January 30, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
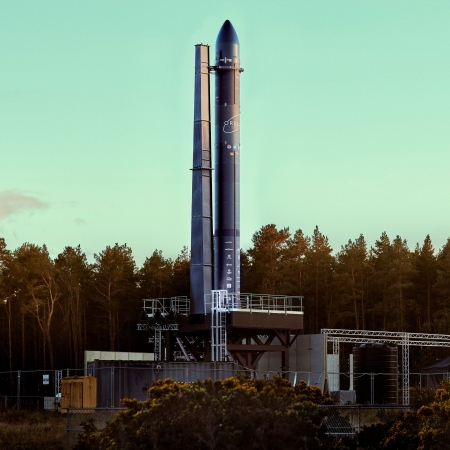
- PLD provides detailed update on construction of its MIURA 5 rocket
Very impressive video. They continue to appear on schedule for a 2026 launch.
- Astrolab touts its FLEX unmanned demo lunar rover, and its compact configuration during transport
Once on the Moon it will unfold.
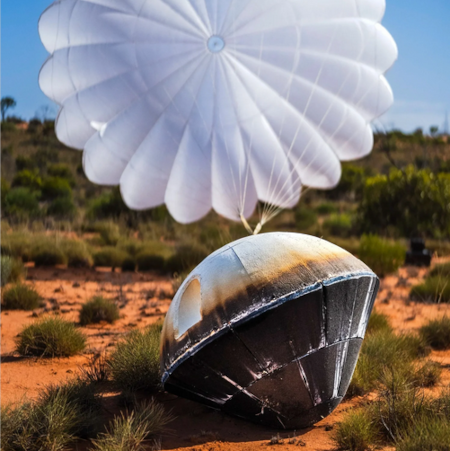
- Chinese pseudo-company Ispace admits the first launch of its Hyperbola-3 rocket will be postponed
The tweet touts tests of their strongback, and only mentions the delay as an aside. Jay says the company is now saying it will slip to 2027.
- SpaceX to offer at no cost to all satellite operators the data from its Stargaze system used by Starlink satellites to determine positions precisely
It is doing this to help avoid collisions. Others should do the same, though no one knows what the large Chinese satellite constellation operators will do.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- PLD provides detailed update on construction of its MIURA 5 rocket
Very impressive video. They continue to appear on schedule for a 2026 launch.
- Astrolab touts its FLEX unmanned demo lunar rover, and its compact configuration during transport
Once on the Moon it will unfold.
- Chinese pseudo-company Ispace admits the first launch of its Hyperbola-3 rocket will be postponed
The tweet touts tests of their strongback, and only mentions the delay as an aside. Jay says the company is now saying it will slip to 2027.
- SpaceX to offer at no cost to all satellite operators the data from its Stargaze system used by Starlink satellites to determine positions precisely
It is doing this to help avoid collisions. Others should do the same, though no one knows what the large Chinese satellite constellation operators will do.