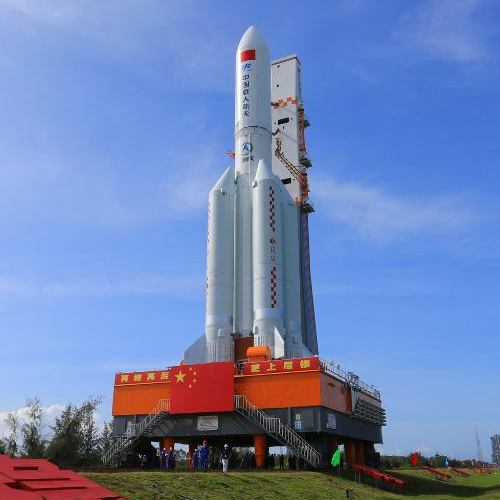
Long March 5B being rolled to launch site
China’s big Long March 5B rocket was successfully rolled to its launch site yesterday in preparation for a July 24, 2022 launch that will put China’s next large space station module, Wentian, into orbit.
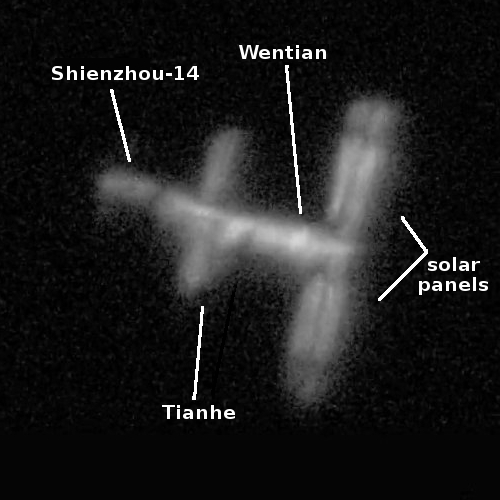
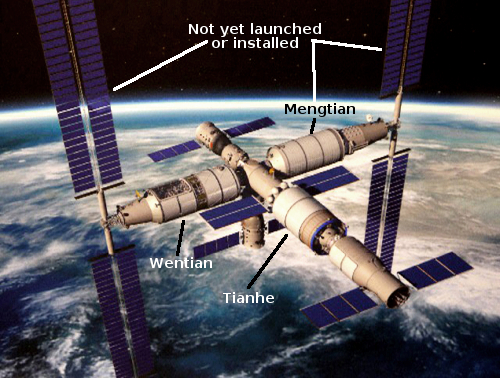
The Wentian module, with a launch weight near 44,000 pounds (20 metric tons), will dock with the Tianhe core module on China’s Tiangong station in low Earth orbit. Chinese astronauts Chen Dong, Liu Yang, and Cai Xuzhe living on the Tiangong complex will monitor Wentian’s arrival, then become the first crew members to float into the station’s new module.
The launch this weekend will add the second of three large pressurized modules needed to complete the initial construction of the Tiangong space station. The Tianhe core module launched on a Long March 5B rocket in April 2021, and Chinese ground teams are preparing the Mengtian module for launch on a Long March 5B rocket in October.
The big question mark however concerning this upcoming launch is the central core stage of the Long March 5B, seen in the picture above surrounded by four strap-on boosters with Wentian stacked on top. In all previous Long March 5B launches, that core stage reached orbit, deployed its payload, and then crashed to Earth uncontrolled because its main engines could not be restarted. Will this core stage do the same?
The name of this particular Long March 5B also carries with it a new suffix, “Y3”. In the past when the Chinese added letters to a name it was because the rocket had been changed or upgraded in some manner. Furthermore, in March China did some static fire engine tests of what were suggested to be new engines for the core stage.
Developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, the engine is designed for the core stage of the Long March-5 carrier rocket series, which will be used to launch two lab modules of China’s orbiting Tiangong space station this year.
The long-range test, lasting 520 seconds, has verified the reliability of the engine, and there will be more than 20 experimental tasks that the rocket engine will undergo to further test its performance, the company disclosed.
Based on this meager information, it appears that China might have upgraded the core stage’s engines so they can be restarted and the stage’s de-orbit can be controlled so it crashes over the ocean, not over some random point of inhabited land. We shall have to wait until after the launch on July 24th to find out.