Florida approves expansion of spaceport territories
The Florida legislature has now approved two new locations in Florida where rocket launches can take place.
Governor Ron DeSantis signed off on a bill that, as of Monday, will add South Florida’s Homestead Air Reserve Base and the panhandle’s Tyndall Air Force Base to Florida’s growing spaceport territories.
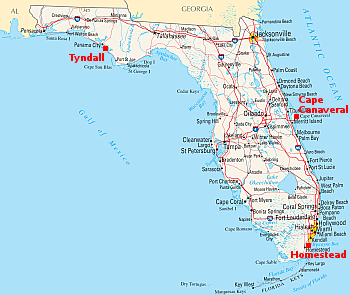
The map to the right shows the spaceport locations within Florida. While the state government might now allow launches from these locations, it is unclear if either military facility is entertaining the idea.
Regardless, the Florida government is clearly intent on encouraging and attracting this new industry to its state.

The Florida legislature has now approved two new locations in Florida where rocket launches can take place.
Governor Ron DeSantis signed off on a bill that, as of Monday, will add South Florida’s Homestead Air Reserve Base and the panhandle’s Tyndall Air Force Base to Florida’s growing spaceport territories.
The map to the right shows the spaceport locations within Florida. While the state government might now allow launches from these locations, it is unclear if either military facility is entertaining the idea.
Regardless, the Florida government is clearly intent on encouraging and attracting this new industry to its state.