Former astronaut once again blasts NASA decision to fly Artemis-2 manned
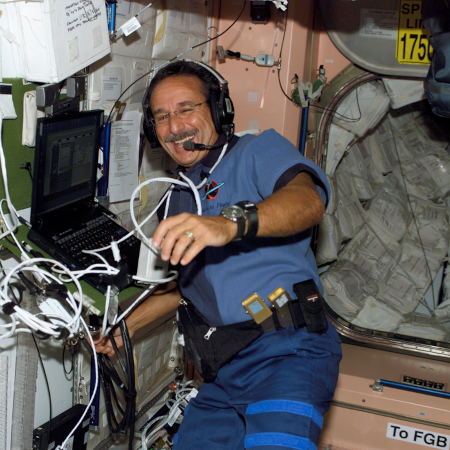

Charles Camarda on the first shuttle flight
after the Columbia failure.
The opposition to NASA’s decision to fly humans in the Orion capsule around the Moon with a questionable heat shield continues. Charles Camarda, an engineer and former NASA astronaut who has repeatedly expressed concerns about that heat shield and had been invited to attend the review meeting that NASA administrator Isaacman had arranged to ease his concerns, has now revealed his concerns were not eased in the slightest by that meeting, and that the Ars Technica article by Eric Berger that suggested otherwise was wrong, and that he is still “outraged” at NASA’s bad engineering decisions.
The rage you witnessed was my observing the exact behaviors used to construct risk and flight rationale which caused both Challenger and Columbia Accidents. Using “tools” inappropriately and then claiming results to be “Conservative.” Not to mention the reliance on Monte Carlo simulations to predict failure probabilities which were also proven to be inaccurate by orders of magnitude in my book “Mission Out of Control” which you claim to have read.
I suggest, in the spirit of transparency, you should ask NASA to release just the “Findings” of NESC Report TI-23-01849 Volume I. Finding 1 states the analysis cannot accurately predict crack initiation and propagation at flight conditions. And there was so much more which was conveniently not presented.
In other words, he finds NASA’s engineering claims that Orion’s heat shield will work using a different less stressful return trajectory as it dives back into the atmosphere about 25,000 mph to be false and untrustworthy. Worse, he sees it as proof that this is a continuation of the same culture at NASA that resulted in the Columbia failure.
Some of the exact same people responsible for failing to understand the shortcomings of the Crater Analysis tool (used tiny pieces of foam impacts to Shuttle tiles to predict a strike from a piece of foam which was 6000 larger and which caused the Columbia Accident) were on the Artemis Tiger Team now claiming they could predict the outcome of the Orion heatshield using a tool (similar to CRATER) called the Crack Identification Tool (CIT) which was also not physics based and relied on predictions of the key paramenter, permeability, which they claim to be the “root” cause, pressure, to vary by three orders of magnitude (that’s over 1000x).
In defense of NASA, those engineers had also presented data that showed Orion’s hull was strong enough to survive re-entry, even if the heat shield failed entirely. It is unclear if Camarda’s objections here apply to that data as well.
Regardless, his strong public disagreement with NASA on this once again raises serious questions about the upcoming manned Artemis-2 mission, set to launch sometime in the February to March time frame.

Charles Camarda on the first shuttle flight
after the Columbia failure.
The opposition to NASA’s decision to fly humans in the Orion capsule around the Moon with a questionable heat shield continues. Charles Camarda, an engineer and former NASA astronaut who has repeatedly expressed concerns about that heat shield and had been invited to attend the review meeting that NASA administrator Isaacman had arranged to ease his concerns, has now revealed his concerns were not eased in the slightest by that meeting, and that the Ars Technica article by Eric Berger that suggested otherwise was wrong, and that he is still “outraged” at NASA’s bad engineering decisions.
The rage you witnessed was my observing the exact behaviors used to construct risk and flight rationale which caused both Challenger and Columbia Accidents. Using “tools” inappropriately and then claiming results to be “Conservative.” Not to mention the reliance on Monte Carlo simulations to predict failure probabilities which were also proven to be inaccurate by orders of magnitude in my book “Mission Out of Control” which you claim to have read.
I suggest, in the spirit of transparency, you should ask NASA to release just the “Findings” of NESC Report TI-23-01849 Volume I. Finding 1 states the analysis cannot accurately predict crack initiation and propagation at flight conditions. And there was so much more which was conveniently not presented.
In other words, he finds NASA’s engineering claims that Orion’s heat shield will work using a different less stressful return trajectory as it dives back into the atmosphere about 25,000 mph to be false and untrustworthy. Worse, he sees it as proof that this is a continuation of the same culture at NASA that resulted in the Columbia failure.
Some of the exact same people responsible for failing to understand the shortcomings of the Crater Analysis tool (used tiny pieces of foam impacts to Shuttle tiles to predict a strike from a piece of foam which was 6000 larger and which caused the Columbia Accident) were on the Artemis Tiger Team now claiming they could predict the outcome of the Orion heatshield using a tool (similar to CRATER) called the Crack Identification Tool (CIT) which was also not physics based and relied on predictions of the key paramenter, permeability, which they claim to be the “root” cause, pressure, to vary by three orders of magnitude (that’s over 1000x).
In defense of NASA, those engineers had also presented data that showed Orion’s hull was strong enough to survive re-entry, even if the heat shield failed entirely. It is unclear if Camarda’s objections here apply to that data as well.
Regardless, his strong public disagreement with NASA on this once again raises serious questions about the upcoming manned Artemis-2 mission, set to launch sometime in the February to March time frame.