Dawn’s farewell tour of the giant asteroid Vesta
An evening pause: As Dawn begins its journey away from Vesta, the science team has put together this stunning video tour of the giant asteroid.
An evening pause: As Dawn begins its journey away from Vesta, the science team has put together this stunning video tour of the giant asteroid.
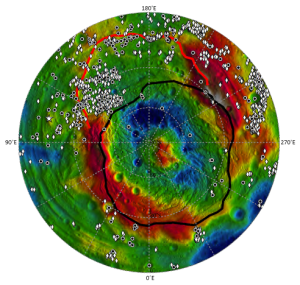
In a preprint paper published today at the Los Alamos astro-ph website, scientists have taken a detailed look at the mysterious dark streaks seen by Dawn on the surface of the asteroid Vesta and have concluded that the material comes from impacts, not from volcanic activity.
The scientists also concluded that
the majority of the spectra of [dark material] are similar to carbonaceous chondrite meteorites mixed with materials indigenous to Vesta.
Carbonaceous chondrite meteorites are considered to be the most primeval material in the solar system. This means that Vesta has the potential to give scientists a convenient laboratory for studying that primeval material and the early formation of the solar system. Ideally, the best way to do this would of course be to go there.
The scientists also theorize that much of this material was brought to Vesta by a single large impact.
» Read more
An update on Dawn’s reaction wheel failure.
Essentially, this will delay the journey to Ceres for about nine days. The spacecraft is left with two working reaction wheels, with which it can complete all its science work. However, if they cannot get the failed wheel working again, Dawn will be left with no backup should another wheel fail.
Uh-oh: One of Dawn’s reaction wheels, used to orient the spacecraft, shut down last week.
During a planned communications pass on Aug. 9, the team learned that the reaction wheel had been powered off. Telemetry data from the spacecraft suggest the wheel developed excessive friction, similar to the experience with another Dawn reaction wheel in June 2010. The Dawn team demonstrated during the cruise to Vesta in 2011 that, if necessary, they could complete the cruise to Ceres without the use of reaction wheels.
That the spacecraft can get to Ceres without reaction wheels is good. However, can it be oriented precisely to do science without these wheels? The JPL press release does not say.
Dawn has begun its slow departure from Vesta in anticipation of its journey to the solar system’s largest asteroid, Ceres.
The departure was actually announced two weeks ago, but since this is a very slow process it isn’t like we have missed anything. Dawn’s ion engines are very efficient, but they work at a very leisurely pace. It will take a month for the engine’s thrusters to push Dawn out of its orbit around Vesta.
New computer models suggest that the Moon was created when a Mars-sized asteroid hit the Earth in a head-on collision at high speed, not a glancing blow at relatively slow speeds, as previously thought.
Watching a big asteroid zip past the earth, live.
The only program surveying the southern sky for dangerous asteroids has lost its NASA funding and will end this month.
Scientists have identified the oldest known impact crater on Earth, three billion years old.
A private organization focused on preventing asteroids from impacting the Earth today announced its plans to build and launch an infrared space telescope by 2017.
Scientists have found a previously unknown mineral embedded in a meteorite that crashed to Earth in 1969.
Dubbed panguite, the new titanium oxide is named after Pan Gu, the giant from ancient Chinese mythology who established the world by separating yin from yang to create the earth and the sky. … “Panguite is an especially exciting discovery since it is not only a new mineral, but also a material previously unknown to science,” says Chi Ma, a senior scientist and director of the Geological and Planetary Sciences division’s Analytical Facility at Caltech and corresponding author on the paper.
An asteroid that was discovered only four days before it flew by the Earth on June 14 has turned out to be much bigger than first thought.
This particular asteroid may not have been a danger, but much of the concern was rooted in the late warning of its detection — 2012 LZ1 was spotted only four days before closest approach. One of the reasons for its late discovery is because it was detected in Southern Hemisphere skies, part of the world were we have few asteroid-watching programs. If it had been on a collision course with Earth, a few days notice is no time at all.
So, in the aftermath of the flyby, astronomers at the famous Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico used radar to image the interplanetary interloper (pictured top). What they uncovered was a surprise: Asteroid 2012 LZ1 is actually bigger than thought… in fact, it is quite a lot bigger. 2012 LZ1 is one kilometer wide (0.62 miles), double the initial estimate.
Astronomers have videotaped the fly-by of a 23-foot-wide asteroid as it zipped past the Earth on May 29 at a distance of only about 12,000 miles. The video is below the fold.
» Read more
O goody: Scientists have concluded that a 460 foot diameter asteroid only has a 1 percent chance of hitting the Earth in 2040.
Observations to date indicate there is a slight chance that AG5 could impact Earth in 2040. Attendees expressed confidence that in the next four years, analysis of space and ground-based observations will show the likelihood of 2011 AG5 missing Earth to be greater than 99 percent.
It appears that they won’t really be able to pin down the impact odds for 2040 until 2023, when the asteroid passes the Earth at a distance of 1.1 million miles.
Watch an asteroid a third of a mile across zip past the Earth tonight.
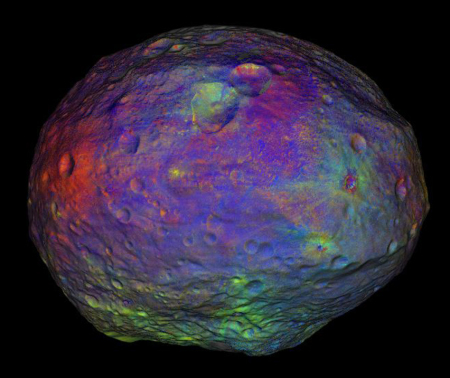
The accumulating data from Dawn has now allowed scientists to compile a global picture of the varied surface makeup of the asteroid Vesta.
The colors were chosen to highlight differences in surface composition that are too subtle for the human eye to see. Scientists are still analyzing what some of the colors mean for the composition of the surface. But it is clear that the orange material thrown out from some impact craters is different from the surrounding surface material. Green shows the relative abundance of iron. Parts of the huge impact basin known as Rheasilvia in Vesta’s southern hemisphere, for instance, have areas with less iron than nearby areas.
It also makes for a very nice image of the giant asteroid.
The scientists building a space probe to go to asteroid 1999 RQ36 have better pinpointed its orbit.
Knowing this asteroid’s orbit is not only important for planning the mission. 1999 RQ36 has a 1in a 1000 chance of hitting the Earth in 2182.
Based on further analysis of the data from WISE, the infrared space telescope, astronomers have now made a better estimate of the population of potentially hazardous asteroids.
Potentially hazardous asteroids, or PHAs, are a subset of the larger group of near-Earth asteroids. The PHAs have the closest orbits to Earth’s, coming within five million miles (about eight million kilometers), and they are big enough to survive passing through Earth’s atmosphere and cause damage on a regional, or greater, scale.
The new results come from the asteroid-hunting portion of the WISE mission, called NEOWISE. The project sampled 107 PHAs to make predictions about the entire population as a whole. Findings indicate there are roughly 4,700 PHAs, plus or minus 1,500, with diameters larger than 330 feet (about 100 meters). So far, an estimated 20 to 30 percent of these objects have been found.
From the Dawn science team: The battered failed planet Vesta.
The results confirm Vesta as the source of a specific family of asteroids, but more interestingly also identify the actual impact that peeled these asteroids from Vesta’s surface.
Read the whole thing, Dawn has found a lot of interesting stuff.
Private companies do have the right to mine the asteroids, established by precedent. Hat tip Clark Lindsey.
Duck! New data suggests that the giant ancient asteroid barrage during the early solar system may have lasted much longer than previously thought.
To mine the asteroids, first build small cheap space telescopes.
The space telescope will be based on the same design Planetary Resources will eventually use for its asteroid-prospecting spacecraft: a 30-kilogram to 50-kilogram flier packed with imaging sensors and a laser-optical communication system the company is developing to avoid encumbering its spacecraft with large antennas. The company, which says it has about two dozen employees, will market these spacecraft as cheap but effective telescopes for both astronomical and Earth-observing applications. Sales would provide cash for the company’s core work on asteroid mining, Eric Anderson, co-founder and co-chairman of Planetary Resources, said.
The telescope slated for launch sometime in the next two years “would be something, let’s say, a university buys [for astronomical observations], or a commercial company that wants to monitor shipping traffic or something like that,” Anderson said in a phone interview. The cost for the telescope, which Planetary Resources is calling Arkyd-101, would be “millions of dollars, including launch.”
At the Planetary Resources press conference today, there was a lot of talk about the benefits and profits to be gained from mining the asteroids. However, this ain’t gonna happen for quite a few years. In the meantime, the company plans to make money building space telescopes which scientists and others can use, for a fee, to do research.
In other words, the government and astronomers dropped the ball on replacing the Hubble Space Telescope. Now, private enterprise is going to pick it up and run with it.
No announcement yet, but of the many stories available this Wired article appears to provide the best overview of the asteroid mining plans of Planetary Resources.
The company’s first phase is most interesting:
Within the next 18 to 24 months, Planetary Resources hopes to launch between two and five space-based telescopes at an estimated cost of a few million dollars each that will identify potentially valuable asteroids. Other than their size and orbit, little detailed information is available about the current catalog of near-Earth asteroids. Planetary Resources’ Arkyd-101 Space Telescopes will figure out whether any are worth the trouble of resource extraction.
The actual press conference is scheduled for 10:30 am (Pacific). Stay tuned.
Update: The Planetary Resources website has now been updated. You can read more about their space telescope proposal here.
Want to get a jumpstart on Tuesday’s asteroid-mining announcement by Planetary Resources? Read this NASA report [pdf], released April 2.
Is asteroid mining about to begin?
Considering some of the major players who are either investors or advisers for this company, this story could get very exciting when the company’s full plans are revealed on April 24.
Dawn’s mission at Vesta has been extended for forty days, while still allowing the spacecraft to reach Ceres as scheduled.
Fly me to the other moons! A computer simulation suggests that the Earth normally has several asteroid-sized smaller moons in temporary orbit around it.
New close-up photos of the asteroid Vesta from Dawn have discovered numerous bright spots scattered across the face of the asteroid Vesta.
The photos show surprisingly bright spots all over Vesta, with the most predominant ones located inside or around the asteroid’s many craters. The bright areas range from large spots (around several hundred feet across) to simply huge, with some stretching across 10 miles (16 kilometers) of terrain.
The scientists believe the bright spots might be the asteroid’s oldest material, excavated from below by impacts.
Duck! The orbit of a 150 foot wide asteroid that zipped past the Earth in February, has an orbit that will bring it past the Earth again on February 15, 2013 by less than 15,000 miles.
The team use several automated telescopes to scan the sky, and the discovery came somewhat serendipitously after they decided to search areas of the sky where asteroids are not usually seen. “A preliminary orbit calculation shows that 2012 DA14 has a very Earth-like orbit with a period of 366.24 days, just one more day than our terrestrial year, and it ‘jumps’ inside and outside of the path of Earth two times per year,” says Jaime.
While an impact with Earth has been ruled out on the asteroid’s next visit, astronomers will use that close approach for more studies and calculate the Earth and Moon’s gravitational effects on it.
Because this newly discovered asteroid passes so close and frequently to both the Earth and Moon, astronomers will need a lot more data before they can pin down its orbit precisely, and thus predict the chances of a collision in the near future.