Lace on Mars
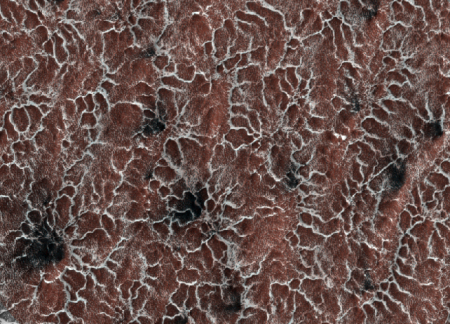
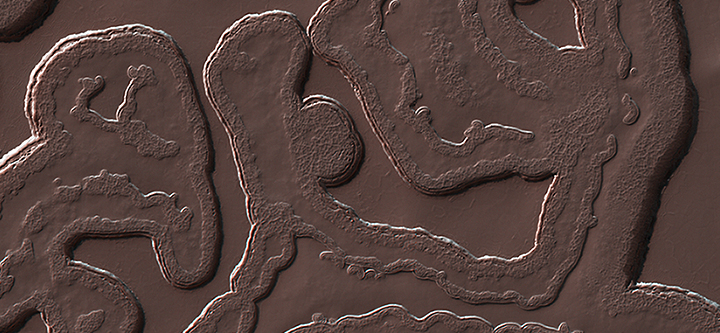
Cool image time! The image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to show here, was taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter June 21, 2016. It shows a region in the high northern latitudes, 80 degrees.
Some seasonal ice on Mars is transparent so that the sunlight penetrates to the bottom of the ice. Heat from this sunlight can turn the ice directly into a gas in a process called sublimation and this gas can scour channels in the loose dirt under the ice. Channels formed by sublimation of a layer of seasonal dry ice are so dense in this area that they look like lace. Gas flow erodes channels as it escapes to the surface of the overlying seasonal ice layer seeking the path of least resistance.
The resolution of the full image is 9.7 feet per pixel. This means that if Curiosity was driving across this surface we would see it. I guarantee however that Curiosity would not find driving here very easy. The ice surface is likely very delicate, and would likely cause any vehicle to bog down. The surface is also likely very alien-looking, which makes me very much want to see what it looks like, up close. This look will unfortunately have to wait, as we as yet do not have the right technology to do it. We would need I think a drone, capable of flying in Mars’s thin atmosphere.

Cool image time! The image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to show here, was taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter June 21, 2016. It shows a region in the high northern latitudes, 80 degrees.
Some seasonal ice on Mars is transparent so that the sunlight penetrates to the bottom of the ice. Heat from this sunlight can turn the ice directly into a gas in a process called sublimation and this gas can scour channels in the loose dirt under the ice. Channels formed by sublimation of a layer of seasonal dry ice are so dense in this area that they look like lace. Gas flow erodes channels as it escapes to the surface of the overlying seasonal ice layer seeking the path of least resistance.
The resolution of the full image is 9.7 feet per pixel. This means that if Curiosity was driving across this surface we would see it. I guarantee however that Curiosity would not find driving here very easy. The ice surface is likely very delicate, and would likely cause any vehicle to bog down. The surface is also likely very alien-looking, which makes me very much want to see what it looks like, up close. This look will unfortunately have to wait, as we as yet do not have the right technology to do it. We would need I think a drone, capable of flying in Mars’s thin atmosphere.