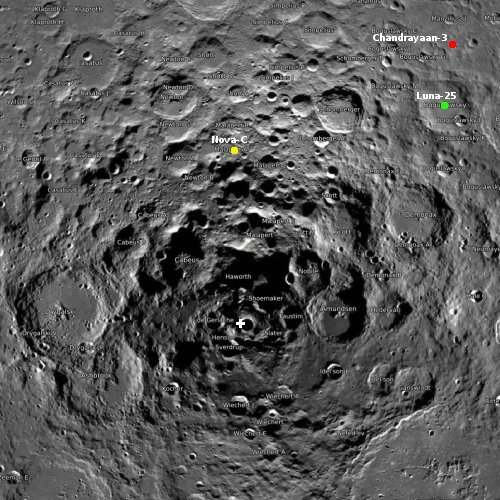
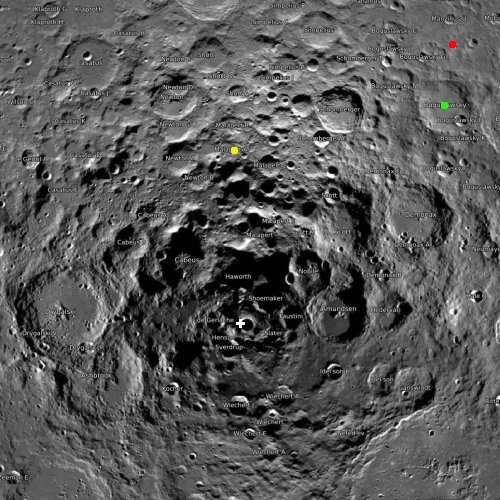
The original Chinese-Russian lunar base plan, from June 2021.
In outlining today China’s long term plans for establishing a manned lunar base near the south pole of the Moon, the project’s chief designer, Wu Weiren, revealed several changes in the program, almost all of which were indicated by what he did not say than what he did.
The graph to the right was released when this program was first announced in June 2021. At that time the plan was announced as a partnership of China and Russia, and was aiming to begin intermittent manned operations on the Moon in 2036.
According to Wu’s presentation today however, China apparently no longer considers Russia to be a full equal partner. It appears instead that Russia was mentioned as part of Wu’s effort to encourage many other countries to join the project. As reported by China’s state-run press:
During Tuesday’s event, Wu also highlighted the cooperation initiative for countries, organizations, and scientists worldwide to join the construction of the research station. In 2021, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) released a partnership guideline for the International Lunar Research Station.
That the state-run press made no mention of Russia in this description indicates strongly China’s devaluation of Russia’s contribution. This devaluation is not a surprise. As I noted in 2021,
[B]ased on Russia’s recent track record in the past two decades for promised space projects, we have no guarantee they will fly as scheduled, or even fly at all.
Since then Russia invaded the Ukraine and has suffered economically because of it. Its own first contribution to this partnership, Luna-25, has been delayed repeatedly, with its present launch now scheduled for July. It was always obvious that Russia — in its present state — could not match China, nor was it likely it would meet its promised targets.
Wu’s presentation also indicated that the third phase, when intermittent manned operations will begin, has been delayed from 2036 to 2040.
Overall, however, the Chinese plan remains stable and rational, and is likely to be carried out with reasonable success, based on how the country proposed and then achieved construction of its space station. The station was built essentially as described by the plan, with only a delay of a few years.