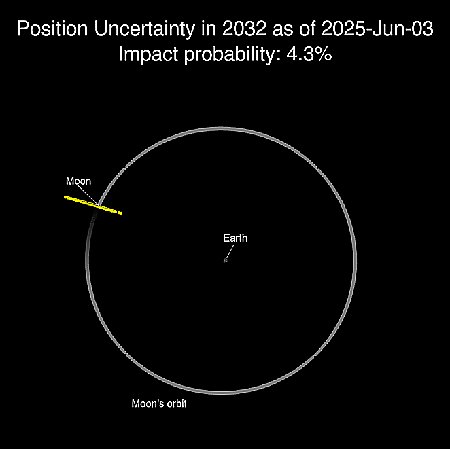
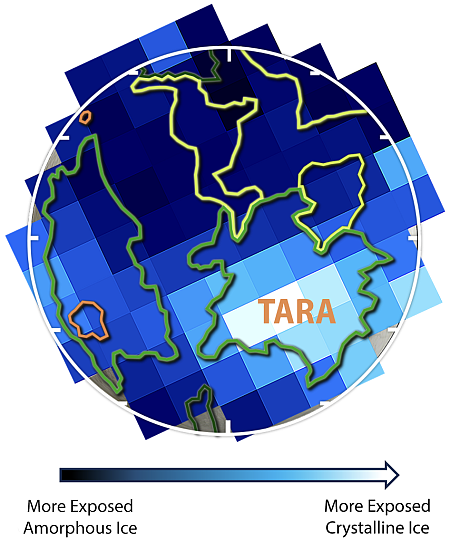
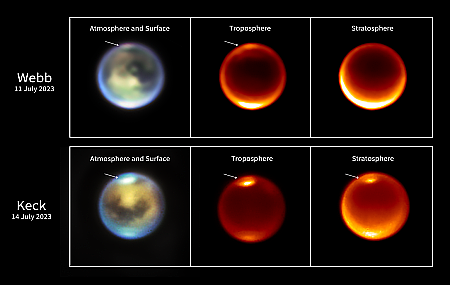
Astronomers discover a “surprisingly mature” cluster of galaxies in early universe
The uncertainty of science strikes again! Astronomers using both the Webb Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory now think they have discovered a just-forming protocluster of galaxies only one billion years after the Big Bang, when such galaxy clusters should not yet exist.
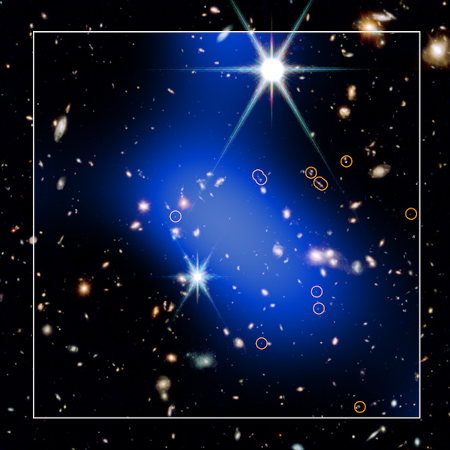
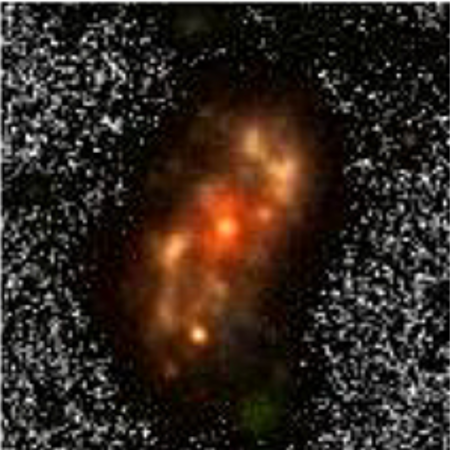
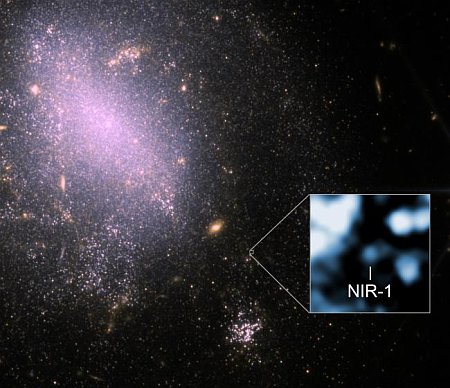
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows the Webb infrared data as the background of stars and galaxies, with the galaxies thought to be part of this protocluster circled. The blue cloud is Chandra’s X-ray data. From the press release:
The Chandra and Webb data reveal that JADES-ID1 contains the two properties that confirm the presence of a protocluster: a large number of galaxies held together by gravity (Webb sees at least 66 potential members) that are also sitting in a huge cloud of hot gas (detected by Chandra). As a galaxy cluster forms, gas falls inward and is heated by shock waves, reaching temperatures of millions of degrees and glowing in X-rays.
What makes JADES-ID1 exceptional is the remarkably early time when it appears in cosmic history. Most models of the universe predict that there likely would not be enough time and a large enough density of galaxies for a protocluster of this size to form only a billion years after the big bang. The previous record holder for a protocluster with X-ray emission is seen much later, about three billion years after the big bang.
It increasingly appears that there are aspects of the universe we simply do not yet understand, which in turn make our theories of its birth and formation either incomplete or invalid. Those theories might be right in principle, but the data suggests they are wrong in detail.
The uncertainty of science strikes again! Astronomers using both the Webb Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory now think they have discovered a just-forming protocluster of galaxies only one billion years after the Big Bang, when such galaxy clusters should not yet exist.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows the Webb infrared data as the background of stars and galaxies, with the galaxies thought to be part of this protocluster circled. The blue cloud is Chandra’s X-ray data. From the press release:
The Chandra and Webb data reveal that JADES-ID1 contains the two properties that confirm the presence of a protocluster: a large number of galaxies held together by gravity (Webb sees at least 66 potential members) that are also sitting in a huge cloud of hot gas (detected by Chandra). As a galaxy cluster forms, gas falls inward and is heated by shock waves, reaching temperatures of millions of degrees and glowing in X-rays.
What makes JADES-ID1 exceptional is the remarkably early time when it appears in cosmic history. Most models of the universe predict that there likely would not be enough time and a large enough density of galaxies for a protocluster of this size to form only a billion years after the big bang. The previous record holder for a protocluster with X-ray emission is seen much later, about three billion years after the big bang.
It increasingly appears that there are aspects of the universe we simply do not yet understand, which in turn make our theories of its birth and formation either incomplete or invalid. Those theories might be right in principle, but the data suggests they are wrong in detail.