows this streak more closely. To my eye, it strongly resembles a slope streak, a strange geological feature unique to Mars.
If I am right, expect the rover team to focus in on this streak. The cause of slope streaks remains unknown. From orbit, the streaks look like avalanches at first glance, but they don’t change the topography, have no debris pile at their base, and sometimes even travel up and over rises as they head downhill. They can occur randomly throughout the year, can be bright or dark, can occur anywhere, and fade with time.
There are a number of theories (see here, here, and here) attempting to explain their cause, but none has been confirmed. If this is a streak, it will be the first that any scientist can see up close.
It is also very likely my guess is wrong, and this is not a streak. Stay tuned for updates.









