Astronomers detect a seven-hour-long gamma ray burst, the longest many times over

Astronomers have detected the longest gamma ray burst (GRB) ever measured, lasting more than seven hours when most GRBs at most last mere seconds.
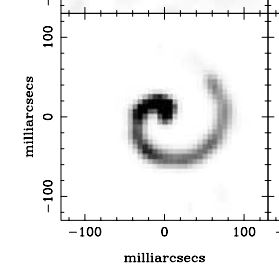
The image to the right was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and is taken from figure 1 of the peer-reviewed paper [pdf]. The two hash marks indicate the location of the GRB, within the outer reaches of its host galaxy and inside one of its spiral arms, based on other data. The data also suggested the host galaxy is “massive [100 billion solar masses], dusty, and [an] extremely asymmetric system that is consistent with two galaxies undergoing a major merger.”
The GRB’s long length means that none of the known theories for its origin work. From the press release:
Of the roughly 15,000 GRBs observed since the phenomenon was first recognized in 1973, only a half dozen come close to the length of GRB 250702B. Their proposed origins range from the collapse of a blue supergiant star, a tidal disruption event, or a newborn magnetar. GRB 250702B, however, doesn’t fit neatly into any known category.
From the data obtained so far, scientists have a few ideas of possible origin scenarios: (1) a black hole falling into a star that’s been stripped of its hydrogen and is now almost purely helium, (2) a star (or sub-stellar object such as a planet or brown dwarf) being disrupted during a close encounter with a stellar compact object, such as a stellar black hole or a neutron star, in what is known as a micro-tidal disruption event, (3) a star being torn apart as it falls into an intermediate-mass black hole — a type of black hole with a mass ranging from one hundred to one hundred thousand times the mass of our Sun that is believed to exist in abundance, but has so far been very difficult to find. If it is the latter scenario, this would be the first time in history that humans have witnessed a relativistic jet from an intermediate mass black hole in the act of consuming a star.
None of these proposed explanations are confirmed. What is known is that this GRB was unique in all ways, defying all theoretical expectations.

Astronomers have detected the longest gamma ray burst (GRB) ever measured, lasting more than seven hours when most GRBs at most last mere seconds.
The image to the right was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and is taken from figure 1 of the peer-reviewed paper [pdf]. The two hash marks indicate the location of the GRB, within the outer reaches of its host galaxy and inside one of its spiral arms, based on other data. The data also suggested the host galaxy is “massive [100 billion solar masses], dusty, and [an] extremely asymmetric system that is consistent with two galaxies undergoing a major merger.”
The GRB’s long length means that none of the known theories for its origin work. From the press release:
Of the roughly 15,000 GRBs observed since the phenomenon was first recognized in 1973, only a half dozen come close to the length of GRB 250702B. Their proposed origins range from the collapse of a blue supergiant star, a tidal disruption event, or a newborn magnetar. GRB 250702B, however, doesn’t fit neatly into any known category.
From the data obtained so far, scientists have a few ideas of possible origin scenarios: (1) a black hole falling into a star that’s been stripped of its hydrogen and is now almost purely helium, (2) a star (or sub-stellar object such as a planet or brown dwarf) being disrupted during a close encounter with a stellar compact object, such as a stellar black hole or a neutron star, in what is known as a micro-tidal disruption event, (3) a star being torn apart as it falls into an intermediate-mass black hole — a type of black hole with a mass ranging from one hundred to one hundred thousand times the mass of our Sun that is believed to exist in abundance, but has so far been very difficult to find. If it is the latter scenario, this would be the first time in history that humans have witnessed a relativistic jet from an intermediate mass black hole in the act of consuming a star.
None of these proposed explanations are confirmed. What is known is that this GRB was unique in all ways, defying all theoretical expectations.