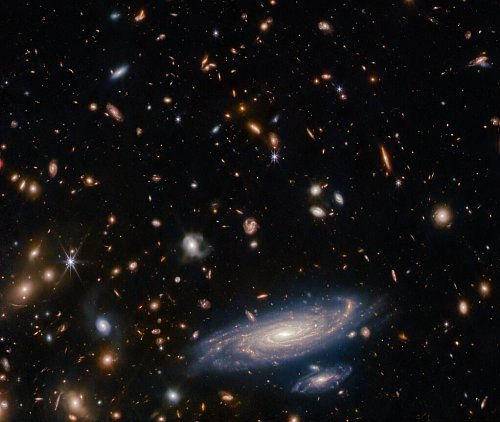
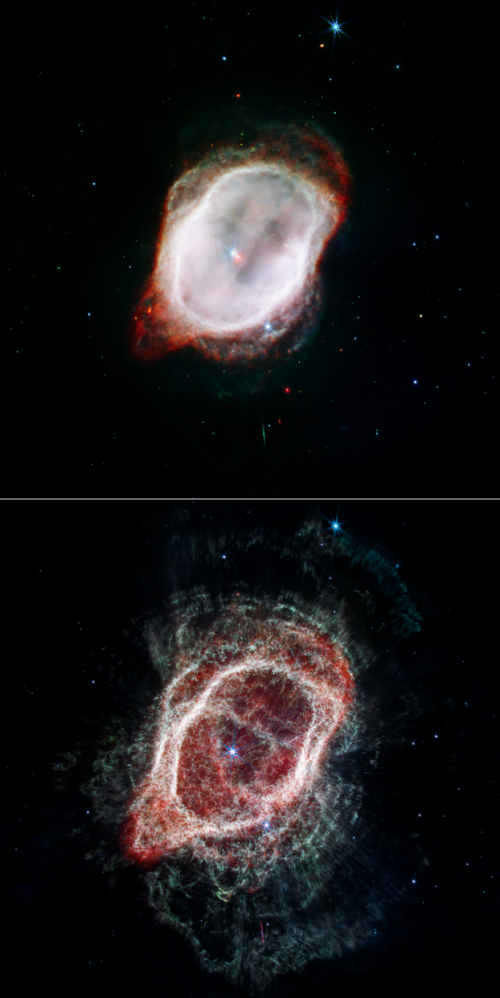
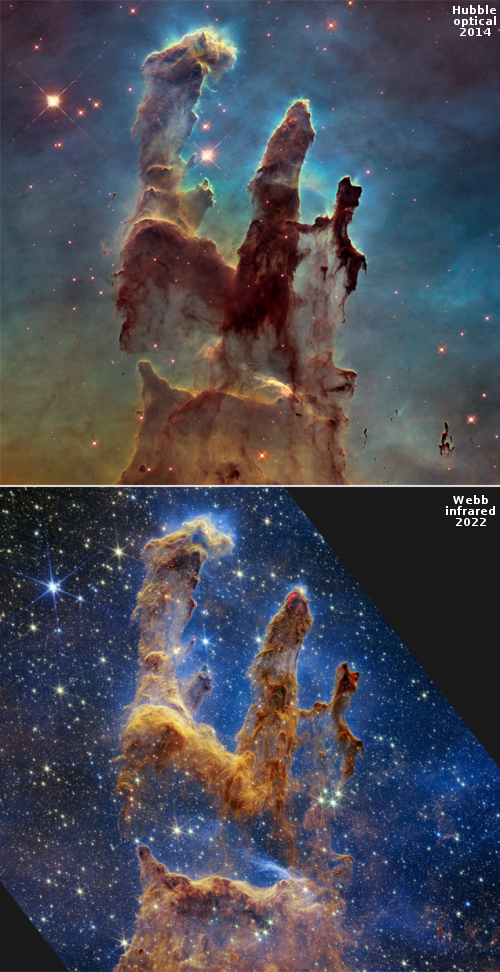
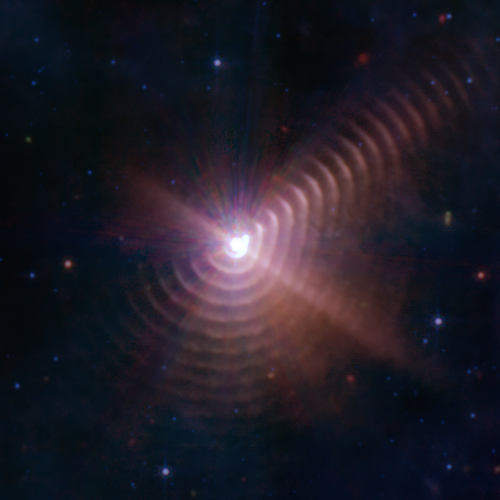
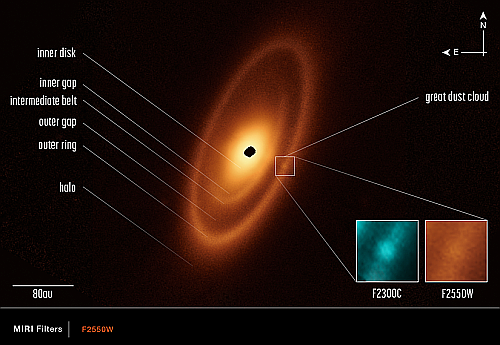
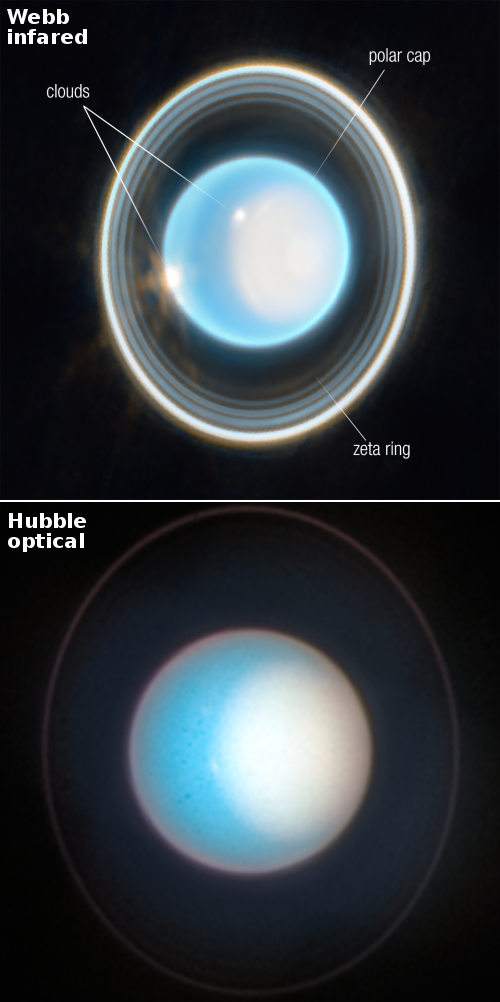
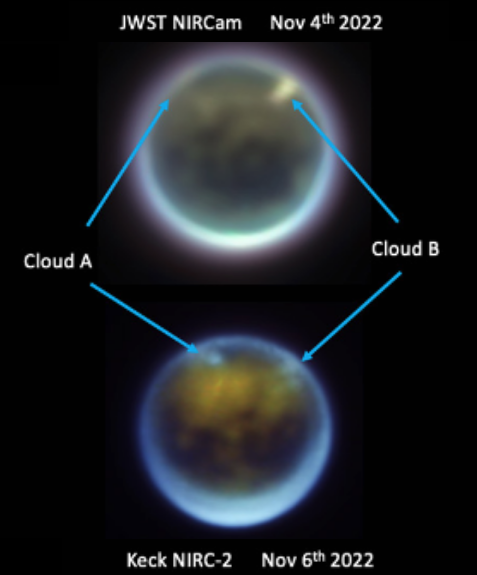
Webb takes infrared image of the disk of dust and debris surrounding Fomalhaut
Using the mid-infrared instrument on the Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have obtained a new high resolution infrared image of the disk of dust and debris that surrounds the star Fomalhaut, and (surprise!) have it to be more complex than they previously believed.
That image is to the right, annotated by the science team.
Overall, there are three nested belts extending out to 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) from the star; that’s 150 times the distance of Earth from the Sun. The scale of the outermost belt is roughly twice the scale of our solar system’s Kuiper Belt of small bodies and cold dust beyond Neptune. The inner belts – which had never been seen before – were revealed by Webb for the first time.
The dust cloud identified in the outer ring is possibly left over from a recent collusion of larger bodies.
Using the mid-infrared instrument on the Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have obtained a new high resolution infrared image of the disk of dust and debris that surrounds the star Fomalhaut, and (surprise!) have it to be more complex than they previously believed.
That image is to the right, annotated by the science team.
Overall, there are three nested belts extending out to 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) from the star; that’s 150 times the distance of Earth from the Sun. The scale of the outermost belt is roughly twice the scale of our solar system’s Kuiper Belt of small bodies and cold dust beyond Neptune. The inner belts – which had never been seen before – were revealed by Webb for the first time.
The dust cloud identified in the outer ring is possibly left over from a recent collusion of larger bodies.