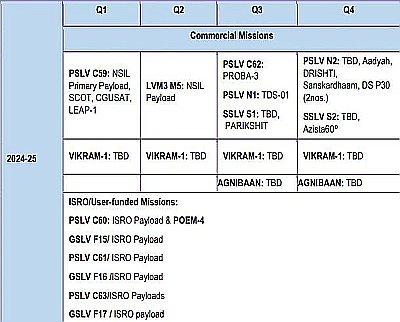
SpaceX launches two military prototype satellites
SpaceX today successfully launched two prototype reconnaissance satellites for the U.S. military, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral at 5:30 pm (Eastern) time.
The first stage successfully completed its seventh flight, landing back on at Cape Canaveral.
This is the first of four launches scheduled for the next eleven hours. Next up is another Falcon 9 launch, carrying 22 Starlink satellites and lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
13 SpaceX
8 China
2 Iran
At present American private enterprise leads the entire world combined 15 to 13 in successful launches, with SpaceX by itself tied with the rest of the world combined (excluding American companies) 13 all.
SpaceX today successfully launched two prototype reconnaissance satellites for the U.S. military, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral at 5:30 pm (Eastern) time.
The first stage successfully completed its seventh flight, landing back on at Cape Canaveral.
This is the first of four launches scheduled for the next eleven hours. Next up is another Falcon 9 launch, carrying 22 Starlink satellites and lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
13 SpaceX
8 China
2 Iran
At present American private enterprise leads the entire world combined 15 to 13 in successful launches, with SpaceX by itself tied with the rest of the world combined (excluding American companies) 13 all.