Blue Origin completes ground simulation of Orbital Reef space station

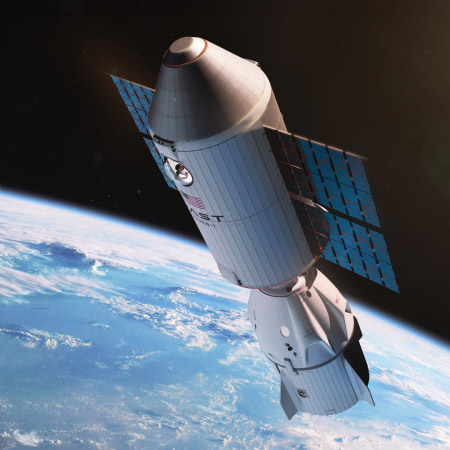
Artist rendering of Orbital Reef design, as of
April 2025. Click for original image.
According to a NASA press release today, Blue Origin has successfully completed a ” human-in-the-loop test” in a ground mock-up of the commercial Orbital Reef space station.
The human-in-the-loop test scenarios utilized individual participants or small groups to perform day-in-the-life walkthroughs in life-sized mockups of major station components. Participants provided feedback while simulating microgravity operations, including cargo transfer, trash transfer, stowage, and worksite assessments.
…The milestone is part of a NASA Space Act Agreement originally awarded to Blue Origin in 2021 and focused on the design progress for multiple worksites, floors, and translation paths within the station. This ensures a commercial station can support human life, which is critical to advancing scientific research in a microgravity environment and maintaining a continuous human presence in low Earth orbit.
Though this test might be providing useful information, it leaves me cold. While Blue Origin’s partner in this project, Sierra Space, has been testing real hardware for its LIFE inflatable module (as seen on the left side of the artist’s rendering above), Blue Origin itself appears to have built nothing real. Instead, it is following the old big space paradigm of companies like Boeing that invest none of its own money in development. Instead, the company uses NASA’s development money solely for PR mockups, in the hope the PR will convince NASA to give it the full contract, worth billions. Only then will the real work begin.
Boeing did this with Starliner, and we can all see now how well that turned out.
It also appears that the overall scale of Orbital Reef has been reduced significantly when comparing the current design above with the earlier artist renderings.
Based on this new information, I have dropped Orbital Reef to the bottom in my rankings of the four private space stations presently under development. While Starlab has built as little (following the same play-it-safe paradigm), the company has at least gotten its final design approved. It has also signed a partnership with the European Space Agency, giving it a powerful government backer in addition to NASA.
- Haven-1, being built by Vast, with no NASA funds. The company is moving fast, with Haven-1 to launch and be occupied in 2026 for a 30 day mission. It hopes this actual hardware and manned mission will put it in the lead to win NASA’s phase 2 contract, from which it will build its much larger mult-module Haven-2 station..
- Axiom, being built by Axiom, has launched three tourist flights to ISS, with a fourth scheduled for this spring, carrying passengers from India, Hungary, and Poland. Though there have been rumors it has cash flow issues, development of its first module has been proceeding more or less as planned.
- Starlab, being built by a consortium led by Voyager Space, Airbus, and Northrop Grumman, with an extensive partnership agreement with the European Space Agency. It recently had its station design approved by NASA.
- Orbital Reef, being built by a consortium led by Blue Origin and Sierra Space. Overall, Blue Origin has built almost nothing, while Sierra Space has successfully tested its inflatable modules, including a full scale version, and appears ready to start building its module for launch.

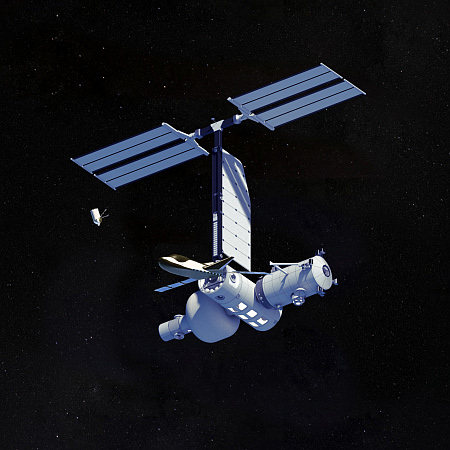
Artist rendering of Orbital Reef design, as of
April 2025. Click for original image.
According to a NASA press release today, Blue Origin has successfully completed a ” human-in-the-loop test” in a ground mock-up of the commercial Orbital Reef space station.
The human-in-the-loop test scenarios utilized individual participants or small groups to perform day-in-the-life walkthroughs in life-sized mockups of major station components. Participants provided feedback while simulating microgravity operations, including cargo transfer, trash transfer, stowage, and worksite assessments.
…The milestone is part of a NASA Space Act Agreement originally awarded to Blue Origin in 2021 and focused on the design progress for multiple worksites, floors, and translation paths within the station. This ensures a commercial station can support human life, which is critical to advancing scientific research in a microgravity environment and maintaining a continuous human presence in low Earth orbit.
Though this test might be providing useful information, it leaves me cold. While Blue Origin’s partner in this project, Sierra Space, has been testing real hardware for its LIFE inflatable module (as seen on the left side of the artist’s rendering above), Blue Origin itself appears to have built nothing real. Instead, it is following the old big space paradigm of companies like Boeing that invest none of its own money in development. Instead, the company uses NASA’s development money solely for PR mockups, in the hope the PR will convince NASA to give it the full contract, worth billions. Only then will the real work begin.
Boeing did this with Starliner, and we can all see now how well that turned out.
It also appears that the overall scale of Orbital Reef has been reduced significantly when comparing the current design above with the earlier artist renderings.
Based on this new information, I have dropped Orbital Reef to the bottom in my rankings of the four private space stations presently under development. While Starlab has built as little (following the same play-it-safe paradigm), the company has at least gotten its final design approved. It has also signed a partnership with the European Space Agency, giving it a powerful government backer in addition to NASA.
- Haven-1, being built by Vast, with no NASA funds. The company is moving fast, with Haven-1 to launch and be occupied in 2026 for a 30 day mission. It hopes this actual hardware and manned mission will put it in the lead to win NASA’s phase 2 contract, from which it will build its much larger mult-module Haven-2 station..
- Axiom, being built by Axiom, has launched three tourist flights to ISS, with a fourth scheduled for this spring, carrying passengers from India, Hungary, and Poland. Though there have been rumors it has cash flow issues, development of its first module has been proceeding more or less as planned.
- Starlab, being built by a consortium led by Voyager Space, Airbus, and Northrop Grumman, with an extensive partnership agreement with the European Space Agency. It recently had its station design approved by NASA.
- Orbital Reef, being built by a consortium led by Blue Origin and Sierra Space. Overall, Blue Origin has built almost nothing, while Sierra Space has successfully tested its inflatable modules, including a full scale version, and appears ready to start building its module for launch.