This morning saw a string of launches from China, Russia, America, and Europe, with all four appearing to get their payloads into orbit though the American launch, by ULA’s Vulcan rocket, appeared to have a problem with one of its solid-fueled boosters.
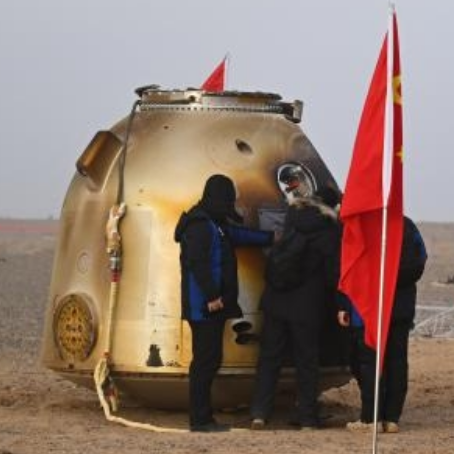
First, a Chinese pseudo-company owned entirely by a Chinese government agency successfully placed seven satellites in orbit, its Smart Dragon-3 rocket (also called Jielong-3) lifting off from a platform off the coast of northeast China. Of the satellites, the prime payload was a Pakistani Earth observation satellite.
Though this launch was from a pseudo-company, I think I can safely say that the pause in launches by China’s so-called commercial market continues. Smart Dragon-3 was built by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), which while structured as a private company is owned and controlled by several agencies of the Chinese government.
Next, Russia successfully launched a new weather satellite, its Proton rocket launching from Baikonur in Kazakhstan. This was the first Proton launch in three years, a pause partly because Russia is in the process of retiring that rocket. The lower stages crashed in a range of spots in Kazakhstan and across southern Russia, just missing China in two places.
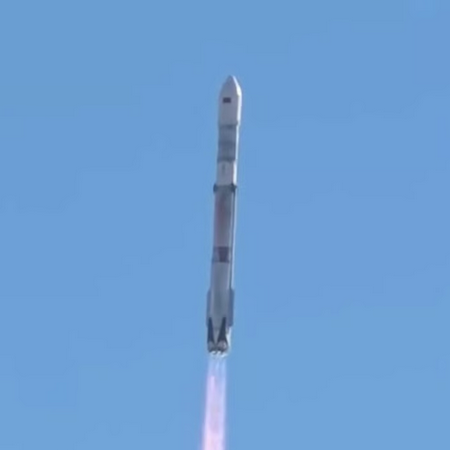
The American company ULA then followed with its first launch in 2026, its Vulcan rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida and carrying two military satellites designed to track other satellite operations in high geosynchronous orbit.
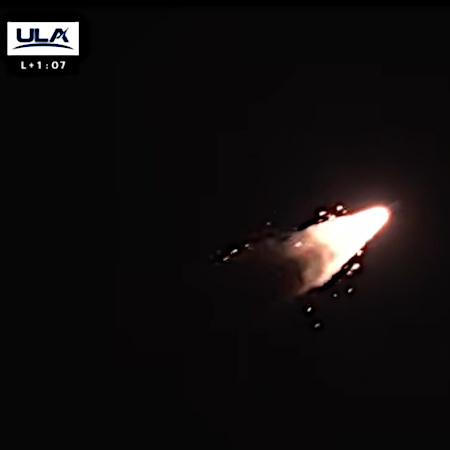

Unexpected debris falling from rocket at about T-1:00
While it appears the launch was able to get the satellites into their correct orbits, the Vulcan rocket had an issue during the launch. According to ULA, one of the rocket’s four solid-fueled boosters had a problem during its flight. More details can be found here, suggesting the booster, built by Northrop Grumman, might have had a been a failure of the booster’s nozzle, similar to the same burn-through that occurred on a booster during Vulcan’s second launch in 2024, and also occurred during a Northrop Grumman static fire test in 2025.
This issue is likely going to delay further Vulcan launches, and will likely make it impossible for ULA to meet its goal of launching 16 to 18 Vulcan missions this year. It will also raise hackles within the Pentagon, which certified Vulcan for military launches in 2025. That certification will likely be questioned, and possibly even pulled.
Finally, Arianespace sent 32 Leo satellites into orbit for Amazon, its Ariane-6 rocket lifting off from French Guiana. This was the first Ariane-6 launch in its most powerful variant, using four strap-on boosters.
Amazon has now launched 212 Leo satellites. Its FCC license however requires it to have 1,616 in orbit by July. The company has requested a waiver on that requirement, and is likely to get it, since it is now demonstrating that it is serious about launching the constellation.
The 2026 launch race:
16 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)