If ordinary people don’t show up at those upcoming FAA Starship/Superheavy public meetings they WILL be screwed
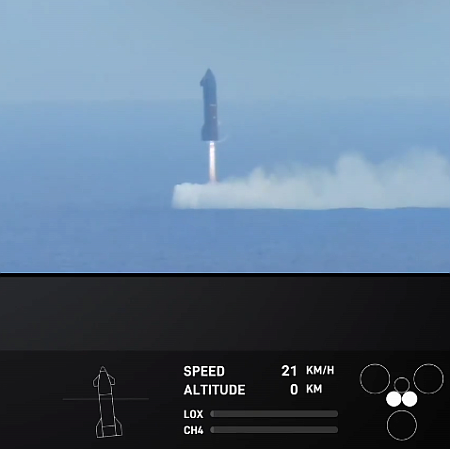
Starship splashing down vertically in the
Gulf of Mexico on November 19, 2024
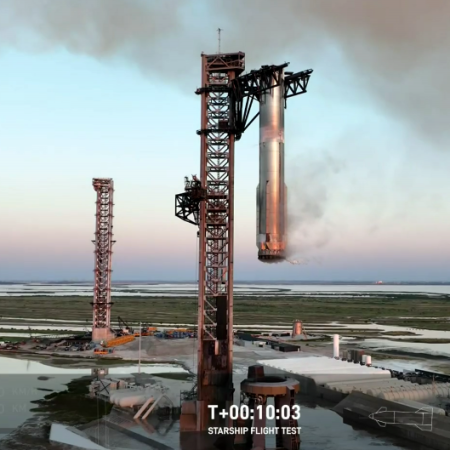
Yesterday radio host Robert Pratt sent me a news story from a Texas newspaper, the Texas Tribune, which attempted quite surprisingly to capture fairly the local response to the most recent Starship/Superheavy test launch out of Boca Chica on November 19, 2024.
The reporter, Bernice Garcia, clearly made it a point to talk to a lot of people, especially those who came out to see the launch. As a result, she showed that in general, no matter what people felt about Donald Trump or Elon Musk, the local population was almost entirely in favor of SpaceX’s efforts there. For example:
Sanchez was slightly concerned about [the rocket’s sonic booms] but believed the benefits of jobs created by SpaceX was worth the risk. “They know what they’re doing,” Sanchez said.
But his favorable opinion of Musk’s company did not extend to Trump. A naturalized citizen who gained amnesty under the Reagan administration, Sanchez didn’t view Trump’s immigration policies as logistically sound. “If you throw those people out, who’s going to work?” Sanchez said. “You don’t see a white man laboring out in the sun. On the other hand, Mexicans, foreigners, people from other countries –– that’s why they come here, to work.”
While the story found locals with a whole range of opinions about Trump, both positive and negative, it only quoted one person who was hostile to SpaceX, and that quote and person tells us a great deal about the bankrupt nature of that opposition:
» Read more

Starship splashing down vertically in the
Gulf of Mexico on November 19, 2024
Yesterday radio host Robert Pratt sent me a news story from a Texas newspaper, the Texas Tribune, which attempted quite surprisingly to capture fairly the local response to the most recent Starship/Superheavy test launch out of Boca Chica on November 19, 2024.
The reporter, Bernice Garcia, clearly made it a point to talk to a lot of people, especially those who came out to see the launch. As a result, she showed that in general, no matter what people felt about Donald Trump or Elon Musk, the local population was almost entirely in favor of SpaceX’s efforts there. For example:
Sanchez was slightly concerned about [the rocket’s sonic booms] but believed the benefits of jobs created by SpaceX was worth the risk. “They know what they’re doing,” Sanchez said.
But his favorable opinion of Musk’s company did not extend to Trump. A naturalized citizen who gained amnesty under the Reagan administration, Sanchez didn’t view Trump’s immigration policies as logistically sound. “If you throw those people out, who’s going to work?” Sanchez said. “You don’t see a white man laboring out in the sun. On the other hand, Mexicans, foreigners, people from other countries –– that’s why they come here, to work.”
While the story found locals with a whole range of opinions about Trump, both positive and negative, it only quoted one person who was hostile to SpaceX, and that quote and person tells us a great deal about the bankrupt nature of that opposition:
» Read more






