A satellite startup in Oman signs on to China’s lunar base partnership

Oman Lens, a satellite startup in Oman, has signed an agreement with China to participate in its International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) lunar base project.
This follows Oman’s first suborbital launch, which according to Oman’s state-run press lifted off from its Duqm proposed spaceport facility and reached space. None of this however has been confirmed, though government officials said they hope to do three more suborbital test flights in the next year.
The Duqm spaceport hopes to be fully operational for orbital flights by 2026. Besides China, Oman has also been in negotiations with various American rocket startup companies, though no deals have been announced, mostly because of the State Department’s ITAR restrictions protecting American technology from hostile foreign theft. Oman is not necessarily considered a friendly country.
It appears Oman decided to make a deal with China when it couldn’t make one with the U.S.
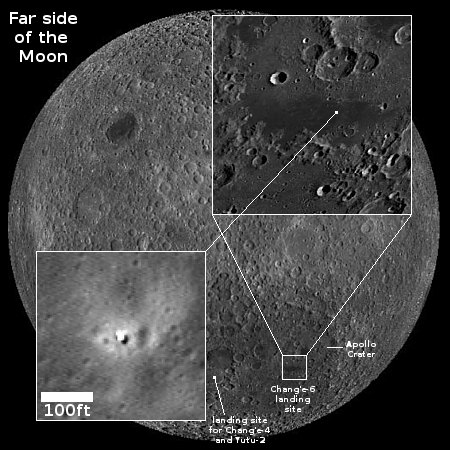
As for China’s ILRS project — it formed in competition with the U.S. Artemis Accords — it has now signed thirteen countries and about a dozen academic institutions and international companies. It claims it hopes to get fifty countries on board, but that number likely includes such institutions, not nations.

Oman Lens, a satellite startup in Oman, has signed an agreement with China to participate in its International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) lunar base project.
This follows Oman’s first suborbital launch, which according to Oman’s state-run press lifted off from its Duqm proposed spaceport facility and reached space. None of this however has been confirmed, though government officials said they hope to do three more suborbital test flights in the next year.
The Duqm spaceport hopes to be fully operational for orbital flights by 2026. Besides China, Oman has also been in negotiations with various American rocket startup companies, though no deals have been announced, mostly because of the State Department’s ITAR restrictions protecting American technology from hostile foreign theft. Oman is not necessarily considered a friendly country.
It appears Oman decided to make a deal with China when it couldn’t make one with the U.S.
As for China’s ILRS project — it formed in competition with the U.S. Artemis Accords — it has now signed thirteen countries and about a dozen academic institutions and international companies. It claims it hopes to get fifty countries on board, but that number likely includes such institutions, not nations.