Study identifies range of interference produced by Starlink satellites
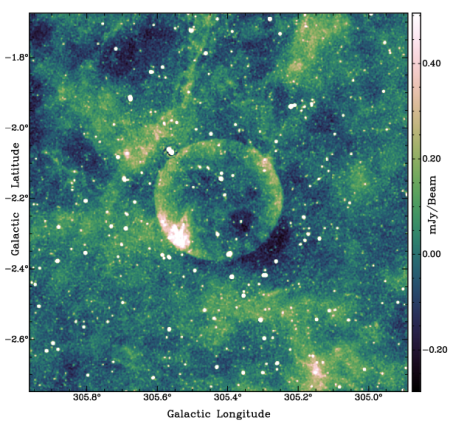
In analyzing about 76 million radio images produced by the new Square Kilometer Array (SKA) in Australia scientists have found within them signals produced by SpaceX’s Starlink satellites.
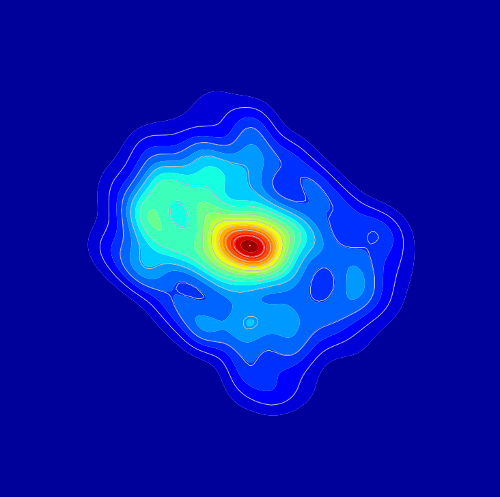
PhD candidate and study lead Dylan Grigg said the team detected more than 112,000 radio emissions from 1806 Starlink satellites, making it the most comprehensive catalogue of satellite radio emissions at low frequencies to date. “Starlink is the most immediate and frequent source of potential interference for radio astronomy: it launched 477 satellites during this study’s four-month data collection period alone,” Mr Grigg said. “In some datasets, we found up to 30 per cent of our images showed interference from a Starlink satellite.”
Mr Grigg said the issue wasn’t just the number of satellites, but the strength of the signals and the frequencies they were visible at. “Some satellites were detected emitting in bands where no signals are supposed to be present at all, such as the 703 satellites we identified at 150.8 MHz, which is meant to be protected for radio astronomy,” Mr Grigg said. “Because they may come from components like onboard electronics and they’re not part of an intentional signal, astronomers can’t easily predict them or filter them out.”
The researchers were careful to note that SpaceX has been following all international regulations, and that these signals are not a violation of any law or regulation. Further, they emphasized that “Discussions we have had with SpaceX on the topic have been constructive.”
Because many other such constellations are now being launched — with several from China that normally does not negotiate these issues like SpaceX — the scientists want new international regulations imposed to protect their work.
More and more it seems astronomers should simply move their operations into space or the Moon, where such issues will not exist. Getting above the atmosphere and away from our modern technological society provides so many benefits for research the move should be a no-brainer. That it is now also much cheaper to do it (thanks to SpaceX) makes the move even more practical.
For some reason however the idea seems too difficult for many astronomers to fathom.
In analyzing about 76 million radio images produced by the new Square Kilometer Array (SKA) in Australia scientists have found within them signals produced by SpaceX’s Starlink satellites.
PhD candidate and study lead Dylan Grigg said the team detected more than 112,000 radio emissions from 1806 Starlink satellites, making it the most comprehensive catalogue of satellite radio emissions at low frequencies to date. “Starlink is the most immediate and frequent source of potential interference for radio astronomy: it launched 477 satellites during this study’s four-month data collection period alone,” Mr Grigg said. “In some datasets, we found up to 30 per cent of our images showed interference from a Starlink satellite.”
Mr Grigg said the issue wasn’t just the number of satellites, but the strength of the signals and the frequencies they were visible at. “Some satellites were detected emitting in bands where no signals are supposed to be present at all, such as the 703 satellites we identified at 150.8 MHz, which is meant to be protected for radio astronomy,” Mr Grigg said. “Because they may come from components like onboard electronics and they’re not part of an intentional signal, astronomers can’t easily predict them or filter them out.”
The researchers were careful to note that SpaceX has been following all international regulations, and that these signals are not a violation of any law or regulation. Further, they emphasized that “Discussions we have had with SpaceX on the topic have been constructive.”
Because many other such constellations are now being launched — with several from China that normally does not negotiate these issues like SpaceX — the scientists want new international regulations imposed to protect their work.
More and more it seems astronomers should simply move their operations into space or the Moon, where such issues will not exist. Getting above the atmosphere and away from our modern technological society provides so many benefits for research the move should be a no-brainer. That it is now also much cheaper to do it (thanks to SpaceX) makes the move even more practical.
For some reason however the idea seems too difficult for many astronomers to fathom.