Third Indian state announces a space policy to encourage private enterprise
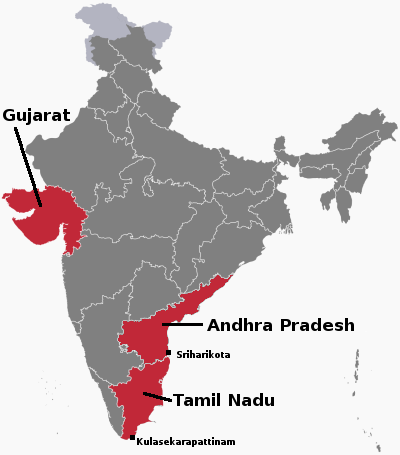
A third state in India, Andhra Pradesh, has now released its own space policy, designed to create what it calls “manufacturing clusters”, centered around India’s main spaceport at Sriharikota.
The A.P. Space Policy (4.0) 2025-30 is valid for five years from the date of issue (July 13, 2025), or till a new policy is announced. A technical committee will be constituted under the Commissioner of Industries to vet and process applications for land allotment in the Space Cities proposed to be developed along the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor in Sri Sathya Sai district and in Tirupati (Routhasuramala).
The government will form an SPV, ‘AP Space City Corporation’, which will drive all initiatives related to the development of the above Space Cities, and serve as the central agency to coordinate infrastructure development, raise start-up funds, attract investments, facilitate industry partnerships, build partnerships to attract global demand, and liaise with all GoI [Government of India] entities for tapping the domestic demand.
The previous two state space policies in Tamil Nadu and Gujarat, announced in April, had similar goals aimed at promoting the establishment of private aerospace companies within their regions.
Whether Andhra Pradesh’s policy will work carries uncertainties. Its advantage is that it is linked to India’s primary spaceport. Its disadvantage lies in the complex bureaucracy the state is creating in conjunction with these “Space Cities.” Such bureaucracies are rarely helpful for new businesses.

A third state in India, Andhra Pradesh, has now released its own space policy, designed to create what it calls “manufacturing clusters”, centered around India’s main spaceport at Sriharikota.
The A.P. Space Policy (4.0) 2025-30 is valid for five years from the date of issue (July 13, 2025), or till a new policy is announced. A technical committee will be constituted under the Commissioner of Industries to vet and process applications for land allotment in the Space Cities proposed to be developed along the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor in Sri Sathya Sai district and in Tirupati (Routhasuramala).
The government will form an SPV, ‘AP Space City Corporation’, which will drive all initiatives related to the development of the above Space Cities, and serve as the central agency to coordinate infrastructure development, raise start-up funds, attract investments, facilitate industry partnerships, build partnerships to attract global demand, and liaise with all GoI [Government of India] entities for tapping the domestic demand.
The previous two state space policies in Tamil Nadu and Gujarat, announced in April, had similar goals aimed at promoting the establishment of private aerospace companies within their regions.
Whether Andhra Pradesh’s policy will work carries uncertainties. Its advantage is that it is linked to India’s primary spaceport. Its disadvantage lies in the complex bureaucracy the state is creating in conjunction with these “Space Cities.” Such bureaucracies are rarely helpful for new businesses.