Click for full resolution. For original images go here and here.
Click for interactive map.
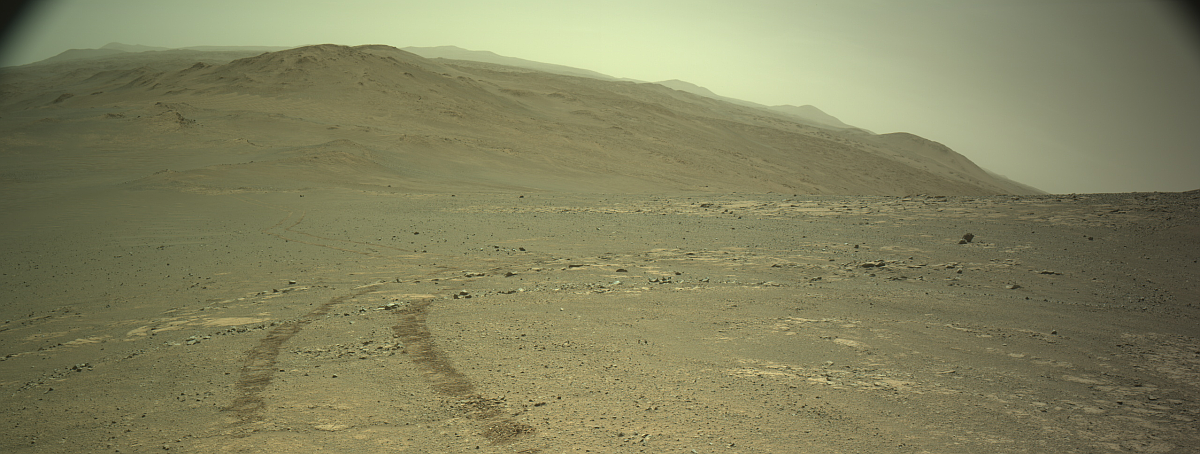
Cool image time! The panorama above, reduced and sharpened to post here, was created using two pictures taken on August 28, 2025 by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Perseverance (here and here).
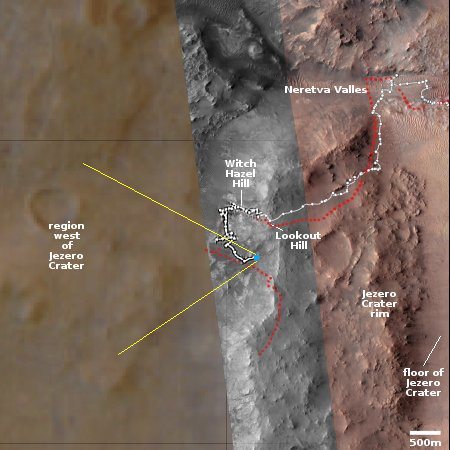
The blue dot on the overview map to the right marks Perseverance’s location when it took these pictures. The yellow lines indicate the approximate area covered by the panorama. The red dotted line indicates the rover’s planned route, with the white dotted line its actual travels.
The recent geological research focused on the lighter-colored ridge on the right center, dubbed Soroya. From the August 27, 2025 update by the science team:
Soroya was first picked out from orbital images as a target of interest because, as can be seen in the above image, it appears as a much lighter color compared to the surroundings. In previous landscape images from the surface, Mars 2020 scientists have been able to pick out the light-toned Soryoa outcrop, and they noted it forms a ridge-like structure, protruding above the surface. Soroya was easily identifiable from rover images as Perseverance approached since it indeed rises above the surrounding low-lying terrain.
The view is looking downhill away from Jezero Crater. The curve of the horizon is an artifact of the navigation camera’s wide view, accentuated by the slope that the rover sits on. The low resolution of this western region on the overview map is because the science team has not yet had Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) get highest resolution pictures there yet.
Note the utter barrenness of this terrain. This is Mars, a lifeless world that has only the future potential for life, once we humans start to colonize it. Whether there was ever any past life remains uncertain, but the nature of its terrain as seen by both Perseverance and Curiosity suggests strongly that past life never existed, or if it did it barely survived and was quickly wiped out, a long time ago.