Tag: commercial
SpaceX inks Starlink deals with India’s two largest telecom operators
In a sign that suggests OneWeb is losing the competition to begin satellite internet access to India, SpaceX this week has signed two Starlink deals with India’s two largest telecom operators.
Jio Platforms, the subsidiary of India’s conglomerate Reliance Industries and the country’s largest telecom operator, Wednesday announced a partnership with Elon Musk’s SpaceX to offer Starlink’s satellite broadband internet services to its customers in India. Under the agreement, which is subject to regulatory approvals, Jio and SpaceX will explore using Starlink to extend the telco’s offerings, while Jio will sell Starlink equipment through its retail outlets and online storefronts, the telco said in a press statement.
…Earlier Wednesday, Airtel, India’s second-biggest telco, announced a similar partnership with SpaceX to offer Starlink through its channels. The Airtel partnership is also subject to SpaceX’s regulatory approvals in the country, which are in process with IN-SPACe and the Department of Telecommunications.
SpaceX had previously tried to bring Starlink to India by selling subscriptions directly to customers but was forced to pull back when the government denied it regulatory approval. These two deals suggest that the government wanted SpaceX to partner with Indian companies, keeping some of its profits in-country.
These deals also suggest that OneWeb is failing to provide good service to the Indian market, even though it is half owned by a major Indian investor and got regulatory approval several years ago. The design of OneWeb’s system requires the construction of ground stations to link its satellite constellation with the ground operations, and it appears this added step is causing delays that is forcing the telecom industry to look elsewhere. For example, the same thing has happened in the Falkland Islands, which signed first with OneWeb (which is also half owned by the UK government) but has now approved Starlink because OneWeb wasn’t able to provide its service on time.
In a sign that suggests OneWeb is losing the competition to begin satellite internet access to India, SpaceX this week has signed two Starlink deals with India’s two largest telecom operators.
Jio Platforms, the subsidiary of India’s conglomerate Reliance Industries and the country’s largest telecom operator, Wednesday announced a partnership with Elon Musk’s SpaceX to offer Starlink’s satellite broadband internet services to its customers in India. Under the agreement, which is subject to regulatory approvals, Jio and SpaceX will explore using Starlink to extend the telco’s offerings, while Jio will sell Starlink equipment through its retail outlets and online storefronts, the telco said in a press statement.
…Earlier Wednesday, Airtel, India’s second-biggest telco, announced a similar partnership with SpaceX to offer Starlink through its channels. The Airtel partnership is also subject to SpaceX’s regulatory approvals in the country, which are in process with IN-SPACe and the Department of Telecommunications.
SpaceX had previously tried to bring Starlink to India by selling subscriptions directly to customers but was forced to pull back when the government denied it regulatory approval. These two deals suggest that the government wanted SpaceX to partner with Indian companies, keeping some of its profits in-country.
These deals also suggest that OneWeb is failing to provide good service to the Indian market, even though it is half owned by a major Indian investor and got regulatory approval several years ago. The design of OneWeb’s system requires the construction of ground stations to link its satellite constellation with the ground operations, and it appears this added step is causing delays that is forcing the telecom industry to look elsewhere. For example, the same thing has happened in the Falkland Islands, which signed first with OneWeb (which is also half owned by the UK government) but has now approved Starlink because OneWeb wasn’t able to provide its service on time.
SpaceX launches NASA space telescope plus four solar satellites; China launches 18 communication satellites
Two launches to report: First, China yesterday successfully completed its first Long March 8 launch from its new launchpad at its coastal Wenchang spaceport, placing 18 satellites for SpaceSail internet constellation, the fifth group so far launched.
China’s state run press noted that the launchpad is designed to allow the Long March 8 rocket to launch every seven days, a pace needed to place these giant Chinese satellite constellations into orbit.
Next, in the early morning hours today SpaceX successfully launched two different NASA science missions, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The prime payload was SPHEREx, a space telescope designed to make an all-sky survey. The secondary payload was PUNCH, four satellites forming a constellation to study the Sun.
The rocket’s first stage completed its third flight, landing back at Vandenberg.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
27 SpaceX
11 China
3 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
As happened last year, SpaceX handily leads the rest of the world, including American companies, in total launches, 27 to 20. This lead will be extended tonight should the company’s next manned Dragon launch to ISS go off as planned.
Two launches to report: First, China yesterday successfully completed its first Long March 8 launch from its new launchpad at its coastal Wenchang spaceport, placing 18 satellites for SpaceSail internet constellation, the fifth group so far launched.
China’s state run press noted that the launchpad is designed to allow the Long March 8 rocket to launch every seven days, a pace needed to place these giant Chinese satellite constellations into orbit.
Next, in the early morning hours today SpaceX successfully launched two different NASA science missions, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The prime payload was SPHEREx, a space telescope designed to make an all-sky survey. The secondary payload was PUNCH, four satellites forming a constellation to study the Sun.
The rocket’s first stage completed its third flight, landing back at Vandenberg.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
27 SpaceX
11 China
3 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
As happened last year, SpaceX handily leads the rest of the world, including American companies, in total launches, 27 to 20. This lead will be extended tonight should the company’s next manned Dragon launch to ISS go off as planned.
Liz Callaway – Meadowlark
Relativity provides detailed video update on the development of its Terran-R rocket
The rocket startup Relativity yesterday uploaded a 42-minute long video on Youtube describing in great detail the status of its Terran-R rocket, providing a great deal of information about its design, construction, and goals, including the significant changes the company has made from its much smaller Terran-1 rocket.
I have embedded that video below.
Several take-aways: First, the video devotes a long segment explaining why the company has abandoned its long expressed goal of making a rocket entirely 3D printed. It found with Terran-1 that 3D printing the rocket’s body and fairing was not cost effective. It took too long and was too expensive. Using aluminum is faster and cheaper, especially as Relativity is no longer doing this in-house. Instead, it appears they are partnering long term with specific outside vendors for the rocket shells, tanks, and domes, as well as the fairings.
Second, the company is aiming to make the rocket’s first stage reusable from the start, making the first landing attempts on the first launch. They also recognize that success will take time and many attempts, similar to SpaceX’s experience a decade ago.
Third, they are pushing to go into major production of the rocket by 2026, so that when they launch the first time they will have more rockets ready to quickly follow up with more launches. This schedule is extremely fast, as they only started rocket development in the spring of 2023.
Finally and most important, the video provides no dates for that first launch. Previous releases from the company had suggested a 2026 first launch, and officials in the video implied that they might be ready by 2026, but no one said so directly. My guess is that 2026 is no longer realistic (not that it ever was), and they are beginning to prepare the public for a later launch date.
One other new development at Relativity not mentioned in the video. The company has named former Google CEO Eric Schmidt as its new CEO, with the company’s founder, Tim Ellis, stepping down as CEO to transition to the company’s board of directors. This change could be related to rumors last year that the company was having problems.
» Read more
The rocket startup Relativity yesterday uploaded a 42-minute long video on Youtube describing in great detail the status of its Terran-R rocket, providing a great deal of information about its design, construction, and goals, including the significant changes the company has made from its much smaller Terran-1 rocket.
I have embedded that video below.
Several take-aways: First, the video devotes a long segment explaining why the company has abandoned its long expressed goal of making a rocket entirely 3D printed. It found with Terran-1 that 3D printing the rocket’s body and fairing was not cost effective. It took too long and was too expensive. Using aluminum is faster and cheaper, especially as Relativity is no longer doing this in-house. Instead, it appears they are partnering long term with specific outside vendors for the rocket shells, tanks, and domes, as well as the fairings.
Second, the company is aiming to make the rocket’s first stage reusable from the start, making the first landing attempts on the first launch. They also recognize that success will take time and many attempts, similar to SpaceX’s experience a decade ago.
Third, they are pushing to go into major production of the rocket by 2026, so that when they launch the first time they will have more rockets ready to quickly follow up with more launches. This schedule is extremely fast, as they only started rocket development in the spring of 2023.
Finally and most important, the video provides no dates for that first launch. Previous releases from the company had suggested a 2026 first launch, and officials in the video implied that they might be ready by 2026, but no one said so directly. My guess is that 2026 is no longer realistic (not that it ever was), and they are beginning to prepare the public for a later launch date.
One other new development at Relativity not mentioned in the video. The company has named former Google CEO Eric Schmidt as its new CEO, with the company’s founder, Tim Ellis, stepping down as CEO to transition to the company’s board of directors. This change could be related to rumors last year that the company was having problems.
» Read more
SpaceX officials provide cause of loss Falcon 9 first stage after successful landing
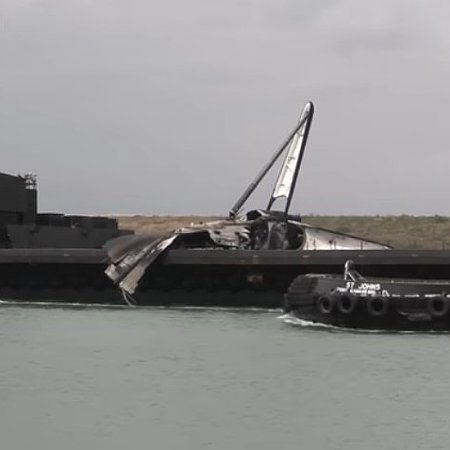

The damaged Falcon 9 booster laying on its side
on its drone ship as it returns to port.
At a press conference yesterday, SpaceX officials outlined the results of its investigation into the loss of Falcon 9 first stage when it fell over on its drone ship shortly after a successful landing.
Speaking at a news conference following a flight readiness review for the Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station, Bill Gerstenmaier, vice president of Build and Flight Reliability at SpaceX, said about 85 seconds into the launch of the Starlink 12-20 mission, there was a fuel leak in the first stage booster, tail number B1086, and kerosene sprayed onto a hot component of the engine. He said that caused it to vaporize and become flammable.
Because there wasn’t enough oxygen to interact with the leaked fuel, it didn’t catch fire during the ascent, he said. But about 45 seconds after B1086 landed on their droneship, ‘Just Read the Instructions,’ there was enough oxygen available to get into the engine compartment and a fire broke out. “It subsequently blew out the barrel panel on the side of the rocket, just like it was designed to. The fire was all contained in the engine compartment,” Gerstenmaier said. “Even if we would’ve had a problem during ascent, this shows that the fire and the damage would be contained in just a single engine out, which still allows us to accomplish the entire mission.”
The company is still working to determine the cause of the leak itself.
Though the article and video at the link make a big deal about the FAA grounding SpaceX’s Falcon 9 fleet, the agency’s actions here were quite trivial compared to its behavior when Biden was president. It grounded the fleet for only a few days, while SpaceX did its initial investigation, and then immediately accepted the above conclusions from SpaceX and lifted the grounding, even though the company has not yet determined the leak’s cause.

The damaged Falcon 9 booster laying on its side
on its drone ship as it returns to port.
At a press conference yesterday, SpaceX officials outlined the results of its investigation into the loss of Falcon 9 first stage when it fell over on its drone ship shortly after a successful landing.
Speaking at a news conference following a flight readiness review for the Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station, Bill Gerstenmaier, vice president of Build and Flight Reliability at SpaceX, said about 85 seconds into the launch of the Starlink 12-20 mission, there was a fuel leak in the first stage booster, tail number B1086, and kerosene sprayed onto a hot component of the engine. He said that caused it to vaporize and become flammable.
Because there wasn’t enough oxygen to interact with the leaked fuel, it didn’t catch fire during the ascent, he said. But about 45 seconds after B1086 landed on their droneship, ‘Just Read the Instructions,’ there was enough oxygen available to get into the engine compartment and a fire broke out. “It subsequently blew out the barrel panel on the side of the rocket, just like it was designed to. The fire was all contained in the engine compartment,” Gerstenmaier said. “Even if we would’ve had a problem during ascent, this shows that the fire and the damage would be contained in just a single engine out, which still allows us to accomplish the entire mission.”
The company is still working to determine the cause of the leak itself.
Though the article and video at the link make a big deal about the FAA grounding SpaceX’s Falcon 9 fleet, the agency’s actions here were quite trivial compared to its behavior when Biden was president. It grounded the fleet for only a few days, while SpaceX did its initial investigation, and then immediately accepted the above conclusions from SpaceX and lifted the grounding, even though the company has not yet determined the leak’s cause.
Space Force awards development contracts to eight startups
The Space Force’s commercial office, dubbed SpaceWERX, announced March 8, 2025 that it has awarded development contracts to eight startups totaling $440 million.
Each STRATFI agreement is worth up to $60 million, with SpaceWERX and several defense agencies contributing up to $30 million per project. Private investors provide matching funds to scale innovations that have already demonstrated viability through prototype development.
The winners — Albedo, Beast Code, CesiumAstro, Gravitics, LeoLabs, Rise8, Umbra and Xona — were announced March 8 at an event at the Capital Factory in Austin, Texas.
Of these companies, Gravitics is probably the most interesting, as it is attempting to become a major American provider of space station modules. It already has a $125 million contract with Axiom to build a small module for that company’s station. This new contract from the Space Force suggests the Pentagon is considering launching its own space station, or possibly attaching a Gravitics module to one of the four private stations presently being built. Below is my present ranking of these four stations:
- Haven-1, being built by Vast, with no NASA funds. The company is moving fast, with Haven-1 to launch and be occupied in 2026 for a 30 day mission. It hopes this actual hardware and manned mission will put it in the lead to win NASA’s phase 2 contract, from which it will build its much larger mult-module Haven-2 station..
- Axiom, being built by Axiom, has launched three tourist flights to ISS. There are rumors it is experiencing cash flow issues, but it is also going to do a fourth ISS tourist flight this spring, carrying passengers from India, Hungary, and Poland.
- Orbital Reef, being built by a consortium led by Blue Origin and Sierra Space. Though Blue Origin has apparently done little, Sierra Space has successfully tested its inflatable modules, including a full scale version, and appears ready to start building the station’s modules for launch.
- Starlab, being built by a consortium led by Voyager Space, Airbus, and Northrop Grumman. It recently had its station design approved by NASA.
The Space Force’s commercial office, dubbed SpaceWERX, announced March 8, 2025 that it has awarded development contracts to eight startups totaling $440 million.
Each STRATFI agreement is worth up to $60 million, with SpaceWERX and several defense agencies contributing up to $30 million per project. Private investors provide matching funds to scale innovations that have already demonstrated viability through prototype development.
The winners — Albedo, Beast Code, CesiumAstro, Gravitics, LeoLabs, Rise8, Umbra and Xona — were announced March 8 at an event at the Capital Factory in Austin, Texas.
Of these companies, Gravitics is probably the most interesting, as it is attempting to become a major American provider of space station modules. It already has a $125 million contract with Axiom to build a small module for that company’s station. This new contract from the Space Force suggests the Pentagon is considering launching its own space station, or possibly attaching a Gravitics module to one of the four private stations presently being built. Below is my present ranking of these four stations:
- Haven-1, being built by Vast, with no NASA funds. The company is moving fast, with Haven-1 to launch and be occupied in 2026 for a 30 day mission. It hopes this actual hardware and manned mission will put it in the lead to win NASA’s phase 2 contract, from which it will build its much larger mult-module Haven-2 station..
- Axiom, being built by Axiom, has launched three tourist flights to ISS. There are rumors it is experiencing cash flow issues, but it is also going to do a fourth ISS tourist flight this spring, carrying passengers from India, Hungary, and Poland.
- Orbital Reef, being built by a consortium led by Blue Origin and Sierra Space. Though Blue Origin has apparently done little, Sierra Space has successfully tested its inflatable modules, including a full scale version, and appears ready to start building the station’s modules for launch.
- Starlab, being built by a consortium led by Voyager Space, Airbus, and Northrop Grumman. It recently had its station design approved by NASA.
Blue Ghost activates NASA drill, prepares for hot lunar noon

Landing sites for both Firefly’s Blue Ghost and
Ispace’s Resilience
More than a week after landing in Mare Crisium, ground controllers have prepared Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander for surviving the very hot lunar noon while also activating NASA’s LISTER drill, which proceeded to successfully drill down into the lunar surface below the lander.
Mounted below Blue Ghost’s lower deck, NASA’s Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity (LISTER) payload is a pneumatic, gas-powered drill developed by Texas Tech University and Honeybee Robotics that measures the temperature and flow of heat from the Moon’s interior.
I have embedded below the video of this drilling operation. At this moment it appears that nine of the lander’s payloads have completed their tasks successfully, with no indication yet that the tenth playload will have problems. All in all, Firefly has succeeded in establishing itself now as the leading private company capable of launching spacecraft to other worlds.
» Read more

Landing sites for both Firefly’s Blue Ghost and
Ispace’s Resilience
More than a week after landing in Mare Crisium, ground controllers have prepared Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander for surviving the very hot lunar noon while also activating NASA’s LISTER drill, which proceeded to successfully drill down into the lunar surface below the lander.
Mounted below Blue Ghost’s lower deck, NASA’s Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity (LISTER) payload is a pneumatic, gas-powered drill developed by Texas Tech University and Honeybee Robotics that measures the temperature and flow of heat from the Moon’s interior.
I have embedded below the video of this drilling operation. At this moment it appears that nine of the lander’s payloads have completed their tasks successfully, with no indication yet that the tenth playload will have problems. All in all, Firefly has succeeded in establishing itself now as the leading private company capable of launching spacecraft to other worlds.
» Read more
Johnny Nash – I Can See Clearly Now
Blue Ghost landed almost dead center within its target zone
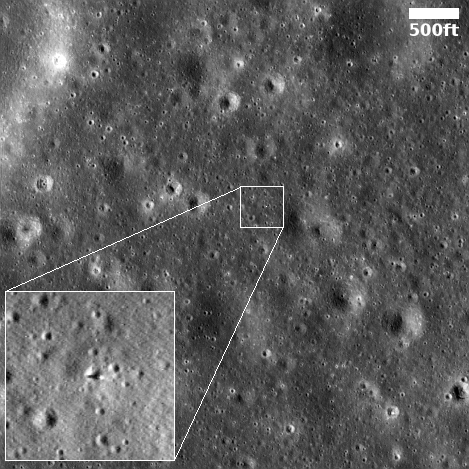
Click for before and after blink animation
The picture to the right, taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) prior to the successful landing of Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander, shows its entire landing region. The inset in the lower left is a picture taken by LRO on March 3, 2025, after landing.
The full picture was taken near sunset, with sunlight coming from the left. The inset was taken at sunrise, with sunlight coming from the right. This explains the difference in shadows between the two. Blue Ghost is the white dot in the inset with its long shadow, the black streak, cutting through the nearby crater. The first picture taken from the lander after landing looked down that shadow, looking across the crater.
The new picture tells us that Blue Ghost landed almost dead center in its target zone, indicating that the engineering worked as planned. The lander also used its computer brain to pick a good landing spot and avoid the nearby craters.

Click for before and after blink animation
The picture to the right, taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) prior to the successful landing of Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander, shows its entire landing region. The inset in the lower left is a picture taken by LRO on March 3, 2025, after landing.
The full picture was taken near sunset, with sunlight coming from the left. The inset was taken at sunrise, with sunlight coming from the right. This explains the difference in shadows between the two. Blue Ghost is the white dot in the inset with its long shadow, the black streak, cutting through the nearby crater. The first picture taken from the lander after landing looked down that shadow, looking across the crater.
The new picture tells us that Blue Ghost landed almost dead center in its target zone, indicating that the engineering worked as planned. The lander also used its computer brain to pick a good landing spot and avoid the nearby craters.
Anonymous sources: Starship will need a major rebuild after two consecutive failures

Starship just before loss of signal on March 6, 2025
According to information at this tweet from anonymous sources, parts of Starship will likely require a major redesign due to the spacecraft’s break-up shortly after stage separation on its last two test flights.
These are the key take-aways, most of which focus on the redesign of the first version of Starship (V1) to create the V2 that flew unsuccessfully on those flights:
- Hot separation also aggravates the situation in the compartment.
- Not related to the flames from the Super Heavy during the booster turn.
- This is a fundamental miscalculation in the design of the Starship V2 and the engine section.
- The fuel lines, wiring for the engines and the power unit will be urgently redone.
- The fate of S35 and S36 is still unclear. Either revision or scrap.
- For the next ships, some processes may be paused in production until a decision on the design is made.
- The team was rushed with fixes for S34, hence the nervous start. There was no need to rush.
- The fixes will take much longer than 4-6 weeks.
- Comprehensive ground testing with long-term fire tests is needed. [emphasis mine]
It must be emphasized that this information comes from leaks from anonymous sources, and could be significantly incorrect. It does however fit the circumstances, and suggests that the next test flight will not occur in April but will be delayed for an unknown period beyond.
I think the tweet however is much too pessimistic. If the problems are all within the fuel lines, engine wiring, and the power unit, they are well localized. Moreover, the design of these components on version 1 of Starship apparently worked reasonably well, which gives them a good basis for that redesign. Nonetheless, if these facts are correct, my guess is the next test flight won’t occur before June.
The one saving grace is that FAA red tape is clearly no longer an additional obstacle. It is very clear now that with the change from Biden to Trump it is letting SpaceX lead all investigations, and immediately accepting its conclusions and fixes, rather than sitting on those conclusions as it retyped them for weeks or months in its own report.
Hat tip to reader Richard M.

Starship just before loss of signal on March 6, 2025
According to information at this tweet from anonymous sources, parts of Starship will likely require a major redesign due to the spacecraft’s break-up shortly after stage separation on its last two test flights.
These are the key take-aways, most of which focus on the redesign of the first version of Starship (V1) to create the V2 that flew unsuccessfully on those flights:
- Hot separation also aggravates the situation in the compartment.
- Not related to the flames from the Super Heavy during the booster turn.
- This is a fundamental miscalculation in the design of the Starship V2 and the engine section.
- The fuel lines, wiring for the engines and the power unit will be urgently redone.
- The fate of S35 and S36 is still unclear. Either revision or scrap.
- For the next ships, some processes may be paused in production until a decision on the design is made.
- The team was rushed with fixes for S34, hence the nervous start. There was no need to rush.
- The fixes will take much longer than 4-6 weeks.
- Comprehensive ground testing with long-term fire tests is needed. [emphasis mine]
It must be emphasized that this information comes from leaks from anonymous sources, and could be significantly incorrect. It does however fit the circumstances, and suggests that the next test flight will not occur in April but will be delayed for an unknown period beyond.
I think the tweet however is much too pessimistic. If the problems are all within the fuel lines, engine wiring, and the power unit, they are well localized. Moreover, the design of these components on version 1 of Starship apparently worked reasonably well, which gives them a good basis for that redesign. Nonetheless, if these facts are correct, my guess is the next test flight won’t occur before June.
The one saving grace is that FAA red tape is clearly no longer an additional obstacle. It is very clear now that with the change from Biden to Trump it is letting SpaceX lead all investigations, and immediately accepting its conclusions and fixes, rather than sitting on those conclusions as it retyped them for weeks or months in its own report.
Hat tip to reader Richard M.
After a decade of development, ESA finally starts testing a part of its Callisto grasshopper
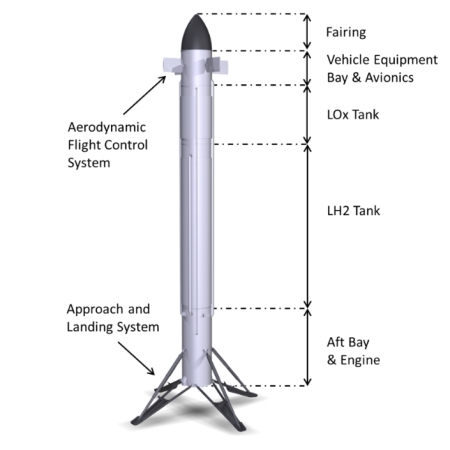
Callisto’s basic design
My heart be still! First proposed in 2015 as Europe’s answer to SpaceX’s Falcon 9, the European Space Agency, in partnership with Japan, has finally begun acoustical testing of just one part of its Callisto grasshopper-type reusable test prototype, as shown on the right.
Callisto consists of five main sections: the Aft Bay, which includes the engine and landing legs, the LH2 Tank, the LOx Tank, the VEB, and the Fairing. The VEB houses much of the demonstrator’s electronics, including its onboard computer, avionics, and a reaction control system that uses H2O2 propellant. Its distinctive features include a pair of control fins.
In addition to confirming that the VEB had been transported to the CNES facilities in Toulouse, the 4 March Institute of Space Systems update also revealed that the acoustic test campaign for the key Callisto module had commenced last week. The acoustic test campaign simulates the intense sound vibrations the demonstrator will experience during flight to ensure structural integrity and component reliability.
The whole project has a budget of $100 million. The first test hop won’t occur until 2026, eleven years after the project began, and six years behind its original launch date. In that same time, SpaceX has completed several hundred commercial landings of its Falcon 9 first stage, reusing those stages up to two dozen times.
Nor is Callisto part of any program to develop a similar reusable rocket. It is a typical dead-end government project, with ESA having no clear goal to apply it commercially. The best Europe can hope for is that the engineering lessons from its tests will be given freely to the new European commercial rocket startups, so that they can use it someday.

Callisto’s basic design
My heart be still! First proposed in 2015 as Europe’s answer to SpaceX’s Falcon 9, the European Space Agency, in partnership with Japan, has finally begun acoustical testing of just one part of its Callisto grasshopper-type reusable test prototype, as shown on the right.
Callisto consists of five main sections: the Aft Bay, which includes the engine and landing legs, the LH2 Tank, the LOx Tank, the VEB, and the Fairing. The VEB houses much of the demonstrator’s electronics, including its onboard computer, avionics, and a reaction control system that uses H2O2 propellant. Its distinctive features include a pair of control fins.
In addition to confirming that the VEB had been transported to the CNES facilities in Toulouse, the 4 March Institute of Space Systems update also revealed that the acoustic test campaign for the key Callisto module had commenced last week. The acoustic test campaign simulates the intense sound vibrations the demonstrator will experience during flight to ensure structural integrity and component reliability.
The whole project has a budget of $100 million. The first test hop won’t occur until 2026, eleven years after the project began, and six years behind its original launch date. In that same time, SpaceX has completed several hundred commercial landings of its Falcon 9 first stage, reusing those stages up to two dozen times.
Nor is Callisto part of any program to develop a similar reusable rocket. It is a typical dead-end government project, with ESA having no clear goal to apply it commercially. The best Europe can hope for is that the engineering lessons from its tests will be given freely to the new European commercial rocket startups, so that they can use it someday.
Ballinator – History & Lore of 32nd of an Inch Bolts
An evening pause: Some engineering history for the weekend. I know the title makes this sound boring, but it is worth watching, because it illustrates the incredible complexity of some of what we think are the simplest tools. I wonder if the engineers in the space business are thinking about these issues.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
Intuitive Machines confirms Athena fell over at landing; ends mission


Intuitive Machines today officially ended its Athena lunar lander mission after it released a picture taken from the top of the lander showing clearly that it had fallen over on its side after landing.
That picture, cropped, reduced, and brightened to post here, is to the right. You can clearly see two of the landing legs in the air, with the horizon in the background.
“With the direction of the sun, the orientation of the solar panels, and extreme cold temperatures in the crater, Intuitive Machines does not expect Athena to recharge,” the company stated. “The mission has concluded and teams are continuing to assess the data collected throughout the mission.”
This is the second Intuitive Machines lunar lander to tip over. More and more it does appear that the tall design of this lander is fundamentally flawed. The artist rendering to the right illustrates this. Most unmanned lunar landers are much wider than they are tall. Intuitive Machines’ Nova design has the lander’s height matching the spread of its legs. It creates a center of gravity high enough that the lander will tip over too easily if conditions are not perfect.
The company denies this, saying the center of gravity is much lower than this graphic makes it appear, but the proof is in the pudding. Their design has tried to land on the Moon twice, and both times the lander tipped over.
It is not clear what the company can do to fix this. Expanding its diameter to lower its height is a major redesign. It also might make the lander too wide to fit inside most rocket fairings. A better solution might be to redesign the legs, making their spread wider, and even increasing their number.
Fortunately, NASA’s shift to capitalism in space has produced a number of different companies building lunar landers. Firefly’s Blue Ghost is clearly a success. In June Ispace will make its second attempt to soft land its private lander design on the Moon. And Astrobotic has a contract to try again after it had a fuel line leak after launch last year that prevented it from even attempting a landing.
And of course, Intuitive Machines is still in the game. It has a contract for one more landing mission, plus a mission to put two data relay satellites in lunar orbit.


Intuitive Machines today officially ended its Athena lunar lander mission after it released a picture taken from the top of the lander showing clearly that it had fallen over on its side after landing.
That picture, cropped, reduced, and brightened to post here, is to the right. You can clearly see two of the landing legs in the air, with the horizon in the background.
“With the direction of the sun, the orientation of the solar panels, and extreme cold temperatures in the crater, Intuitive Machines does not expect Athena to recharge,” the company stated. “The mission has concluded and teams are continuing to assess the data collected throughout the mission.”
This is the second Intuitive Machines lunar lander to tip over. More and more it does appear that the tall design of this lander is fundamentally flawed. The artist rendering to the right illustrates this. Most unmanned lunar landers are much wider than they are tall. Intuitive Machines’ Nova design has the lander’s height matching the spread of its legs. It creates a center of gravity high enough that the lander will tip over too easily if conditions are not perfect.
The company denies this, saying the center of gravity is much lower than this graphic makes it appear, but the proof is in the pudding. Their design has tried to land on the Moon twice, and both times the lander tipped over.
It is not clear what the company can do to fix this. Expanding its diameter to lower its height is a major redesign. It also might make the lander too wide to fit inside most rocket fairings. A better solution might be to redesign the legs, making their spread wider, and even increasing their number.
Fortunately, NASA’s shift to capitalism in space has produced a number of different companies building lunar landers. Firefly’s Blue Ghost is clearly a success. In June Ispace will make its second attempt to soft land its private lander design on the Moon. And Astrobotic has a contract to try again after it had a fuel line leak after launch last year that prevented it from even attempting a landing.
And of course, Intuitive Machines is still in the game. It has a contract for one more landing mission, plus a mission to put two data relay satellites in lunar orbit.
Once again the leftist propaganda press takes out its knives to stab SpaceX and Musk

Superheavy captured safely yesterday by the chopsticks,
for the third time in four attempts
As should be expected, the destruction of Starship yesterday just before it made orbit on its eighth test flight was immediately used by partisan leftist media outlets to play “Let’s beat up on SpaceX and Elon Musk because he’s a friend of Trump!”
- Politico: FAA grounds traffic at four Florida airports after SpaceX craft breaks apart
- CNN: SpaceX’s Starship spacecraft explodes midflight for a second time, disrupting Florida air traffic
- Washington Post: Another SpaceX test flight ends in flames, with debris grounding planes
- CNBC: FAA briefly halts flights to several Florida airports after SpaceX rocket testing failure
- BBC: SpaceX rocket explodes, raining debris from sky for second time in a row
- San Antonio Express-News: In second-straight test flight failure, SpaceX loses control of Starship
All these outlets decided to emphasize the falling debris and disruption to air traffic, but in doing so they all spun the story in a very dishonest way. First, both SpaceX and the FAA had been prepared for this possibility, and had used well-established procedures — in league with all other involved nations — to respond to the launch failure. The air space was cleared for only about fifteen minutes, as only this Florida Today article noted. Take-off delays at affected airports ranged from minutes to almost an hour, but hardly much different that normal delays seen every day.
Most important, no one was hurt, no planes were damaged, and there were no negative consequences. If anything, yesterday’s Starship flight illustrated the competence shown by SpaceX as it runs a very ambitious and radical development program of the most powerful rocket ever built. For example, why so little mention of the successful catch of Superheavy, something SpaceX has been able to do three times in the first four test flights? That achievement is truly mind-blowing.
The obviousness of these attacks is truly getting tedious. Moreover, why the hostility to one of the most spectacular efforts by an American company? Shouldn’t the American news outlets above be enthused by this effort? Have they become so hateful of their own country in all things, they want it to fail, always?
Sadly, I think we know the answer to that last question. The leftist indoctrination effort that now dominates almost all of America’s universities has produced a generation that does hate America, because they literally know nothing of its history except the distorted lies put forth by these Marxist colleges. They would rather destroy success than have America succeed.
It is both tragic and shameful, and a perfect example of someone cutting off their own nose to spite their face.
French official lauds Ariane 6 launch; demands Europe have its own launch capability
Philippe Baptiste, France’s Minister for Higher Education and Research, yesterday loudly touted the second successful launch of Ariane 6 rocket, even though it occurred years late and costs far more than any other rocket on the market today.
Baptiste did so even as he insisted the Europe must continue to have its own launch capability so that it need not depend on rockets from other countries.
Europe must have sovereignty in space and “not yield to the temptation of preferring SpaceX or another competitor that may seem trendier, more reliable, or cheaper,” Baptiste [said]. “This first commercial launch of Ariane 6 is not just a technical and one-off success. It marks a new milestone, essential in the choice of European space independence and sovereignty. In the labyrinth of the global space race, Ariane 6 is the guiding thread of our strategic autonomy for the years to come.
“We must also collectively advance, as Europeans, on the governance of Europe’s space ambitions. We must ask ourselves all the questions, without taboos. For Europe in space, I am convinced that the European Union must fully assume its role as the political leader in this matter. The challenges are immense, no one knows this better than we do.”
Note Baptiste’s focus on having the European Union (EU) run things, with a focus on Ariane-6, despite its high cost. He was previously head of France’s space agency CNES, which for years has used the EU and the European Space Agency’s (ESA) partners help pay for France’s space program by requiring that all rocket launches be run by ESA’s commercial division, Arianespace.
That situation is now changing, with other ESA nations (Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom) all breaking free from Arianespace and instead encouraging the development of competing private rocket startups independent of ESA or Arianespace. Moreover, these ESA partners have aggressive reduced Arianespace’s areas of control. It no longer runs the French Guiana spaceport. Its management of the Vega-C rocket has been transferred back to the Italian company Avio, which builds it. All it now has is Ariane-6, which has limited value because it is so expensive.
So while Baptiste desire for European autonomy matches the efforts of these European countries, his apparent desire to keep all control within the continent’s centralized government authority has been rejected. Europe has a chance to compete, but only because it is freeing its rocket startups from government control.
Philippe Baptiste, France’s Minister for Higher Education and Research, yesterday loudly touted the second successful launch of Ariane 6 rocket, even though it occurred years late and costs far more than any other rocket on the market today.
Baptiste did so even as he insisted the Europe must continue to have its own launch capability so that it need not depend on rockets from other countries.
Europe must have sovereignty in space and “not yield to the temptation of preferring SpaceX or another competitor that may seem trendier, more reliable, or cheaper,” Baptiste [said]. “This first commercial launch of Ariane 6 is not just a technical and one-off success. It marks a new milestone, essential in the choice of European space independence and sovereignty. In the labyrinth of the global space race, Ariane 6 is the guiding thread of our strategic autonomy for the years to come.
“We must also collectively advance, as Europeans, on the governance of Europe’s space ambitions. We must ask ourselves all the questions, without taboos. For Europe in space, I am convinced that the European Union must fully assume its role as the political leader in this matter. The challenges are immense, no one knows this better than we do.”
Note Baptiste’s focus on having the European Union (EU) run things, with a focus on Ariane-6, despite its high cost. He was previously head of France’s space agency CNES, which for years has used the EU and the European Space Agency’s (ESA) partners help pay for France’s space program by requiring that all rocket launches be run by ESA’s commercial division, Arianespace.
That situation is now changing, with other ESA nations (Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom) all breaking free from Arianespace and instead encouraging the development of competing private rocket startups independent of ESA or Arianespace. Moreover, these ESA partners have aggressive reduced Arianespace’s areas of control. It no longer runs the French Guiana spaceport. Its management of the Vega-C rocket has been transferred back to the Italian company Avio, which builds it. All it now has is Ariane-6, which has limited value because it is so expensive.
So while Baptiste desire for European autonomy matches the efforts of these European countries, his apparent desire to keep all control within the continent’s centralized government authority has been rejected. Europe has a chance to compete, but only because it is freeing its rocket startups from government control.
Samantha Fish – No Angels
An evening pause: Performed live 2018. Good music and playing, but the cameraman was clearly not listening to the music, as he often couldn’t find the person playing or singing.
Hat tip Judd Clark.
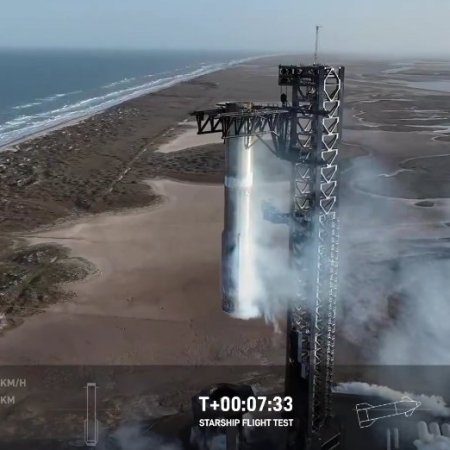
SpaceX’s eighth orbital test flight of Starship/Superheavy ends like the seventh flight

Starship just before loss of signal
Today’s eighth orbital test flight of SpaceX’s Starship/Superheavy giant rocket has turned out to be almost identical to the seventh flight, with Superheavy completing its mission with a perfect chopstick catch at the launch tower in Boca Chica and Starship failing just before engine shutdown that would have put it into its orbit.
The screen capture to the right shows that moment. Note that graphic on the far lower right. It indicates that only two of the outside engines are firing, in an asymmetrical configuration. As a result Starship began tumbling, as shown by the fact that the Earth is not visible in the background. Shortly thereafter contact was lost, and I expect the flight termination system took over to destroy the ship. Expect videos from the Caribbean of it burning up overhead in the next day or so.
Superheavy however completed the third ever capture by the launch tower chopsticks. Musk has indicated that the company is pushing to reuse a Superheavy booster as soon as possible. The lose of Starship and the fact that two Superheavy engines shut down prematurely during the boost-back burn after stage separation likely delays that reuse at least one or two test flights. First, this Superheavy had issues, that might be solvable but they nonetheless exist.
More important, the loss of Starship just before its orbital coast once again means SpaceX was unable to do any of its orbital and return test program. It will not make sense to risk the next Starship flight with a used Superheavy when testing Starship has now been delayed twice.
Nor does it matter much. It will take many more launches before this rocket is reliably reusable. The first priority now is to make it more reliable on its first launches. Expect SpaceX to target the next test flight for sometime in mid- to-late April.

Starship just before loss of signal
Today’s eighth orbital test flight of SpaceX’s Starship/Superheavy giant rocket has turned out to be almost identical to the seventh flight, with Superheavy completing its mission with a perfect chopstick catch at the launch tower in Boca Chica and Starship failing just before engine shutdown that would have put it into its orbit.
The screen capture to the right shows that moment. Note that graphic on the far lower right. It indicates that only two of the outside engines are firing, in an asymmetrical configuration. As a result Starship began tumbling, as shown by the fact that the Earth is not visible in the background. Shortly thereafter contact was lost, and I expect the flight termination system took over to destroy the ship. Expect videos from the Caribbean of it burning up overhead in the next day or so.
Superheavy however completed the third ever capture by the launch tower chopsticks. Musk has indicated that the company is pushing to reuse a Superheavy booster as soon as possible. The lose of Starship and the fact that two Superheavy engines shut down prematurely during the boost-back burn after stage separation likely delays that reuse at least one or two test flights. First, this Superheavy had issues, that might be solvable but they nonetheless exist.
More important, the loss of Starship just before its orbital coast once again means SpaceX was unable to do any of its orbital and return test program. It will not make sense to risk the next Starship flight with a used Superheavy when testing Starship has now been delayed twice.
Nor does it matter much. It will take many more launches before this rocket is reliably reusable. The first priority now is to make it more reliable on its first launches. Expect SpaceX to target the next test flight for sometime in mid- to-late April.
Athena sits at an unknown angle on the Moon, hampering operations
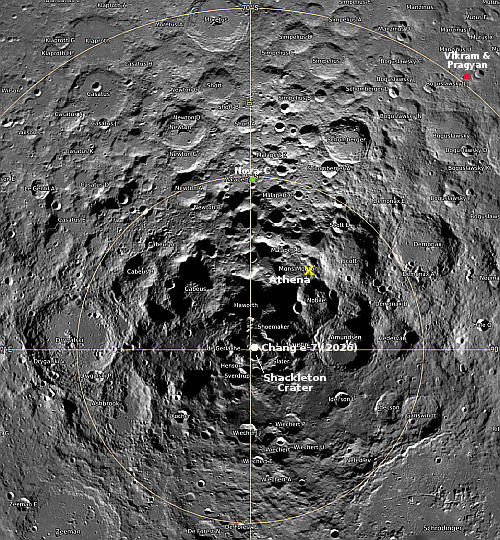
Yellow cross indicates Athena’s targeted landing site
According to the CEO of Intuitive Machines, Athena is sitting an an unknown angle on the Moon, impacting the possibility of all surface science operations.
The tilt is hampering their ability to use the high gain antenna which they need use to download most of their data. They do not know the angle, or the cause of this issue. It could simply be that the ground slope is too severe. It is also possible the spacecraft, which has a relatively high center of gravity, fell over on its side because of that slope. Moreover, they do not know at the moment exactly where the spacecraft landed, though they know it landed on Mons Mouton as planned. They need to download pictures from the spacecraft, as well as from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) in orbit to determine precisely the location and the situation.
It is also unclear what payloads will be impacted by this situation. It could be that most if all could be utilized, but that question cannot be answered until they learn more. I suspect both the mini-rover and the Grace hopper will be affected the most, as the tilt might make it impossible to deploy either.
For Intuitive Machines this situation is very unfortunate. It has sent two unmanned lunar landers, and both have had issues at landing, though it must be emphasized that the issue on today’s second landing might have nothing to do with the company’s engineering at all.

Yellow cross indicates Athena’s targeted landing site
According to the CEO of Intuitive Machines, Athena is sitting an an unknown angle on the Moon, impacting the possibility of all surface science operations.
The tilt is hampering their ability to use the high gain antenna which they need use to download most of their data. They do not know the angle, or the cause of this issue. It could simply be that the ground slope is too severe. It is also possible the spacecraft, which has a relatively high center of gravity, fell over on its side because of that slope. Moreover, they do not know at the moment exactly where the spacecraft landed, though they know it landed on Mons Mouton as planned. They need to download pictures from the spacecraft, as well as from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) in orbit to determine precisely the location and the situation.
It is also unclear what payloads will be impacted by this situation. It could be that most if all could be utilized, but that question cannot be answered until they learn more. I suspect both the mini-rover and the Grace hopper will be affected the most, as the tilt might make it impossible to deploy either.
For Intuitive Machines this situation is very unfortunate. It has sent two unmanned lunar landers, and both have had issues at landing, though it must be emphasized that the issue on today’s second landing might have nothing to do with the company’s engineering at all.
Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander touches down softly; engineers are assessing spacecraft condition
Though Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander has apparently softly landed near the south pole of the Moon, there remains uncertainty about the spacecraft’s status. Engineers have contact with Athena, and are apparently shutting down the landing equipment in order to make Athena safe for surface operations.
Unlike the previous landing, the spacecraft is upright and responding fully as expected. It appears the main issue is the position of Athena relative to the horizon. This is important as it determines the best antenna’s to use to upload and download data to and from Earth.
A full update will be provided at a press conference scheduled for 4 pm (Eastern) today. I have embedded the live stream of that conference below.
» Read more
Though Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander has apparently softly landed near the south pole of the Moon, there remains uncertainty about the spacecraft’s status. Engineers have contact with Athena, and are apparently shutting down the landing equipment in order to make Athena safe for surface operations.
Unlike the previous landing, the spacecraft is upright and responding fully as expected. It appears the main issue is the position of Athena relative to the horizon. This is important as it determines the best antenna’s to use to upload and download data to and from Earth.
A full update will be provided at a press conference scheduled for 4 pm (Eastern) today. I have embedded the live stream of that conference below.
» Read more
Blue Ghost lunar surface operations proceeding as planned
According to a Firefly update today, all of Blue Ghost’s planned lunar surface operations are working as planned.
Eight out of 10 NASA payloads, including LPV, EDS, NGLR, RAC, RadPC, LuGRE, LISTER, and SCALPSS, have already met their mission objectives with more to come. Lunar PlanetVac for example successfully collected, transferred, and sorted lunar soil from the Moon using pressurized nitrogen gas.
I have embedded below the video posted at the link of Lunar PlanetVac deploying and then blowing that gas to capture surface soil.
» Read more
According to a Firefly update today, all of Blue Ghost’s planned lunar surface operations are working as planned.
Eight out of 10 NASA payloads, including LPV, EDS, NGLR, RAC, RadPC, LuGRE, LISTER, and SCALPSS, have already met their mission objectives with more to come. Lunar PlanetVac for example successfully collected, transferred, and sorted lunar soil from the Moon using pressurized nitrogen gas.
I have embedded below the video posted at the link of Lunar PlanetVac deploying and then blowing that gas to capture surface soil.
» Read more
Tim McGraw & Faith Hill – I Need You
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter snaps picture of Blue Ghost on the Moon
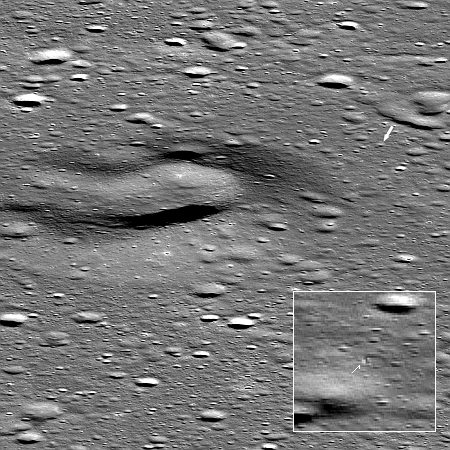

Click for full image. For original of inset go here.
Shortly after Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander touched down within Mare Crisium on the Moon, the science team for Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) used it to capture a picture of lander on the surface of the Moon.
That image is to the right, reduced to post here. The inset was expanded and sharpened to bring out the details, with the arrow showing Blue Ghost, that tiny dot in the center with a shadow to the right.
The Firefly Blue Ghost lunar lander set down on 2nd March 2025. The landing site (arrow) is about 4000 meters from the center of Mons Latreille, a large volcanic cone [seen to the left].
…LRO was 175 kilometers east (19.294°N, 67.956°E) of the landing site when the NACs acquired this dramatic view of the landing site on 02 March 2025 at 17:49 UTC.
Blue Ghost landed shortly after lunar sunrise, and is designed to operate for one full lunar day (fourteen Earth days). Whether it can survive the 14-day-long lunar night won’t be known until the next sunrise.

Click for full image. For original of inset go here.
Shortly after Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander touched down within Mare Crisium on the Moon, the science team for Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) used it to capture a picture of lander on the surface of the Moon.
That image is to the right, reduced to post here. The inset was expanded and sharpened to bring out the details, with the arrow showing Blue Ghost, that tiny dot in the center with a shadow to the right.
The Firefly Blue Ghost lunar lander set down on 2nd March 2025. The landing site (arrow) is about 4000 meters from the center of Mons Latreille, a large volcanic cone [seen to the left].
…LRO was 175 kilometers east (19.294°N, 67.956°E) of the landing site when the NACs acquired this dramatic view of the landing site on 02 March 2025 at 17:49 UTC.
Blue Ghost landed shortly after lunar sunrise, and is designed to operate for one full lunar day (fourteen Earth days). Whether it can survive the 14-day-long lunar night won’t be known until the next sunrise.
Watch the eighth orbital test launch of SpaceX’s Starship/Superheavy
SpaceX is now targeting a 60-minute launch window on March 6, 2025 beginning at 5:30 pm (Central) for its eighth orbital test launch of its gigantic Starship/Superheavy rocket.
I have embedded the Space Affairs live stream below, as SpaceX’s X feed does not become active until it starts broadcasting about 40 minutes before the opening of that window.
As noted prior to the first launch attempt on March 3, 2025:
This flight has the same essential flight plan as the seventh flight, mainly because the prototype Starship on that previous flight was lost before it could achieve any of its goals. After Superheavy separates and attempts a chopstick landing at Boca Chica, Starship will go into a low orbit that will bring it down over the Indian Ocean. During the coast phase it will attempt to deploy four dummy Starlink satellites to test its deployment equipment, as well as do a Raptor-2 engine restart to demonstrate this works in order to prepare for a full orbit flight on a future test flight, possibly as soon as the next test flight.
Starship will also be testing a new configuration of thermal protection during its return, including leaving some places on its hull with no protection to see how those locations fare.
That first attempt was scrubbed at T-40 seconds because of issues on both Superheavy and Starship. Though it appears the team might have gotten those issues solved and launched, the decision was made to stand down and get them fixed properly, rather than rush things and possibly cause the mission to fail.
» Read more
SpaceX is now targeting a 60-minute launch window on March 6, 2025 beginning at 5:30 pm (Central) for its eighth orbital test launch of its gigantic Starship/Superheavy rocket.
I have embedded the Space Affairs live stream below, as SpaceX’s X feed does not become active until it starts broadcasting about 40 minutes before the opening of that window.
As noted prior to the first launch attempt on March 3, 2025:
This flight has the same essential flight plan as the seventh flight, mainly because the prototype Starship on that previous flight was lost before it could achieve any of its goals. After Superheavy separates and attempts a chopstick landing at Boca Chica, Starship will go into a low orbit that will bring it down over the Indian Ocean. During the coast phase it will attempt to deploy four dummy Starlink satellites to test its deployment equipment, as well as do a Raptor-2 engine restart to demonstrate this works in order to prepare for a full orbit flight on a future test flight, possibly as soon as the next test flight.
Starship will also be testing a new configuration of thermal protection during its return, including leaving some places on its hull with no protection to see how those locations fare.
That first attempt was scrubbed at T-40 seconds because of issues on both Superheavy and Starship. Though it appears the team might have gotten those issues solved and launched, the decision was made to stand down and get them fixed properly, rather than rush things and possibly cause the mission to fail.
» Read more
Watch the landing of Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander on the Moon tomorrow

NASA has now announced its live stream arrangement for the landing of Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander on the Moon tomorrow at 12:32 pm (Eastern).
The live stream will begin about sixty minutes before landing. The NASA live stream is available here. I have also embedded it below.
The map to the right shows the landing site by the yellow “X”, about 100 miles from the Moon’s south pole on a high relatively flat plateau dubbed Mons Mouton. This will be the closest any lander has come to the pole, and was the original site chosen for NASA’s now-canceled VIPER rover. If the landing is successful Athena will land close to a small crater that is believed to have permanently shadowed areas. The plan had been to have VIPER travel into it. Now the small Grace hopper that Athena carries will attempt this instead.
This will also be the second attempt by Intuitive Machines to soft land on the Moon. Its first attempt last year was able to land and communicate back to Earth, but the landing was not completely successful. The lander, named Nova-C as well as Odysseus, was moving too fast sideways when it touched down, thus breaking one leg so that the lander fell on its side.
» Read more

NASA has now announced its live stream arrangement for the landing of Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander on the Moon tomorrow at 12:32 pm (Eastern).
The live stream will begin about sixty minutes before landing. The NASA live stream is available here. I have also embedded it below.
The map to the right shows the landing site by the yellow “X”, about 100 miles from the Moon’s south pole on a high relatively flat plateau dubbed Mons Mouton. This will be the closest any lander has come to the pole, and was the original site chosen for NASA’s now-canceled VIPER rover. If the landing is successful Athena will land close to a small crater that is believed to have permanently shadowed areas. The plan had been to have VIPER travel into it. Now the small Grace hopper that Athena carries will attempt this instead.
This will also be the second attempt by Intuitive Machines to soft land on the Moon. Its first attempt last year was able to land and communicate back to Earth, but the landing was not completely successful. The lander, named Nova-C as well as Odysseus, was moving too fast sideways when it touched down, thus breaking one leg so that the lander fell on its side.
» Read more
France opens public comment period for adapting old French Guiana launchpad for commercial rockets
CNES, France’s space agency that now runs the French Guiana spaceport, is now running public meetings for the public to comment on its plans for adapting the old, long-abandoned Diamant rocket pad there for use by a number of commercial rocket startups.
On 17 February, the first of four public consultation sessions into the construction of the new Multi-Launcher Launch Complex (ELM1) at the Guiana Space Centre was held at Kourou Town Hall. This process allows local residents, stakeholders, and organizations to review the project and provide feedback before construction begins. A second session was completed on 23 February, with the remaining two sessions set for 10 and 18 March.
The construction of ELM1 will include common structures like the nodal building, guard post, offices, and storage areas, as well as more specific structures like assembly and preparation buildings, roads, and fences. The project is subject to a building permit, a unique environmental authorization under the regulations for Classified Installations for Environmental Protection, the Water Law, and a request for exemption from the prohibition on the destruction of protected species.
CNES in 2024 approved seven rocket startups to use the site. It later announced its plan to standardize the launchpad so that all users will have to arrive with identical engineering, something that these startups did not like. This comment period will allow them to voice those objections, and likely get the standardization minimized to only those places where it really matters. For example, the impression initially given was that the assembly and preparation buildings would require matching systems from all companies, something that makes no sense.
CNES, France’s space agency that now runs the French Guiana spaceport, is now running public meetings for the public to comment on its plans for adapting the old, long-abandoned Diamant rocket pad there for use by a number of commercial rocket startups.
On 17 February, the first of four public consultation sessions into the construction of the new Multi-Launcher Launch Complex (ELM1) at the Guiana Space Centre was held at Kourou Town Hall. This process allows local residents, stakeholders, and organizations to review the project and provide feedback before construction begins. A second session was completed on 23 February, with the remaining two sessions set for 10 and 18 March.
The construction of ELM1 will include common structures like the nodal building, guard post, offices, and storage areas, as well as more specific structures like assembly and preparation buildings, roads, and fences. The project is subject to a building permit, a unique environmental authorization under the regulations for Classified Installations for Environmental Protection, the Water Law, and a request for exemption from the prohibition on the destruction of protected species.
CNES in 2024 approved seven rocket startups to use the site. It later announced its plan to standardize the launchpad so that all users will have to arrive with identical engineering, something that these startups did not like. This comment period will allow them to voice those objections, and likely get the standardization minimized to only those places where it really matters. For example, the impression initially given was that the assembly and preparation buildings would require matching systems from all companies, something that makes no sense.
Blue Ghost: Earth’s GPS constellations work on the Moon
Using an engineering test GPS-type receiver built by the Italian Space Agency, engineers have successfully been able to use the GPS-type satellites from two different constellations to pinpoint the location of Firefly’s Blue Ghost lander on the Moon.
The road to the historic milestone began on March 2 when the Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander touched down on the Moon and delivered LuGRE, one of 10 NASA payloads intended to advance lunar science. Soon after landing, LuGRE payload operators at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, began conducting their first science operation on the lunar surface.
With the receiver data flowing in, anticipation mounted. Could a Moon-based mission acquire and track signals from two GNSS constellations, GPS and Galileo, and use those signals for navigation on the lunar surface?
Then, at 2 a.m. EST on March 3, it was official: LuGRE acquired and tracked signals on the lunar surface for the first time ever and achieved a navigation fix — approximately 225,000 miles away from Earth.
Obviously, this is a first-time engineering test. A portable version of LuGRE will now have to be developed. However, this success means that any operation on the near side of the Moon will not need the addition of a new GPS-type constellation in lunar orbit. It also will likely simplify the design of any constellation for providing this capability to the far side.
Meanwhile, Blue Ghost continues to operate as planned on the surface, with all instruments functioning and several already collecting data.
Using an engineering test GPS-type receiver built by the Italian Space Agency, engineers have successfully been able to use the GPS-type satellites from two different constellations to pinpoint the location of Firefly’s Blue Ghost lander on the Moon.
The road to the historic milestone began on March 2 when the Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander touched down on the Moon and delivered LuGRE, one of 10 NASA payloads intended to advance lunar science. Soon after landing, LuGRE payload operators at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, began conducting their first science operation on the lunar surface.
With the receiver data flowing in, anticipation mounted. Could a Moon-based mission acquire and track signals from two GNSS constellations, GPS and Galileo, and use those signals for navigation on the lunar surface?
Then, at 2 a.m. EST on March 3, it was official: LuGRE acquired and tracked signals on the lunar surface for the first time ever and achieved a navigation fix — approximately 225,000 miles away from Earth.
Obviously, this is a first-time engineering test. A portable version of LuGRE will now have to be developed. However, this success means that any operation on the near side of the Moon will not need the addition of a new GPS-type constellation in lunar orbit. It also will likely simplify the design of any constellation for providing this capability to the far side.
Meanwhile, Blue Ghost continues to operate as planned on the surface, with all instruments functioning and several already collecting data.
The Teskey Brothers – Take My Heart
SpaceX reschedules Starship/Superheavy launch to March 5, 2025
SpaceX has now rescheduled the eighth orbital test flight of its giant Starship/Superheavy rocket for tomorrow, March 5, 2025, with its one-hour launch window opening at 5:30 pm (Central).
The new launch time was caused by the launch scrub yesterday for unspecified issues with both the spacecraft.
I have once again embedded below the Space Affairs youtube live feed of this launch. The SpaceX X feed will only be available once it goes live at about 4:40 pm (Central).
» Read more
SpaceX has now rescheduled the eighth orbital test flight of its giant Starship/Superheavy rocket for tomorrow, March 5, 2025, with its one-hour launch window opening at 5:30 pm (Central).
The new launch time was caused by the launch scrub yesterday for unspecified issues with both the spacecraft.
I have once again embedded below the Space Affairs youtube live feed of this launch. The SpaceX X feed will only be available once it goes live at about 4:40 pm (Central).
» Read more
Falcon 9 first stage lost after landing yesterday
According to an update on SpaceX’s website, the first stage of the Falcon 9 that launched 21 Starlink satellites (not 23 as initially reported) yesterday was lost shortly after landing.
The first stage booster returned to Earth and landed on the Just Read the Instructions droneship, which was stationed in the Atlantic Ocean ~250 nautical miles off the coast of Florida. Following the successful landing, an off-nominal fire in the aft end of the rocket damaged one of the booster’s landing legs which resulted in it tipping over.
This is only the second time in years that a first stage has been lost in this manner. After the previous occurrence last year during the Biden administration, the FAA grounded all SpaceX launches for several days, an action that indicated clearly an effort to harass the company for political reasons. I will be very surprised if this happens again, with Trump now in office.
According to an update on SpaceX’s website, the first stage of the Falcon 9 that launched 21 Starlink satellites (not 23 as initially reported) yesterday was lost shortly after landing.
The first stage booster returned to Earth and landed on the Just Read the Instructions droneship, which was stationed in the Atlantic Ocean ~250 nautical miles off the coast of Florida. Following the successful landing, an off-nominal fire in the aft end of the rocket damaged one of the booster’s landing legs which resulted in it tipping over.
This is only the second time in years that a first stage has been lost in this manner. After the previous occurrence last year during the Biden administration, the FAA grounded all SpaceX launches for several days, an action that indicated clearly an effort to harass the company for political reasons. I will be very surprised if this happens again, with Trump now in office.
