Marilyn Monroe – Lazy
An eveing pause: From the Hollywood film There’s No Business Like Show Business (1954).
Hat tip Judd Clark.
An eveing pause: From the Hollywood film There’s No Business Like Show Business (1954).
Hat tip Judd Clark.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on September 24, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this as an “avalanche scarp”. At first glance it appears we are looking at a major mass wasting event flowing downward to cover the lighter banded terrain near the bottom of the picture.
The problem is that the overlying material didn’t move as an avalanche down onto that lighter material. Note that it has within it its own layers. To have flowed over that lower terrain it would have had to do that coherently, its many layers moving in unison. This doesn’t seem probable, though who knows considering the alien nature of Mars.
So what is going on? And why was this picture taken?
» Read more

This label would be more accurate if it read
“NOT made in the European Union”
At a conference in Germany this week, officials from the U.S. and several European countries expressed strong reservations about a proposed new European space law that would impose significant regulations on satellite and rocket companies, even if they are not European-based.
The objections by the American representative merely underlined the opposition already expressed by the State Department two weeks ago, when it said the law placed ““unacceptable regulatory burdens on U.S. providers of space services to European customers.”
Objections however were also expressed by officials from the United Kingdom and Liechtenstein. The latter’s comments also suggested further opposition should be expected from other European nations as well.
Liechtenstein is not a member of the EU but is part of the European Economic Area (EEA), said Bianca Lins, lead for space in the Liechtenstein Office for Communications. Since the EU Space Act covers issues like a single market for space services in Europe, “it’s going to be incorporated into the EEA agreement and also means we have to transpose it into national law.”
Her concern, she said, is that the act “does not really consider the international obligations that every sovereign state has,” including responsibilities under the Outer Space Treaty. She expected Liechtenstein, Iceland and Norway — the other EEA states outside the EU — to submit comments on those issues.
The law has also been condemned by companies in the U.S. as well as the U.S. Chamber of Commerce.
It is unclear however if the European Union is reconsidering the bill. If it passes it will do significant harm. One possibility is that American companies will pull much of their satellite and launch business out of Europe. And if they do not, it will likely cause them to defy the law, with State Department backing. The EU has no right to impose its rules on American companies.
If the latter occurs, it will thus set a significant legal precedent that suggests the European Union is a toothless non-entity with no real legal power. I suspect this threat above all will force the EU to reconsider the bill.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.

Billionaire Jared Isaacman
Despite being days from a confirmation vote in June after undergoing a Senate hearing previously — when Trump nominated Jared Isaacman for NASA administrator the first time — the Senate has now demanded a second hearing before it will schedule a second confirmation vote on Isaacman.
Sen. Ted Cruz has scheduled a Dec. 3 hearing for Jared Isaacman, the billionaire entrepreneur and commercial astronaut renominated to lead NASA, before the Senate Commerce, Science and Transportation Committee. … The new hearing will mean that Isaacman will not be confirmed by the Senate in the next batch of nominees, which will likely see the floor in the first week of December.
Trump first nominated Isaacman in December 2024, only to withdraw that nomination in May 2025. Trump then renominated Isaacman two weeks ago.
This extra hearing means Isaacman will likely not be confirmed as NASA administrator until early in 2026. It also means he will probably not be in a position to review and reconsider NASA’s plans to send astronauts around the Moon in the February-April time frame, using an Orion capsule with a questionable heat shield and an untested environmental system.
In fact, I suspect this decision to hold hearings was pushed by Cruz partly to make sure Isaacman couldn’t review those plans. Cruz has made it his goal to save SLS and Orion, no matter the cost, and appears willing to play whatever games necessary to prevent any actions that would delay or impact NASA’s present plans.
This however is not the only reason this new hearing has been scheduled. It appears a lot of Senators, especially the Democrats, want to question Isaacman about Isaacman’s 62-page policy paper that was leaked to many in DC in the past few months. It is certain that questioning will have no impact on the final vote (Isaacman is expected to be confirmed handily), but it will allow these senators to preen before the camera, for no good purpose.
The bottom line however is that Isaacman will not be in place early enough to review and change that Artemis-2 mission. It means that almost certainly NASA will once again fly a manned mission that places schedule above engineering, putting four human lives at risk using a spacecraft that has not be vetted properly.
During a conference yesterday, Canada’s industry minister Mélanie Joly announced that her government has increased its budget for European Space Agency (ESA) projects to a total of $528 million over the next three to five years.
This funding increases is quite significant, approximately ten times greater than Canada’s previous budget commitments to ESA projects.
Few details were provided on how the money would be spent.
Joly said the investment would advance research and development of Canadian-made space technologies for both civilian and defence purposes. These include satellite communications, Earth observation, space exploration, positioning, navigation and timing, and space situational awareness, she said.
While most of the western world is shifting to the capitalism model, where the government buys what it needs from products owned by the private sector, it appears the present leftwing Canadian government under Mark Carney is moving instead in the direction of the Soviet model, whereby the government builds and owns the projects itself. This ESA commitment falls into that latter category, at least on the surface. Much however will depend on how ESA and Canada eventually decide to spend the cash.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
Two launches on opposites sides of the globe this evening.
First, SpaceX launched another 29 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral. The first stage completed its 12th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Next (November 19th local time), China placed three classified satellites into orbit, its Long March 2C rocket lifting off from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China. China’s state-run press would only say the satellites were for “space environment exploration and related technology verification,” an utterly meaningless statement. That state-run press also said nothing about where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
151 SpaceX (a new record)
71 China (a new record)
14 Rocket Lab
13 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 151 to 118.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.

Chicken Little is once again panicking
Mexican anti-Musk activists have now announced new complaints against SpaceX’s Boca Chica launch operations, claiming the soft-splash down of its Superheavy boosters in the Gulf of Mexico is damaging marine life, and the company’s effort to remove its stage and debris is further damaging the ocean floor.
Conibio Global A.C., a marine biodiversity organization in Mexico, launched “Expedition Booster 2025” this summer in partnership with the state of Tamaulipas and the Universidad Autónoma de Tamaulipas. The group is studying how booster landings near Playa Bagdad may be affecting wildlife and nearby communities. “We have 20 kilometers of space debris, which amounts to tons,” said Jesus Elias Ibarra Rodriguez, president of Conibio Global A.C. “If you go right now, you’ll find three or five pieces of plastic or metal or electrical parts from the thruster, even tanks—there is already a lot of debris.”
Researchers report that sea turtles and dolphins often mistake smaller debris for food, which can lead to deadly ingestion. They also documented debris fragments measuring between two and 10 meters long. According to the group, 3-D sonar imaging shows that a platform used in July to remove debris may have caused additional damage to the seafloor. “This platform has three structures that were sunk and anchored to the seafloor,” Rodriguez said. “During the investigation, we realized that it caused damage and holes when its structures were wedged in while removing the engines, and the engines were damaging the seabed and the species that live in the area.”
In other words, SpaceX is evil for dropping Superheavy in the Gulf, and it is also evil for removing it. Or to put this in real terms, these activists simply don’t want SpaceX to do anything. Their goal is to shut the company down entirely.
Moreover, their research is clearly bogus and overwrought. The entire world has been dropping lower stages in the oceans for more than three-quarters of a century, with no documented harm to marine life or the oceans. These faux scientists are simply puffing up their work to use this as a hammer against SpaceX.
Their complaint meanwhile appears somewhat bogus as well. They are “in communication” with Mexican authorities, and only “plan to present [their] findings” to that government eventually. In other words, their complaint hasn’t been filed with the government, but with our compliant propaganda press (in this case a local Texas news outlet), who are always glad to push the leftist agenda, no matter how idiotic.
Hat tip to Robert Pratt of Pratt on Texas.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on September 27, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this “scallop-hosting mantle”. In other words, the surface here has a mantle of material that is for a variety of reason cracking and producing these north-facing scallops. That mantle also appears layered, since it descends downward in terraced steps as you travel north. This particular terrace drops about 40 feet.
Scientists believe [pdf] these scallops are formed in connection with the sublimation of underground ice.
According to [one hypothesis] scallop formation should be ongoing at the present time. Sublimation of interstitial ice could induce a collapse of material, initially as a small pit, then growing southward because of greater solar heating on the southern side. Nearby scallops would coalesce together as can be seen to have occurred.
In the case of the image to the right, this sublimation is also accompanied by a drying process similar to cracks one sees in dried mud. As the ice sublimates away the remain material shrinks and cracks.
» Read more

Spectrum falling seconds after its launch
in March 2025
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace today won a new launch contract from the satellite aggregator SEOPS for a 2028 launch of its new Spectrum rocket.
SEOPS today announced during SpaceTech Expo it has purchased a dedicated launch on Isar Aerospace’s ‘Spectrum’ rocket. Targeted for launch in 2028, this marks SEOPS’ first collaboration with Isar Aerospace, expanding the company’s European launch capabilities.
SEOPS acts as an agent for satellite companies building small cubesats, arranging the launches for them because these companies often don’t have the resources or experience to do the job themselves. The choice of Isar’s Spectrum rocket suggests SEOPS wants to encourage new launch options, since Isar has only launched Spectrum once, and that launch was a failure. This contract acts to strengthen Isar’s future by giving it a powerful customer. It also gives SEOPS a European launch option, something that will attract European smallsat makers to it.
Isar is presently preparing Spectrum for its second launch out of Norway’s Andoya spaceport, with road closure announcements suggesting it will occur prior to December 21, 2025. If successful Isar will be the first new European rocket company in decades to reach orbit. It will also be the first German company to do so, ever. And it will give Andoya spaceport first place in the race to become Europe’s first orbital spaceport.
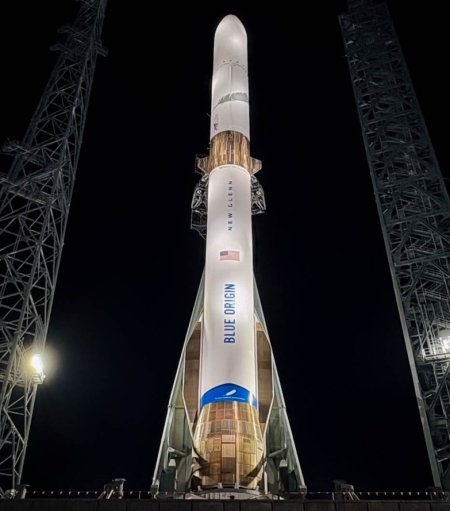

New Glenn on the launchpad prior to its
first launch in January 2025
Following the second successful launch last week of its New Glenn rocket, including a successful recovery of its first stage, Blue Origin’s CEO David Limp says the company’s goal for 2026 will be to attempt between 12 and 24 launches.
Limp said success on New Glenn’s second flight would set the company up for a significant increase in cadence. The company is building enough hardware for “well above” a dozen flights in 2026, with the upper-end limit of 24 launches. The pacing item is second stages. Right now Blue Origin can build one per month, but the production rate is increasing.
A pace of one launch a month would be unprecedented for Blue Origin in numerous ways. Since 2017 the company has built a poor reputation for slow and tentative operations. It took years for it to finally begin building BE-4 engines at a rate that could serve both it and its customer ULA. It took years to get New Glenn off the ground, a half decade later than initially announced. Moving from a lazy tortoise to a enthusiastic hare so quickly would thus seem very unlikely.
Blue Origin however has a major 27-launch contract with Amazon to launch its Amazon LEO constellation (formerly known as “Kuiper”). And Amazon desperately needs those launches to happen soon, as it only has 154 satellites in orbit and needs to get about another 1400 launched by July 2026 to meet its FCC license.
Even so, Limp noted that the next New Glenn launch will be to send its Blue Moon Mark-1 unmanned lunar lander to the Moon, and the best schedule he could offer was a launch sometime in the first quarter of ’26. If so, his prediction for the total launches in 2026 seems overly optimistic, at a minimum.
The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
According to this report at Space News late yesterday, China has issued a road closure notice for its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China suggesting it will launch a Long March 2F rocket carrying a rescue Shenzhou capsule to Tiangong-3 on November 25, 2025, one week from today.
An airspace closure notice issued Nov. 17 indicates that China is preparing the Shenzhou-22 spacecraft and a Long March 2F rocket for launch at around 11:10 p.m. Eastern Nov. 24 (0410 UTC, Nov. 25) from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert. China’s human spaceflight agency has yet to publicly announce the plan. [emphasis mine]
This rescue mission is necessary because the Shenzhou-20 capsule that brought the previous crew to the station is now unusable, having sustained damage in one window from an impact of “space debris.” That crew came back to Earth last week on the Shenzhou-21 that ferried the present crew to space, leaving that present crew without a lifeboat.
The highlighted sentence is important, because it is very possible that road closure notice could be for a different launch not yet announced by China. It is quite routine for China to keep the specifics of a launch secret until the last minute, which means it is dangerous to assume this road closure is specifically for the Long March 2F rocket set to carry the Shenzhou-22 capsule to Tiangong-3.
Previous reports only yesterday had noted that preparing that rocket and capsule would likely take at a minimum 10 to 20 days, and even that schedule would be “difficult.” Getting ready in only one week thus seems unlikely.
At the same time, there is great urgency to launch, as the three-person crew presently on Tiangong-3 has no lifeboat there should anything serious go wrong.
Expect China’s state-run press to clarify the situation, when it decides to do so.
Following the purchase by SpaceX of much of Echostar’s spectrum, its subsidiary Hughesnet appears to be on the verge of shutting down as it is now referring its present and future customers to Starlink.
Hughesnet is preparing to refer its own customers to rival Starlink after its parent company, EchoStar, reached a deal to sell radio spectrum to SpaceX. The referral program is mentioned in a 10-Q SEC filing that Hughesnet released on Friday. The 66-page document includes a section about the EchoStar-SpaceX deal and what it means for Hughesnet’s business. “The commercial agreements will also provide for a fee-based referral program that lets us refer existing HughesNet customers and new Starlink customers to SpaceX,” the document says, without elaborating.
The article also notes that the company lacks the cash on hand to function over the next 12 months, and has lost more than half its customer base in the past year.
A evening pause: Another great cover from this Russian band, this time a song by Chicago. Recorded in 2018, which explains why the lead vocalist is a Ukrainian. It appears he is no longer with the group.
Hat tip Dan Coovert.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
As a historian who likes to read (from real books that I can pick up and feel, not digital versions that make true understanding and absorption difficult), I am routinely reading at least two histories about America’s past at any one time.
For example, I previously had read two great biographies of T.E. Lawrence (of Lawrence of Arabia fame) and Cornelius Vanderbilt (who dominated the American transportation industry in the first half of the 1800s). More about each in future essays, as I think I will start reviewing these books as I finish them.

Believe it or not, this is actually an amazingly
accurate rendering of the first Thanksgiving
Today’s essay however is about two books I finished yesterday, both about two very different periods in American history. Both however had the exact same flaws, typical of the early 2000s when they were written, despite being very detailed and accurate efforts. The books:
The first was published in 2006, and was an attempt to describe in detail the story behind the settlement of Pilgrims in New England in first half century after they arrived in 1620.
The second was published in 2003, and was an attempt to tell the story of the defeat of Japan in World War II, achieved mostly because of the advent of the airplane in reshaping warfare. While ground troops took island after island in the Pacific, in the end it was the air war against Japan itself that eventually forced its surrender. Bradley focuses on telling us the story of the pilots and crews in that air war.
As I already noted, both books do excellent jobs detailing very accurately in vivid terms the events involved. For anyone who wishes to learn something about these significant events of our nation’s history, I recommend them highly.
However, that recommendation comes with one major caveat. In both cases, the authors were handicapped by certain modern academic paradigms that crippled their ability to see the larger context of events. Those paradigms demanded that both historians treat all the cultures involved as morally equivalent, and because of this both writers miss entirely the greater moral fundamentals that moved the Western side of both stories.
For example, let’s take Philbrick’s fascinating history of the Pilgrims.
» Read more

Click for high resolution version. For original images, go here, here, and here.
Cool image time! It appears that during the government shutdown the science team for the Perseverance rover on Mars made the decision to leave an area they had been exploring for the past two months, driving the rover aggressively to the southwest and in a direction that had been unplanned.
The overview map to the right illustrates that move, with the blue dot marking the rover’s present position. The white dotted line indicates its actual travels, while the red dotted line shows the planned route. According to that planned route, the plan had been to move south and back up onto the top of the rim of Jezero Crater. For reasons that the science team has not explained, they decided instead to head to the southwest, away from the crater rim.
The panorama above was created by stitching together three images released today by Perseverance’s left navigation camera (see here, here, and here). The yellow lines on the overview map indicate my guess as to the area covered by this panorama. Note Perseverance’s tracks on the left. I think this panorama shows us the area the rover traveled in this recent move.
Note also the barrenness of the terrain. This is truly an alien world. It has an atmosphere that produces a very faint wind, that over eons can erode things. This is why this exterior wall of the rim of Jezero crater is so relatively smooth. Crater rims are usually places of jagged broken rock, thrown out by the impact. That very thin Martian atmosphere over time has smoothed that terrain.
This landscape also has no life. Except for some spots in the polar regions, it is literally impossible to find any place on Earth so devoid of life.
Because of local laws forbidding the operation of any foreign-owned telecommunications company in Thailand, its government has rejected any sale of Starlink terminals inside the country.
The Digital Economy and Society Ministry has rejected a proposal from SpaceX to provide Starlink low-orbit satellite internet services in Thailand through a 100% foreign-owned company, citing national security concerns and legal restrictions. “If the company wants to set up a wholly owned firm, there will be no opportunity … to cooperate, as telecom ownership is directly linked to our digital security system,” minister Chaichanok Chidchob said on Friday.
This is the same problem that SpaceX has faced in a number of other third world countries, such as India and South Africa. In South Africa the government demanded SpaceX give up some or all of its ownership rights as well as impose a variety of racial or employment quotas that SpaceX considers unacceptable. Thus, no Starlink. In the case of India, the government insisted that its own telecom companies get a cut. SpaceX then managed to negotiate deals with each, where those companies market the Starlink terminals for SpaceX.
Apparently, no such deal has yet been worked out in Thailand.
Expect a deal eventually, however. The article notes that Thailand’s neighbor Vietnam has a Starlink deal allowing its citizens to sign up without restrictions. That agreement is going to put great pressure on Thailand

In an agreement signed on November 14, 2025, the European Space Agency (ESA) completed the transfer of the Vega-C rocket, formerly controlled by the government-owned company Arianespace, back to the Italian company Avio.
Following decisions taken by the ESA Council in 2023, the revision of the Launchers Exploitation Declaration (LED) was finalized on 10 July 2025 and the Guiana Space Centre Agreement was signed on 23 October 2025. The LEAs signed today translate the LED mandate to ESA into concrete detailed implementation arrangements between ESA and the launch operators.
The two arrangements signed today – one with Arianespace and ArianeGroup for Ariane 6, and one with Avio for Vega-C – define the roles and responsibilities of each operator and ESA’s role in monitoring its implementation. They also establish the framework for cooperation between the parties to ensure Europe’s continued autonomous access to space through the exploitation of ESA-developed launchers from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
The quote above also details other changes. The Ariane-6 rocket is now controlled by a partnership of Arianespace and ArianeGroup, with the bulk of control by the latter, a private company that owns the rocket. Though Arianespace retains some management rights, its part in the rocket’s future has been reduced significantly.
Meanwhile, ownership and control of the French Guiana spaceport has now been transferred entirely from Arianespace and back to France’s space agency CNES. CNES has been running things more or less for the past year or so, but this makes the change official.
All in all, these agreements continue ESA’s shift in the past two years away from the government-run model, centralized under Arianespace control, to the capitalism model, where the government is merely a customer, buying what it needs from independent, competing, privately-owned companies. While these agreements highlight Avio and ArianeGroup, Europe also has a flock of new rocket startups (Isar, Rocket Factory Augsburg, PLD) on verge of their first launches.
If Europe maintains its commitment to this shift, it should see some exciting developments in space in the coming years.

The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
According to China’s state run press, it has begun emergency procedures to quickly launch the Shenzhou-22 capsule — originally scheduled to carry the next crew to its Tiangong-3 station in April 2026 — in order to provide the present station crew a lifeboat and a return capsule.
The China Manned Space Agency has started preparations for the launch of an unmanned spacecraft to carry a full cargo load, including provisions for astronauts and equipment for the Tiangong space station, according to a senior engineer. Zhou Yaqiang, who works with the agency’s general technical bureau, told China Central Television on Saturday that all systems involved in the upcoming Shenzhou-22 cargo mission “are busy getting ready for it, testing the rocket and the spaceship and preparing the payloads”.
The Shenzhou-22 spacecraft will be launched in due course to dock with the Tiangong space station, the agency said.
The report provided no details on when this launch would occur, though another Chinese report said getting the rocket (a Long March 2F) and capsule ready in the next 10 to 20 days would be “difficult.”
At the moment, the three astronauts on Tiangong-3 have no lifeboat. Should anything go wrong at the station before that launch they will have no way to get back to Earth, unless they use the damaged Shenzhou-21 capsule still docked to the station. That capsule has cracks in a window, caused by what the Chinese think was an impact from “space debris.” The Chinese have already determined it is not safe for human travel. Thus, using it in an emergency would be a desperate act.
Since the first space station, Salyut-1, was launched and occupied in 1971, this is the first time that a crew has been in space with absolutely no way to get home. The press last year repeatedly claimed the Starliner crew was “stranded” on ISS, but that wasn’t so. They could have always come home on their Starliner craft, as was proven when it returned unmanned with no problems. NASA had simply made the decision to be cautious and wait for the launch of next Dragon to bring them home instead.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) earlier today announced it is lifting the restrictions on airline traffic as well as rocket launch limitations imposed due to the government shutdown.
The change will go into effect 6 am (local time) on November 17, 2025.
The restrictions had limited flights out of 40 major airports across the country. Normal flight schedules should resume tomorrow. For rockets, this means launches can once again take place at any time of the day. The restrictions had placed a curfew on any launches from 6 am to 10 pm local time.
The press release included this intriguing tidbit:
The FAA is aware of reports of non-compliance by carriers over the course of the emergency order. The agency is reviewing and assessing enforcement options.
If the FAA does anything to penalize any airline or rocket company it would be a very typical example of government pettiness. But then, I have learned never to expect anything better from bureaucracies.
SpaceX tonight successfully launched Sentinal-6B, a NASA radar satellite designed to measure the global sea level, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base.
The first stage completed its 3rd flight, landing back at Vandenberg.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
150 SpaceX (a new record)
70 China
14 Rocket Lab
13 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 150 to 117.
Note that until SpaceX began to up its launch rate significantly in 2022, the entire global rocket industry — run entirely by governments — never completed more than 135 successful launches in a single year, and usually failed to make 100 launches. SpaceX is now proving that those global numbers over more than a half century were indicative of the failure of those governments. Those governments controlled everything, and so they prevented innovation, competition, and new ideas.
The transition to capitalism and freedom since 2010 has finally begun to open up space for everyone.
Using Europe’s Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) that is in orbit around Mars, engineers have obtained images of the interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas.
The image to the right is a screen capture of the last image in a movie they created from all the pictures. I have added the arrow to indicate the comet, which underlines the fact that these images really don’t tell us that much about the comet itself. It is hardly more than a few pixels across, with no real detail resolved. However, the data has still been found useful.
Until September, figuring out the location and trajectory of 3I/ATLAS relied on Earth-based telescopes. Then between 1 and 7 October, ESA’s ExoMars TGO turned its eyes towards the interstellar comet from its orbit around Mars. The comet passed relatively close to Mars, approaching to about 29 million km during its closest phase on 3 October.
The Mars probe got about ten times closer to 3I/ATLAS than telescopes on Earth and it observed the comet from a new viewing angle. The triangulation of its data with data from Earth helped to make the comet’s predicted path much more accurate.
While the scientists initially anticipated a modest improvement, the result was an impressive ten-fold leap in accuracy, reducing the uncertainty of the object’s location.
All the data continues to confirm that 3I/Atlas is nothing more than comet, though like all comets unique in its own way. This refined location data will also improve the on-going observations of Europe’s Jupiter probe Juice, presently on its way to Jupiter and in the best position to see 3I/Atlas.
SpaceX yesterday completed two launches, placing a total of 58 Starlink satellites into orbit.
First, a Falcon 9 lifted off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, carrying 29 Starlink satellites. The first stage completed its 8th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Four hours later, a second Falcon 9 lifted off from Cape Canaveral, carrying another 29 Starlink satellites. Its first stage completed its 24th flight, also landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
149 SpaceX
70 China
14 Rocket Lab
13 Russia
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 149 to 117.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
An evening pause: I think we all take for granted the amount of sophisticated engineering that goes into modern construction. No English, but you don’t need it.
Hat tip Cotour.
David Livingston has now uploaded the audio of my appearance on the Space Show earlier this week on November 11, 2025.
You can download the audio of the program here.
To watch the zoom broadcast, go here.
The most important point I made during this show was at the beginning, as described by David Livingston’s summary of the show:
During the program Bob made some predictions about the future of space exploration. Zimmerman claimed that SpaceX, rather than NASA, is currently the most effective American space program. He predicted that in two years, everyone would recognize SpaceX’s dominance. Zimmerman also suggested that NASA’s role should become less significant, with its focus shifting to supporting private space endeavors rather than leading space exploration efforts.
I was actually more blunt. I said that SpaceX is the American space program right now, and that SpaceX doesn’t need NASA or the U.S. government in any way to carry it out, as it is entirely funded from Starlink revenues. I also predicted that NASA and its Artemis program is now irrelevant, though no one yet realizes it.
I added that this is going to be one of my many predictions that everyone will claim they made, two years hence. I’m making it now. I am quite willing to bet I will be right.
Everyone should take a listen. You will find the discussion afterward most revealing.
When India’s Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft arrived in lunar orbit in August 2023, it separated into three units, the lander, a lunar orbiter, and a propulsion unit used to get everything to the Moon.
While the Vikram lander successfully touched down several hundred miles from the Moon’s south pole and the Chandrayaan-3 orbiter continues to make observations of the Moon, in October 2023 engineers had the propulsion module do a burn that sent it out of lunar orbit and into an Earth orbit that was close to one of the Lagrange points where the gravity of the Earth and Moon are balanced.
Now, three years later, that module has drifted back into lunar orbit, where it has since done two close fly-bys of the surface.
This intricate orbital dance culminated when the module once again entered the Moon’s SOI [sphere of influence] on November 4, 2025, an event marking the transition where lunar gravity dominates its motion.
The first recorded lunar flyby occurred on November 6, 2025, at a distance of 3,740 km from the lunar surface, though it was outside the Indian Deep Space Network’s (IDSN) visibility range. A second, closely monitored flyby took place on November 11, 2025, bringing the module within 4,537 km of the Moon and well within observation capabilities.
These events noticeably altered the satellite’s orbital parameters, expanding its orbit size from 100,000 x 300,000 km to a massive 409,000 x 727,000 km and shifting its inclination from 34° to 22°.
It is not clear what happens next. Having this module in lunar orbit could be an issue for present and later orbiters, as no orbit around the Moon can ever be stable. At some point India’s space agency ISRO needs to properly dispose of this unit, either by sending into the Moon or out of the Moon-Earth system entirely. I am of course assuming it has the fuel to do so.