Wind eating away the Martian terrain

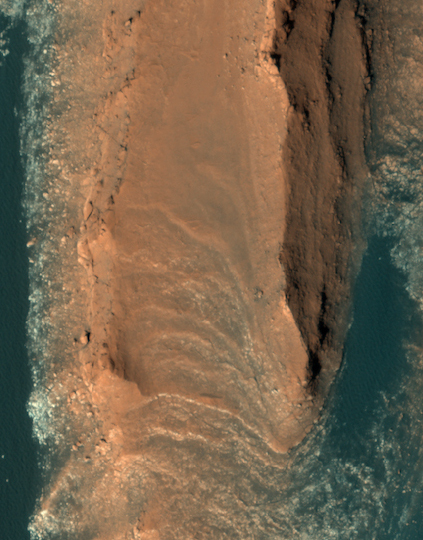
Cool image time! The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here, shows the transition zone between the lower flat plain to the north and the higher but rougher region to the south. What makes it interesting is the north-south aligned mesas. These are yardangs, a geological feature that actually acts like a weather vane.
Yardangs are composed of sand grains that have clumped together and have become more resistant to erosion than their surrounding materials.
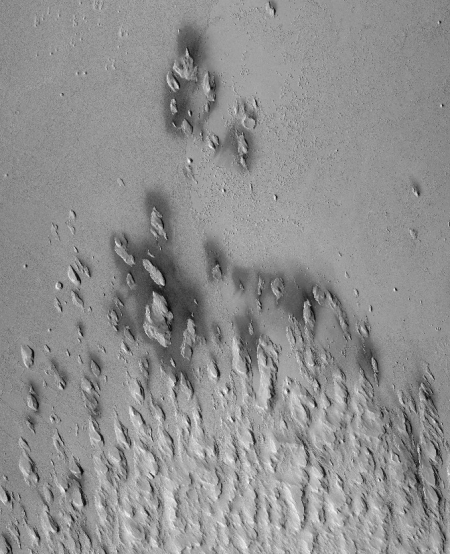
As the winds of Mars blow and erode away at the landscape, the more cohesive rock is left behind as a standing feature. (This Context Camera image shows several examples of yardangs that overlie the darker iron-rich material that makes up the lava plains in the southern portion of Elysium Planitia.) Resistant as they may be, the yardangs are not permanent, and will eventually be eroded away by the persistence of the Martian winds.
For scientists observing the Red Planet, yardangs serve as a useful indicator of regional prevailing wind direction. The sandy structures are slowly eroded down and carved into elongated shapes that point in the downwind direction, like giant weathervanes. In this instance, the yardangs are all aligned, pointing towards north-northwest. This shows that the winds in this area generally gust in that direction.
The wind comes from the southeast and blows to the northwest, and is slowly wearing down the southern rougher terrain. Why some of these yardangs are surrounded by dark material remains a mystery, as noted I noted in a previous post.
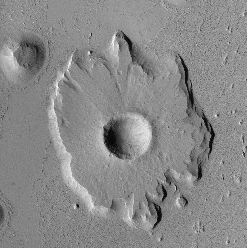
Meanwhile, the northern plain is not as boring as it seems. Only a short distance to the north is an unusual crater, cropped from the full image to show here on the right. To my eye, when this impact occurred it literally caused a splashlike feature of compressed and more resistant material. Over time, the prevailing wind has eroded away the surrounding less resistant regolith to better reveal that splash, leaving behind a mesa with a crater in its center.
Why the impact created this splash tells us something about the density and make-up of the plain. It suggests to me a surface that was once muddy and soft that over time has hardened like sandstone.

Cool image time! The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) image on the right, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here, shows the transition zone between the lower flat plain to the north and the higher but rougher region to the south. What makes it interesting is the north-south aligned mesas. These are yardangs, a geological feature that actually acts like a weather vane.
Yardangs are composed of sand grains that have clumped together and have become more resistant to erosion than their surrounding materials.
As the winds of Mars blow and erode away at the landscape, the more cohesive rock is left behind as a standing feature. (This Context Camera image shows several examples of yardangs that overlie the darker iron-rich material that makes up the lava plains in the southern portion of Elysium Planitia.) Resistant as they may be, the yardangs are not permanent, and will eventually be eroded away by the persistence of the Martian winds.
For scientists observing the Red Planet, yardangs serve as a useful indicator of regional prevailing wind direction. The sandy structures are slowly eroded down and carved into elongated shapes that point in the downwind direction, like giant weathervanes. In this instance, the yardangs are all aligned, pointing towards north-northwest. This shows that the winds in this area generally gust in that direction.

The wind comes from the southeast and blows to the northwest, and is slowly wearing down the southern rougher terrain. Why some of these yardangs are surrounded by dark material remains a mystery, as noted I noted in a previous post.
Meanwhile, the northern plain is not as boring as it seems. Only a short distance to the north is an unusual crater, cropped from the full image to show here on the right. To my eye, when this impact occurred it literally caused a splashlike feature of compressed and more resistant material. Over time, the prevailing wind has eroded away the surrounding less resistant regolith to better reveal that splash, leaving behind a mesa with a crater in its center.
Why the impact created this splash tells us something about the density and make-up of the plain. It suggests to me a surface that was once muddy and soft that over time has hardened like sandstone.

