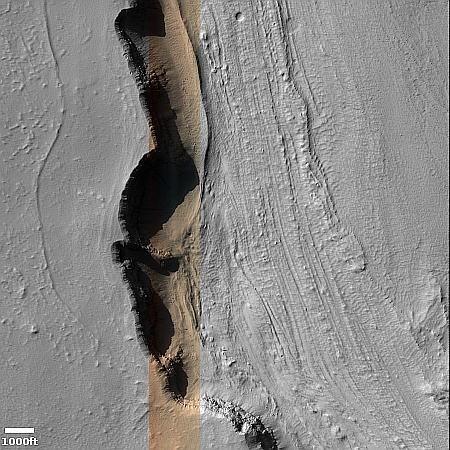
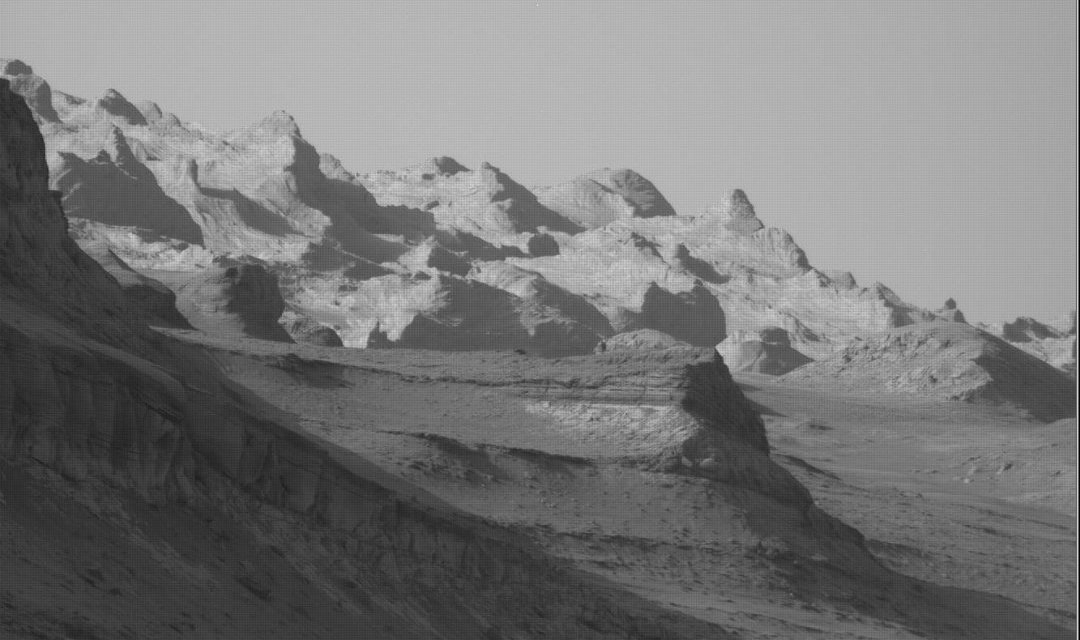
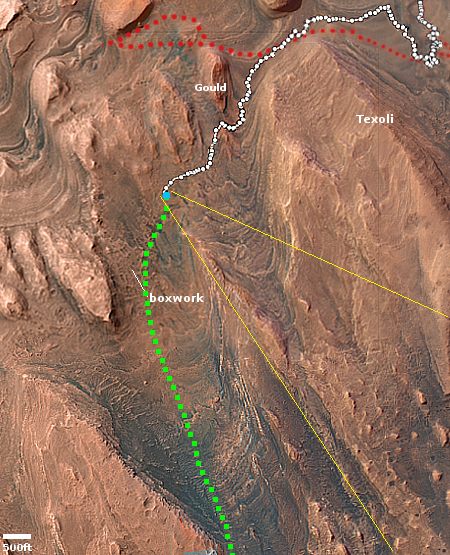
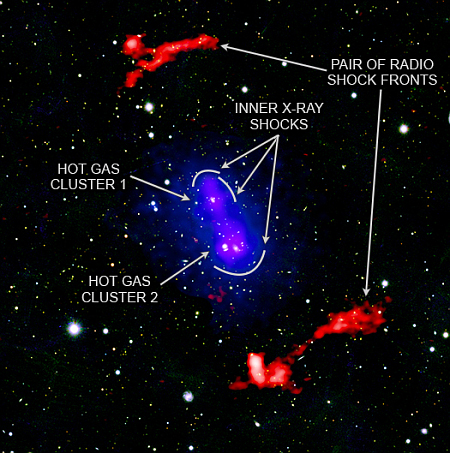
NASA still hoping to save its Lunar Trailblazer mission
Though the odds of success are very dim, NASA has decided to give engineers another few weeks to try to activate its Lunar Trailblazer orbiter, that stopped communicating with Earth the day after it was launched in late February.
NASA has extended recovery efforts of its Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft from mid-June to early July. Updated modeling of the spacecraft’s trajectory by the mission team indicates lighting conditions will continue to be favorable and may provide enough sunlight for the spacecraft’s solar panels to recharge its batteries to an operational state and turn on its radio.
…Should enough sunlight reach Lunar Trailblazer’s solar panels, the batteries may charge to a level that allows the spacecraft’s radio system to boot up. But as Lunar Trailblazer travels farther away, it will soon be too distant to recover because its telecommunications signals to Earth will be too weak for the mission to receive telemetry and command.
The mission team has determined that if they can regain command of the spacecraft, the propulsion system isn’t frozen, and the instruments remain operable, the spacecraft may be able to achieve an elliptical lunar orbit and complete its lunar science objectives.
As I said, the chance of success are not good.
Though the odds of success are very dim, NASA has decided to give engineers another few weeks to try to activate its Lunar Trailblazer orbiter, that stopped communicating with Earth the day after it was launched in late February.
NASA has extended recovery efforts of its Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft from mid-June to early July. Updated modeling of the spacecraft’s trajectory by the mission team indicates lighting conditions will continue to be favorable and may provide enough sunlight for the spacecraft’s solar panels to recharge its batteries to an operational state and turn on its radio.
…Should enough sunlight reach Lunar Trailblazer’s solar panels, the batteries may charge to a level that allows the spacecraft’s radio system to boot up. But as Lunar Trailblazer travels farther away, it will soon be too distant to recover because its telecommunications signals to Earth will be too weak for the mission to receive telemetry and command.
The mission team has determined that if they can regain command of the spacecraft, the propulsion system isn’t frozen, and the instruments remain operable, the spacecraft may be able to achieve an elliptical lunar orbit and complete its lunar science objectives.
As I said, the chance of success are not good.