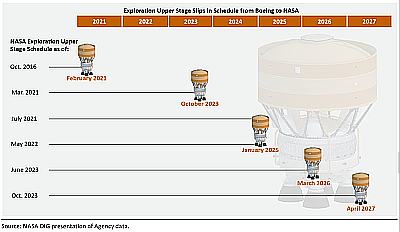
Boeing employees reject deal of union and company and go on strike
In another blow to the company, Boeing’s employees have gone on strike after overwhelming voting to reject a new deal their union officials had negotiated with the company that had called for a 25% salary increase across the board.
Members of the International Association of Machinists District 751, which represents about 33,000 Boeing workers in Washington state, walked off the job when their contract expired at midnight on Thursday night. Almost 95 per cent rejected the deal endorsed by their bargaining team on Sunday and 96 per cent voted to strike, easily exceeding the two-thirds majority needed to trigger a walkout.
Many of the union’s members expressed anger on social media, criticising the deal and accusing IAM leaders of settling for too little. Many had been ready to strike, partly fuelled by residual anger from a 2014 deal that eliminated defined-benefit pensions.
Boeing on Thursday said it was ready to renegotiate a deal to halt a crippling strike.
Right now Boeing’s credit rating is “one notch above junk” and if the strike isn’t settled quickly that rating could drop more. It will also prevent the company from taking any action to recover from its numerous problems that are limiting sales of its airplanes and its military and space products.
In another blow to the company, Boeing’s employees have gone on strike after overwhelming voting to reject a new deal their union officials had negotiated with the company that had called for a 25% salary increase across the board.
Members of the International Association of Machinists District 751, which represents about 33,000 Boeing workers in Washington state, walked off the job when their contract expired at midnight on Thursday night. Almost 95 per cent rejected the deal endorsed by their bargaining team on Sunday and 96 per cent voted to strike, easily exceeding the two-thirds majority needed to trigger a walkout.
Many of the union’s members expressed anger on social media, criticising the deal and accusing IAM leaders of settling for too little. Many had been ready to strike, partly fuelled by residual anger from a 2014 deal that eliminated defined-benefit pensions.
Boeing on Thursday said it was ready to renegotiate a deal to halt a crippling strike.
Right now Boeing’s credit rating is “one notch above junk” and if the strike isn’t settled quickly that rating could drop more. It will also prevent the company from taking any action to recover from its numerous problems that are limiting sales of its airplanes and its military and space products.