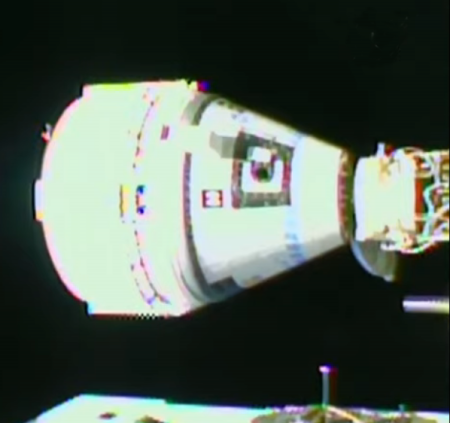
Did SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule have issues with its heat shield during its most recent return to Earth?
According to a May 23rd Space Explored article based on anonymous sources, the heat shield on SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule experienced “dangerously excessive wear upon reentry” because of a propellant leak.
Hypergolic propellant made its way into the Crew Dragon Endeavour’s heat shield, according to sources at SpaceX and NASA who spoke with Space Explored. This hypergolic propellant is used by the Crew Dragon in its Draco engines – hypergolic means that the two parts spontaneously combust upon contact. It is believed that this hypergolic propellant impacted the integrity of the heatshield, causing dangerously excessive wear upon reentry.
NASA however has now bluntly denied these claims:
“The data associated with Dragon’s recent crew reentries was normal — the system performed as designed without dispute. There has not been a hypergol leak during the return of a crewed Dragon mission nor any contamination with the heat shield causing excessive wear,” the NASA statement reads, in part.
“SpaceX and NASA perform a full engineering review of the heat shield’s thermal protection system following each return, including prior to the launch of the Crew-4 mission currently at the International Space Station,” the NASA statement continues. “The heat shield composite structure (structure below the tile) was re-flown per normal planning and refurbishment processes. The thermal protection system on the primary heat shield for Crew-4 was new, as it has been for all human spaceflight missions.”
Such a flat out denial by NASA strongly suggests that the anonymous sources relied on by Space Explored are not reliable, and got their facts wrong. While NASA will often try to hide or spin any issues to make them seem less worrisome, it has almost never denied the existence of a serious problem, when it was revealed that such a problem had occurred.
I know to say this sounds paranoid, but this story also suggests this claim might be part of the growing effort within the federal bureaucracy and the press to attack SpaceX, because of its new irrational hostility to Elon Musk because he supports achievement and free speech.
At the same time, SpaceX has recently had to discard and replace a Dragon heat shield planned for a future mission because of discovered “manufacturing defect” during normal preflight testing. This confirmed story, combined with the unconfirmed and questionable story above, suggests SpaceX needs to take a closer look at the Dragon heat shield design.
According to a May 23rd Space Explored article based on anonymous sources, the heat shield on SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule experienced “dangerously excessive wear upon reentry” because of a propellant leak.
Hypergolic propellant made its way into the Crew Dragon Endeavour’s heat shield, according to sources at SpaceX and NASA who spoke with Space Explored. This hypergolic propellant is used by the Crew Dragon in its Draco engines – hypergolic means that the two parts spontaneously combust upon contact. It is believed that this hypergolic propellant impacted the integrity of the heatshield, causing dangerously excessive wear upon reentry.
NASA however has now bluntly denied these claims:
“The data associated with Dragon’s recent crew reentries was normal — the system performed as designed without dispute. There has not been a hypergol leak during the return of a crewed Dragon mission nor any contamination with the heat shield causing excessive wear,” the NASA statement reads, in part.
“SpaceX and NASA perform a full engineering review of the heat shield’s thermal protection system following each return, including prior to the launch of the Crew-4 mission currently at the International Space Station,” the NASA statement continues. “The heat shield composite structure (structure below the tile) was re-flown per normal planning and refurbishment processes. The thermal protection system on the primary heat shield for Crew-4 was new, as it has been for all human spaceflight missions.”
Such a flat out denial by NASA strongly suggests that the anonymous sources relied on by Space Explored are not reliable, and got their facts wrong. While NASA will often try to hide or spin any issues to make them seem less worrisome, it has almost never denied the existence of a serious problem, when it was revealed that such a problem had occurred.
I know to say this sounds paranoid, but this story also suggests this claim might be part of the growing effort within the federal bureaucracy and the press to attack SpaceX, because of its new irrational hostility to Elon Musk because he supports achievement and free speech.
At the same time, SpaceX has recently had to discard and replace a Dragon heat shield planned for a future mission because of discovered “manufacturing defect” during normal preflight testing. This confirmed story, combined with the unconfirmed and questionable story above, suggests SpaceX needs to take a closer look at the Dragon heat shield design.