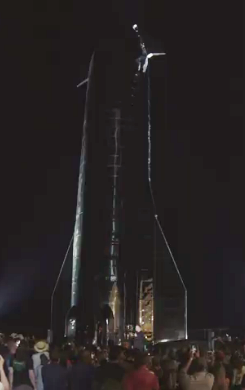
Elon Musk has begun his speech. The image to the right shows him as a tiny figure at the base of the just completed Starship Mk1 prototype. I will be adding details here as the speech proceeds.
First, he wants to inspire and thinks making humanity a multi-world species is the way to do it.
Then, to make us multi-world species requires a completely reusable rocket, what he called “the holy grail of space.”
Next, he goes back to the beginning of SpaceX, the first launch of Falcon 1 on this date years ago. “Getting to orbit is hard. We were very naive.”
From here he discussed Grasshopper, and noted that Starship Mk1 will do the a bigger version of that “in one to two months.” To repeat, they will be doing that quickly, and will be aiming for orbital flights in six months.
He is interspersing the speech with videos, of Falcon 1 launching, of Grasshopper, of Falcon Heavy, I think to illustrate how far SpaceX has come in such a short time. For example, he notes that Falcon Heavy’s first launch was only last February.
He is now outlining Starship as planned. Starship is now expected to be at 120 tons in mass, more than first planned. It will be able put 150 tons in orbit with full reuseability.
Next, getting it back to Earth in reusable form: It will return in many ways like the shuttle, but with its own uniqueness. “It will fall like a skydiver, then become vertical, and land.”
Next, the Raptor engines: Starship will have six, three able to adjust their nozzle and three fixed and optimized for efficiency. The Mk1 prototype has the three adjustable, since these will be used for landing. The other three engines will be for getting into orbit.
The heat shield and hull: They are going to use hexagonal ceramic tiles in the thermally critical areas. Everything else will use stainless steel, which he says is actually stronger when hot them some traditional rocket materials. It also has a high melting point. “You don’t need any shielding on the leeward side.” It is also much cheaper than carbon fiber, and much easier to use, shape, weld, install.
Super Heavy booster: Now estimating it will have 37 Raptor engines, but this number will be changeable, even when it is operational. The fins will be legs (just like the 1950s sci-fi movies!).
Final complete stack, both Starship and and Super Heavy, will be 2 1/2 times taller than Starship Mk1, as shown in the image above. They then showed a simulation of a launch, which I am sure will be online very shortly.
To get to either the Moon or Mars Starship will require refueling in orbit. This technology he considers essential. It will require rendezvous and docking, a skill they are learning with their manned Dragon.
He is also outlining the need to go to both the Moon and Mars, and then beyond. However, his first focus is on finding “the fastest path to building a city on Mars.”
His larger focus is making us multi-planetary, in order to preserve both our existence and all life on Earth. “And we should do it now!”
To sum up, the gist of the speech was to outline how far the entire company has come in a very short time, where they think they are going in the near future with Starship — and that’s the very near future — and then to conclude with Musk’s longer term vision for space exploration. Overall, it appears the goal was to once again sell Starship and the magnificent possibilities it might achieve.