August 14, 2023 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay.
- Safran, Terran Orbital to explore joint production of satellite propulsion systems
- BWXT to begin work on cislunar nuclear rocket engine and fuel
These two stories are from June and July. Though I thought I had covered them, I can’t find them on BtB. They both illustrate the growing diversification occurring within the new commercial space industry.
- Australian company Hypersonix wins contract to build 20 scramjet test vehicles for hypersonic test flights
The vehicles are for a U.S. company, Kratos, which is doing hypersonic test flights for the Pentagon.
- Sierra Space wins $22 million Pentagon contract to develop upper stage rocket engine
The new engine is based on Sierra’s Vortex engine that has already been successfully tested, and uses hydrogen as its fuel.
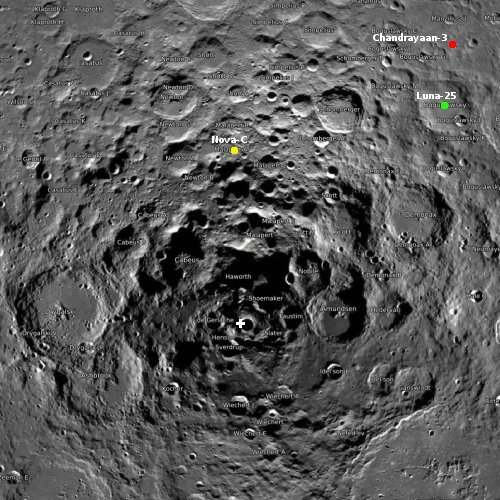
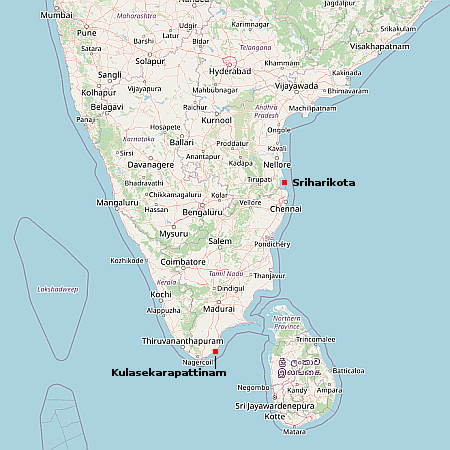
- Luna-25 successfully completed its last mid-course correction burn today
It will enter lunar orbit in two days, with the landing tentatively planned for August 21.
- First photos from Luna-25 released
Taken yesterday, the images confirm the camera and spacecraft are functioning as planned.
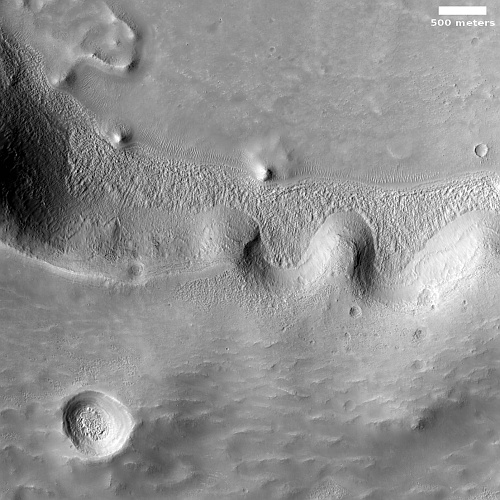
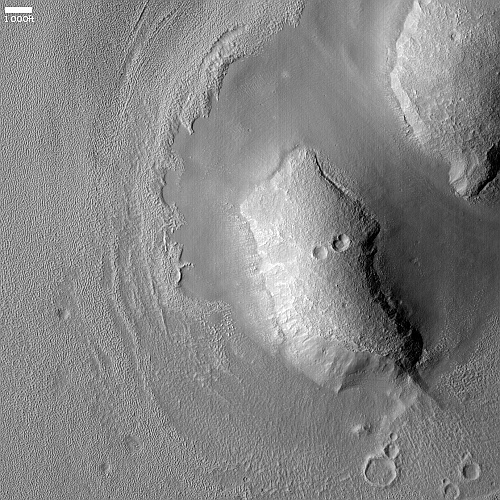
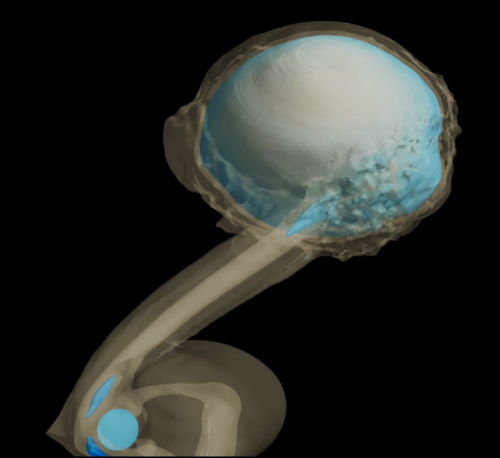
- Another image from China’s Tianwen-1 Mars orbiter
The region of fissures shown, Sacra Sulci, is part of Kasei Valles, one the long valleys draining Mars’ giant volcanoes. See this post from May 2021 for more information.
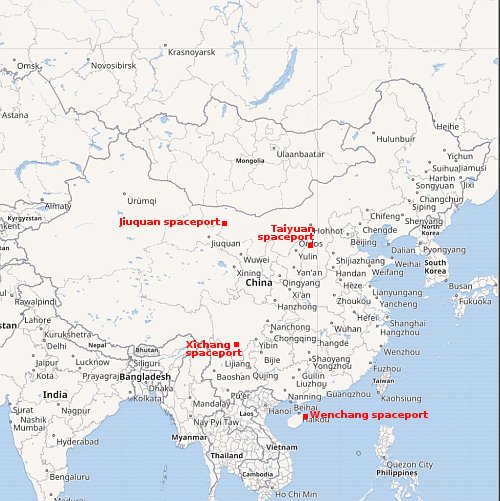
- Rocket Lab will use the facility it obtained from the Virgin Orbit bankruptcy for scaling up production of its new Neutron rocket
The facility will mainly be used to build Neutron’s Archimedes engines. The target date for first launch of Neutron remains 2024.
- A list of the major meteor showers each year
Also includes an interesting animation showing the debris trail and orbit of the Perseid meteor shower, which comes from Comet Swift-Tuttle.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay.
- Safran, Terran Orbital to explore joint production of satellite propulsion systems
- BWXT to begin work on cislunar nuclear rocket engine and fuel
These two stories are from June and July. Though I thought I had covered them, I can’t find them on BtB. They both illustrate the growing diversification occurring within the new commercial space industry.
- Australian company Hypersonix wins contract to build 20 scramjet test vehicles for hypersonic test flights
The vehicles are for a U.S. company, Kratos, which is doing hypersonic test flights for the Pentagon.
- Sierra Space wins $22 million Pentagon contract to develop upper stage rocket engine
The new engine is based on Sierra’s Vortex engine that has already been successfully tested, and uses hydrogen as its fuel.
- Luna-25 successfully completed its last mid-course correction burn today
It will enter lunar orbit in two days, with the landing tentatively planned for August 21.
- First photos from Luna-25 released
Taken yesterday, the images confirm the camera and spacecraft are functioning as planned.
- Another image from China’s Tianwen-1 Mars orbiter
The region of fissures shown, Sacra Sulci, is part of Kasei Valles, one the long valleys draining Mars’ giant volcanoes. See this post from May 2021 for more information.
- Rocket Lab will use the facility it obtained from the Virgin Orbit bankruptcy for scaling up production of its new Neutron rocket
The facility will mainly be used to build Neutron’s Archimedes engines. The target date for first launch of Neutron remains 2024.
- A list of the major meteor showers each year
Also includes an interesting animation showing the debris trail and orbit of the Perseid meteor shower, which comes from Comet Swift-Tuttle.