An island of hundreds of scour pits in Mars’ largest volcanic ash field
Cool image time! The picture to the left, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 25, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
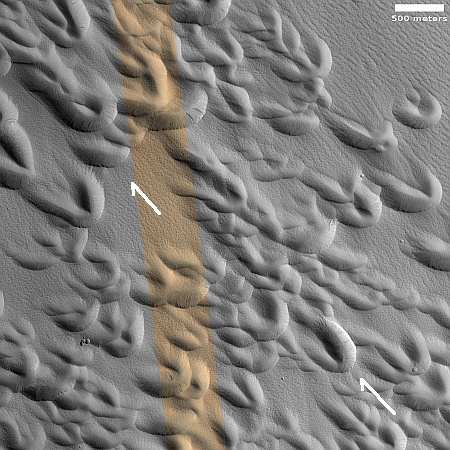
It shows what the science team labels a “scour pit island,” an area about 13 miles long and 3.5 miles wide where the ground is covered by these pits.
Your eye may play tricks on you, reversing the elevations. These are all pits, with most having a central peak or ridgeline. To help, note that the sunlight is coming from the west. The arrow on the center left of the picture sits on a plateau above these pits.
According to this paper [pdf], the pits are slowly dug out by the wind coming from the southeast blowing to the northwest, as indicated by the arrows. The central peaks or ridges are thought to be a hint of the original topography, with the wind only able to pull ash from the terrain around these peaks.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the left, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 25, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
It shows what the science team labels a “scour pit island,” an area about 13 miles long and 3.5 miles wide where the ground is covered by these pits.
Your eye may play tricks on you, reversing the elevations. These are all pits, with most having a central peak or ridgeline. To help, note that the sunlight is coming from the west. The arrow on the center left of the picture sits on a plateau above these pits.
According to this paper [pdf], the pits are slowly dug out by the wind coming from the southeast blowing to the northwest, as indicated by the arrows. The central peaks or ridges are thought to be a hint of the original topography, with the wind only able to pull ash from the terrain around these peaks.
» Read more