Astronomers take first radio image of the supermassive binary system OJ287
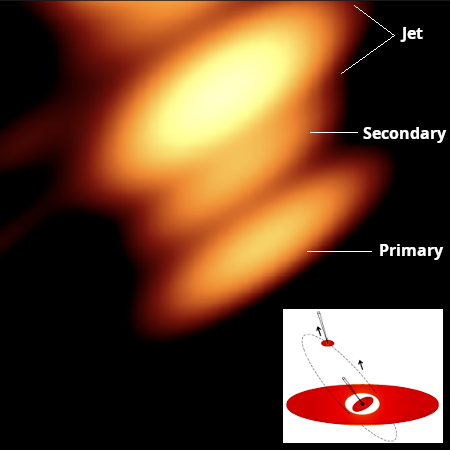
Using archive data from the now retired Russian orbiting radio telescope RadioAstron, scientists have now obtained the first image of the binary supermassive black hole system OJ287 that was previously detected flaring as predicted when the smaller black hole (150 million solar masses) circled near the larger (18 billion solar masses).
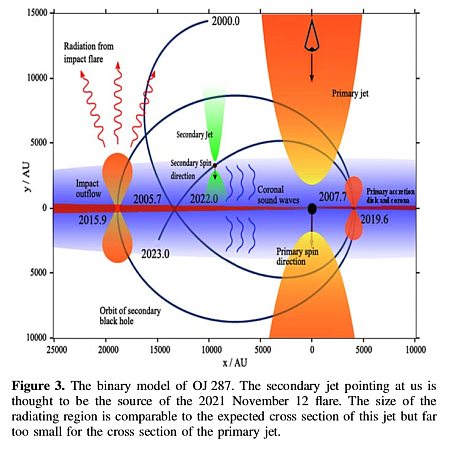
That image is to the right, cropped and annotated to post here. The cartoon in the lower right shows the theorized orientation of the system, taken from figure 2 of the published paper [pdf]. According to the paper the elongation of the three objects is an artifact of the data and is “not real.” From the press release:
In this latest study, the astronomers compared the earlier theoretical calculations with a radio image. The two black holes were there in the image, just where they were expected to be. This gave the researchers an answer to a question that has been open for 40 years: whether black-hole pairs exist in the first place. “For the first time, we managed to get an image of two black holes circling each other. In the image, the black holes are identified by the intense particle jets they emit. The black holes themselves are perfectly black, but they can be detected by these particle jets or by the glowing gas surrounding the hole,” Valtonen says.
The researchers also identified a completely new kind of a jet emanating from a black hole. The jet coming out of the smaller black hole is twisted like a jet of a rotating garden hose. This is because the smaller black hole moves fast around the primary black hole of OJ287, and its jet is diverted depending on its current motion. The researches liken it to “a wagging tail” which should be seen twisting in different directions in the coming years when the smaller black hole changes its speed and direction of motion.
This image is cropped from the full dataset. The jet continues upward and then curves to the right as it “wags” away.
This incredible black hole binary system, estimated to be about 3.5 billion light years away, has been posited since 1982, when one astronomer noticed that it repeatedly flared every twelve years. Since then scientists have successfully predicted several flares, based on the system’s theorized orbit. These images further confirm the system’s shape.

Using archive data from the now retired Russian orbiting radio telescope RadioAstron, scientists have now obtained the first image of the binary supermassive black hole system OJ287 that was previously detected flaring as predicted when the smaller black hole (150 million solar masses) circled near the larger (18 billion solar masses).
That image is to the right, cropped and annotated to post here. The cartoon in the lower right shows the theorized orientation of the system, taken from figure 2 of the published paper [pdf]. According to the paper the elongation of the three objects is an artifact of the data and is “not real.” From the press release:
In this latest study, the astronomers compared the earlier theoretical calculations with a radio image. The two black holes were there in the image, just where they were expected to be. This gave the researchers an answer to a question that has been open for 40 years: whether black-hole pairs exist in the first place. “For the first time, we managed to get an image of two black holes circling each other. In the image, the black holes are identified by the intense particle jets they emit. The black holes themselves are perfectly black, but they can be detected by these particle jets or by the glowing gas surrounding the hole,” Valtonen says.
The researchers also identified a completely new kind of a jet emanating from a black hole. The jet coming out of the smaller black hole is twisted like a jet of a rotating garden hose. This is because the smaller black hole moves fast around the primary black hole of OJ287, and its jet is diverted depending on its current motion. The researches liken it to “a wagging tail” which should be seen twisting in different directions in the coming years when the smaller black hole changes its speed and direction of motion.
This image is cropped from the full dataset. The jet continues upward and then curves to the right as it “wags” away.
This incredible black hole binary system, estimated to be about 3.5 billion light years away, has been posited since 1982, when one astronomer noticed that it repeatedly flared every twelve years. Since then scientists have successfully predicted several flares, based on the system’s theorized orbit. These images further confirm the system’s shape.