Portugal issues spaceport license to Santa Maria Island
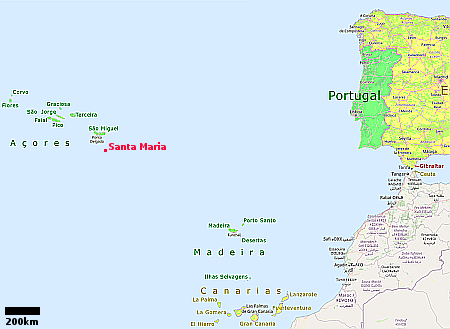
Portugal today issued a spaceport license to the Atlantic Spaceport Consortium (ASC) that wishes to build an orbital spaceport on the island of Santa Maria in the Azores, located about 900 miles west of the mainland.
On 13 August, ASC and the Portuguese Space Agency announced in a joint statement that the consortium had received a licence to operate a launch site on the island. The licence was issued by the country’s Autoridade Nacional de Comunicações (ANACOM), the entity acting as Portugal’s space authority. The licence is valid for five years and does not cover the launch operations themselves, which will be subject to a separate licensing process on a per-launch basis.
ASC has already conducted two demonstration suborbital launches there. In addition, it has signed a deal with the Polish rocket startup SpaceForest for additional suborbital launches.
This location is excellent for orbital launches, though getting rockets to it is an extra cost that will at least initially limit its appeal. Either way, it appears the Portuguese government does not wish to stand in the way of progress, and has been moving fast to clear away the red tape.

Portugal today issued a spaceport license to the Atlantic Spaceport Consortium (ASC) that wishes to build an orbital spaceport on the island of Santa Maria in the Azores, located about 900 miles west of the mainland.
On 13 August, ASC and the Portuguese Space Agency announced in a joint statement that the consortium had received a licence to operate a launch site on the island. The licence was issued by the country’s Autoridade Nacional de Comunicações (ANACOM), the entity acting as Portugal’s space authority. The licence is valid for five years and does not cover the launch operations themselves, which will be subject to a separate licensing process on a per-launch basis.
ASC has already conducted two demonstration suborbital launches there. In addition, it has signed a deal with the Polish rocket startup SpaceForest for additional suborbital launches.
This location is excellent for orbital launches, though getting rockets to it is an extra cost that will at least initially limit its appeal. Either way, it appears the Portuguese government does not wish to stand in the way of progress, and has been moving fast to clear away the red tape.