Cool image time! New data from Cassini has now both confirmed that there is liquid inside some of the river-like formations on Titan, and that this liquid has carved these formations into very deep gorges.
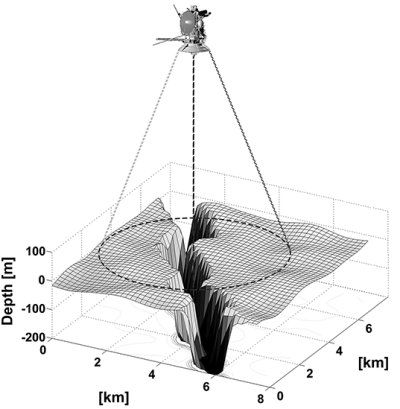
The Cassini observations reveal that the channels — in particular, a network of them named Vid Flumina — are narrow canyons, generally less than half a mile (a bit less than a kilometer) wide, with slopes steeper than 40 degrees. The canyons also are quite deep — those measured are 790 to 1,870 feet (240 to 570 meters) from top to bottom.
The branching channels appear dark in radar images, much like Titan’s methane-rich seas. This suggested to scientists that the channels might also be filled with liquid, but a direct detection had not been made until now. Previously it wasn’t clear if the dark material was liquid or merely saturated sediment — which at Titan’s frigid temperatures would be made of ice, not rock.
The diagram on the above right is from the paper itself, and shows some of the radar data obtained by Cassini. It also illustrates the deep and narrow nature of Via Flumina. This is almost the equivalent of what we call slot canyons on Earth, formed by periodic flash floods that cut their way down as the surface is slowly uplifted by other processes.
The new radar data showed that the surface at the base of the gorge was smooth and flat, just as you’d find if that base was filled with liquid.The altimeter data showed that gorge’s elevation matched that of Titan’s lakes at its insurgence, but as you traveled upstream the elevation rose, just as it does on any river on Earth. Moreover, this data was reasonably trustworthy as they had already used Cassini to successfully do exactly the same thing — identify a known river — when it flew past Earth on its way to Saturn.
Be prepared for one piece of misinformation when the press reports on this story, almost certainly caused by the American Geological Union’s press release about this paper. That press release incorrectly claims that the paper confirmed that these are methane rivers. It does no such thing. It only shows that the gorges have a liquid in them, and that the liquid almost certainly formed the gorges. Though methane is a very likely candidate for this liquid based on what we know of Titan, the actual make-up of the river remains uncertain.
I therefore predict our incompetent modern mainstream press will only read this press release and not the paper itself, and thus they will tout these incorrectly as methane rivers.
Below is a cropped Cassini radar image of Via Flumina, showing its river-like appearance. Scientists always suspected these were formed by flowing liquid. Now they have strong evidence from within the gorge to justify that suspicion.