X-37B photographed in orbit
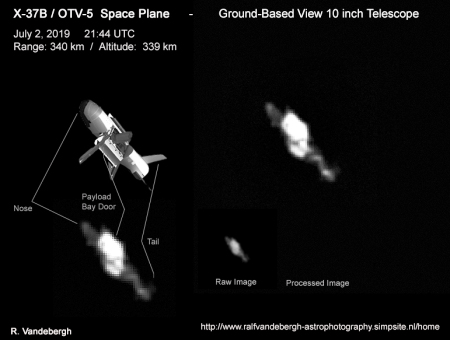
An amateur astronomer this week was able to get a photograph of the X-37B presently in orbit about 200 miles high.
The [X-37B] is a small version of the classic Space Shuttle, it is really a small object, even at only 300 km altitude, so dont expect the detail level of ground based images of the real Space Shuttle. Considering this, the attached images succeeded beyond expectations. We can recognize a bit of the nose, Payload Bay and tail of this mini-shuttle with even a sign of some smaller detail.
The image on the right, reduced and cropped to post here, shows the image with a graphic of the spacecraft in comparison.
The graphic assumes the X-37B’s cargo door is open, but the actual image does not match this, to my eye. Instead, it appears partly open, with some kind of large object protruding from the cargo bay.
This X-37B spacecraft, one of two the Air Force flies, was launched by SpaceX in September 2017 and has now been in space more than 664 days, with no indication yet when it will return to Earth. The present record is 718 days for the longest X-37B flight, set by the Air Force’s other X-37B. It appears likely that this spacecraft will exceed that record.
An amateur astronomer this week was able to get a photograph of the X-37B presently in orbit about 200 miles high.
The [X-37B] is a small version of the classic Space Shuttle, it is really a small object, even at only 300 km altitude, so dont expect the detail level of ground based images of the real Space Shuttle. Considering this, the attached images succeeded beyond expectations. We can recognize a bit of the nose, Payload Bay and tail of this mini-shuttle with even a sign of some smaller detail.
The image on the right, reduced and cropped to post here, shows the image with a graphic of the spacecraft in comparison.
The graphic assumes the X-37B’s cargo door is open, but the actual image does not match this, to my eye. Instead, it appears partly open, with some kind of large object protruding from the cargo bay.
This X-37B spacecraft, one of two the Air Force flies, was launched by SpaceX in September 2017 and has now been in space more than 664 days, with no indication yet when it will return to Earth. The present record is 718 days for the longest X-37B flight, set by the Air Force’s other X-37B. It appears likely that this spacecraft will exceed that record.