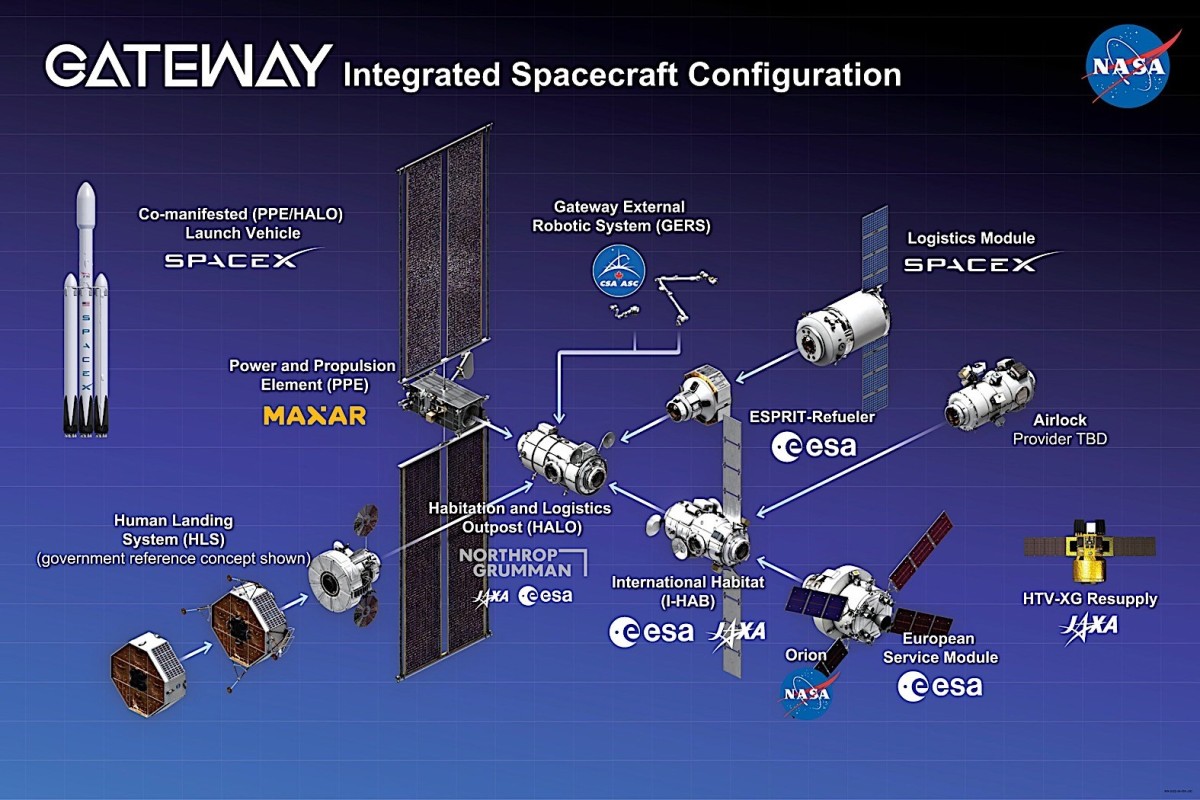
Senate reconciliation budget bill includes Cruz’s big spending additions to NASA

According to a tweet yesterday by Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), the reconciliation budget bill that was passed by the Senate included the budget additions that Senator Ted Cruz (R-Texas) had proposed to save SLS, Orion, and Lunar Gateway.
The graphic to the right lists these budget numbers. It is not clear whether the launch taxes on payloads that Cruz proposed were also included, though likely not based on the rules under which the reconciliation bill was passed.
This additional money for these projects contradicts directly the NASA 2026 budget proposal put forth by Trump that aimed to cancel Lunar Gateway and end SLS and Orion after only two more flights. Their existence in this passed Senate bill suggests that Congress is cool with the idea of spending this money and continuing these projects, even though they do nothing but waste taxpayer money and get us no where in space.
It also appears from the language in the graphic that the Senate is eager to also spend more money on NASA’s Mars sample return project, even though NASA itself still has no idea how to accomplish the task.

According to a tweet yesterday by Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), the reconciliation budget bill that was passed by the Senate included the budget additions that Senator Ted Cruz (R-Texas) had proposed to save SLS, Orion, and Lunar Gateway.
The graphic to the right lists these budget numbers. It is not clear whether the launch taxes on payloads that Cruz proposed were also included, though likely not based on the rules under which the reconciliation bill was passed.
This additional money for these projects contradicts directly the NASA 2026 budget proposal put forth by Trump that aimed to cancel Lunar Gateway and end SLS and Orion after only two more flights. Their existence in this passed Senate bill suggests that Congress is cool with the idea of spending this money and continuing these projects, even though they do nothing but waste taxpayer money and get us no where in space.
It also appears from the language in the graphic that the Senate is eager to also spend more money on NASA’s Mars sample return project, even though NASA itself still has no idea how to accomplish the task.