The flowing formations of Lethe Vallis
Cool image time! The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter science team yesterday released several new images. Below is just one, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here. It shows a large flow channel called Lethe Vallis, formed first by lava, then hit by an impact which created a walled crater in its middle. Flood waters then followed, creating the tear-shaped dune surrounding the crater. In addition, erosion exposed the dark lava basalt below the surface on the edge of that tear-shaped dune. Within the crater itself can be seen ripple dunes formed by wind. As the scientists note,
This single image thus contains features formed by periglacial, volcanic, fluvial, impact, aeolian and mass wasting processes, all in one place.
Be sure to check out the full image.
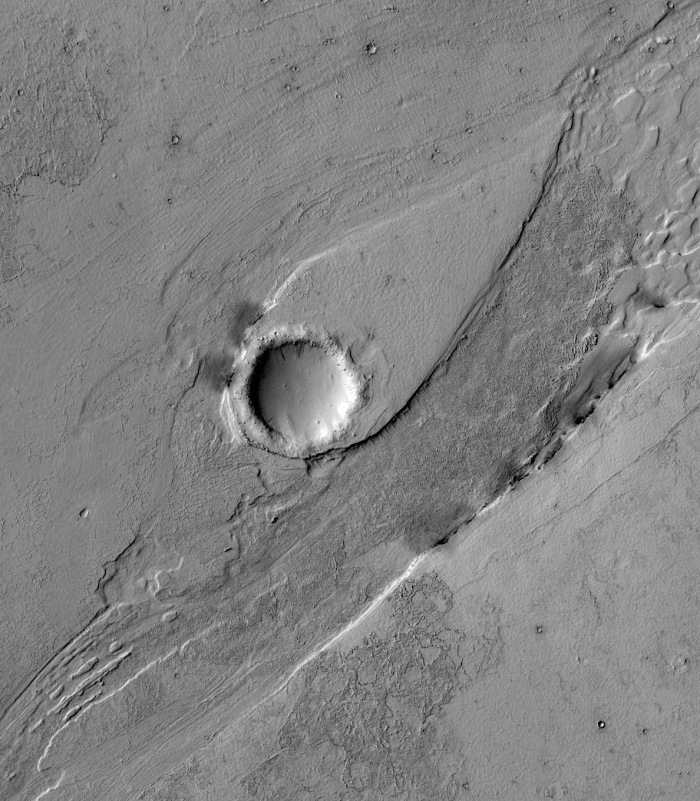
Cool image time! The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter science team yesterday released several new images. Below is just one, cropped and reduced in resolution to post here. It shows a large flow channel called Lethe Vallis, formed first by lava, then hit by an impact which created a walled crater in its middle. Flood waters then followed, creating the tear-shaped dune surrounding the crater. In addition, erosion exposed the dark lava basalt below the surface on the edge of that tear-shaped dune. Within the crater itself can be seen ripple dunes formed by wind. As the scientists note,
This single image thus contains features formed by periglacial, volcanic, fluvial, impact, aeolian and mass wasting processes, all in one place.
Be sure to check out the full image.


