Bahamas allows SpaceX to resume Falcon 9 landings inside Bahamian waters
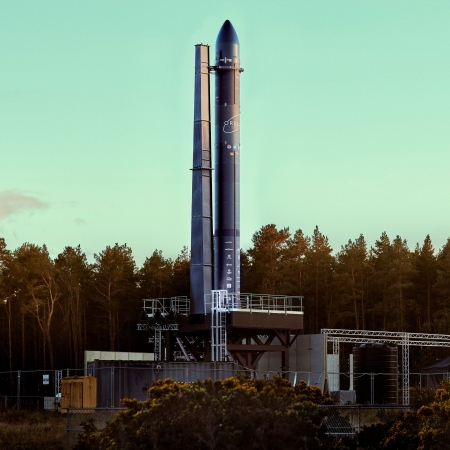
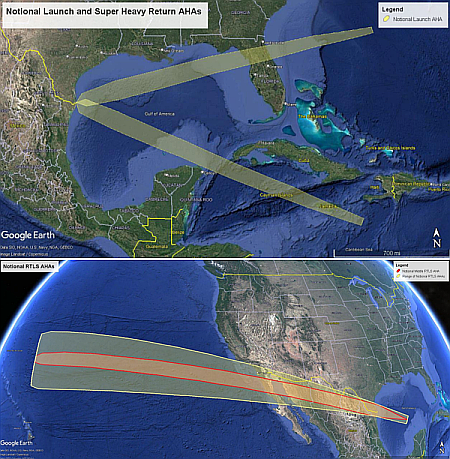
The Civil Aviation Authority of the Bahamas (CAAB) this week announced that it is allowing SpaceX to resume Falcon 9 landings inside Bahamian waters.
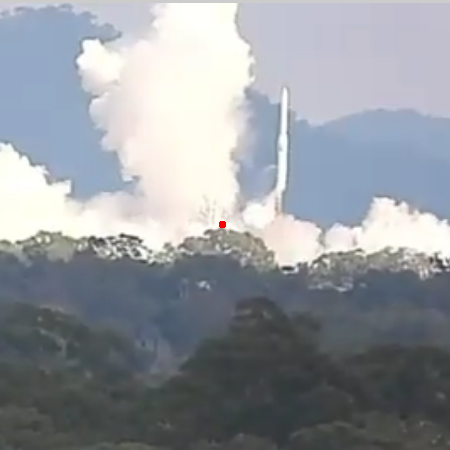
In a statement, CAAB said that one landing is scheduled for Wednesday night between 5:00 pm and 9:30 pm (local time). “All requisite regulatory and environmental reviews and clearances have been completed in accordance with established aerospace safety and operations protocols,” CAAB said, reminding the population that, depending on weather and atmospheric conditions, “one or more sound booms may be heard during the landing sequence”.
SpaceX had completed one landing in February 2025, but the CAAB then paused further landings two months later, claiming it wanted to do a full environmental review.
There was also the issue of a SpaceX $1 million donation to the University of the Bahamas. Maybe the CAAB wanted to wait until the check cleared.
As should be expected, a fringe of anti-Musk activists began screaming “environmental disaster” and getting the full support of the propaganda press. The claim is utterly stupid, considering SpaceX has landed hundreds of Falcon 9s in the past decade harmlessly.
The Civil Aviation Authority of the Bahamas (CAAB) this week announced that it is allowing SpaceX to resume Falcon 9 landings inside Bahamian waters.
In a statement, CAAB said that one landing is scheduled for Wednesday night between 5:00 pm and 9:30 pm (local time). “All requisite regulatory and environmental reviews and clearances have been completed in accordance with established aerospace safety and operations protocols,” CAAB said, reminding the population that, depending on weather and atmospheric conditions, “one or more sound booms may be heard during the landing sequence”.
SpaceX had completed one landing in February 2025, but the CAAB then paused further landings two months later, claiming it wanted to do a full environmental review.
There was also the issue of a SpaceX $1 million donation to the University of the Bahamas. Maybe the CAAB wanted to wait until the check cleared.
As should be expected, a fringe of anti-Musk activists began screaming “environmental disaster” and getting the full support of the propaganda press. The claim is utterly stupid, considering SpaceX has landed hundreds of Falcon 9s in the past decade harmlessly.