Isaacman makes it official: Artemis-2 will fly manned around the Moon, despite Orion’s heat shield concerns

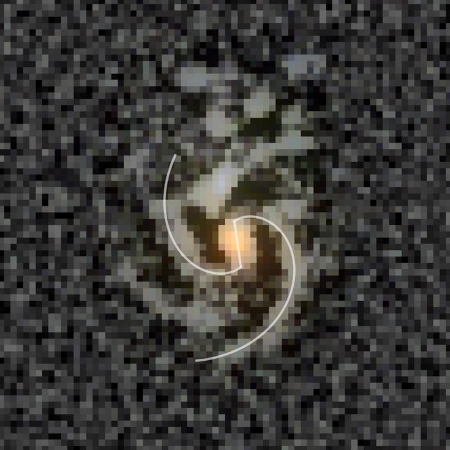
Damage to Orion heat shield caused during re-entry in 2022,
including “cavities resulting from the loss of large chunks”
In a tweet yesterday afternoon, NASA administration Isaacman essentially endorsed the decision of the NASA managers and engineers in its Artemis program who decided they could live with the engineering issues of Orion’s heat shield (as shown in the image to the right) and fly the upcoming Artemis-2 mission around the Moon carrying four astronauts with that same heat shield design.
Isaacman’s statement however suggests to me that he is not looking at this issue as closely as he should.
Human spaceflight will always involve uncertainty. NASA’s standard engineering process is to identify it early, bound the risk through rigorous analysis and testing, and apply operational mitigations that preserve margin and protect the crew. That process works best when concerns are raised early and debated transparently.
I appreciate the willingness of participants to engage on this subject, including former NASA astronaut Danny Olivas, whose perspective reflects how serious technical questions can be addressed through data, analysis, testing, and decisions grounded in the best engineering judgment available. [emphasis mine]
The highlighted sentence is fundamentally incorrect. » Read more