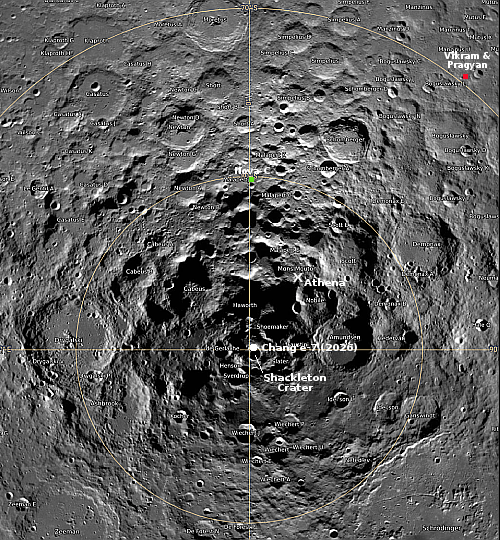
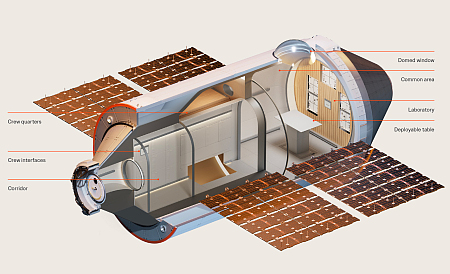
SpaceX launches NASA space telescope plus four solar satellites; China launches 18 communication satellites
Two launches to report: First, China yesterday successfully completed its first Long March 8 launch from its new launchpad at its coastal Wenchang spaceport, placing 18 satellites for SpaceSail internet constellation, the fifth group so far launched.
China’s state run press noted that the launchpad is designed to allow the Long March 8 rocket to launch every seven days, a pace needed to place these giant Chinese satellite constellations into orbit.
Next, in the early morning hours today SpaceX successfully launched two different NASA science missions, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The prime payload was SPHEREx, a space telescope designed to make an all-sky survey. The secondary payload was PUNCH, four satellites forming a constellation to study the Sun.
The rocket’s first stage completed its third flight, landing back at Vandenberg.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
27 SpaceX
11 China
3 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
As happened last year, SpaceX handily leads the rest of the world, including American companies, in total launches, 27 to 20. This lead will be extended tonight should the company’s next manned Dragon launch to ISS go off as planned.
Two launches to report: First, China yesterday successfully completed its first Long March 8 launch from its new launchpad at its coastal Wenchang spaceport, placing 18 satellites for SpaceSail internet constellation, the fifth group so far launched.
China’s state run press noted that the launchpad is designed to allow the Long March 8 rocket to launch every seven days, a pace needed to place these giant Chinese satellite constellations into orbit.
Next, in the early morning hours today SpaceX successfully launched two different NASA science missions, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The prime payload was SPHEREx, a space telescope designed to make an all-sky survey. The secondary payload was PUNCH, four satellites forming a constellation to study the Sun.
The rocket’s first stage completed its third flight, landing back at Vandenberg.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
27 SpaceX
11 China
3 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
As happened last year, SpaceX handily leads the rest of the world, including American companies, in total launches, 27 to 20. This lead will be extended tonight should the company’s next manned Dragon launch to ISS go off as planned.