Today’s Twitter links
Today I am beginning a new mid-day feature on Behind the Black, thanks to the effort of reader Jay, who has recently been acting as a stringer by sending me new stories he finds on Twitter. I don’t do Twitter, so his help has been very much appreciated.
Most of these Twitter stories however do not merit a full post. Most are usually just interesting images, or PR updates from companies and space agencies announcing future events. Up to now I check them out, and then file them away. I decided we might as well post them each day, all at once, in a single post. Jay has agreed to gladly help make this happen.
So, let’s begin:
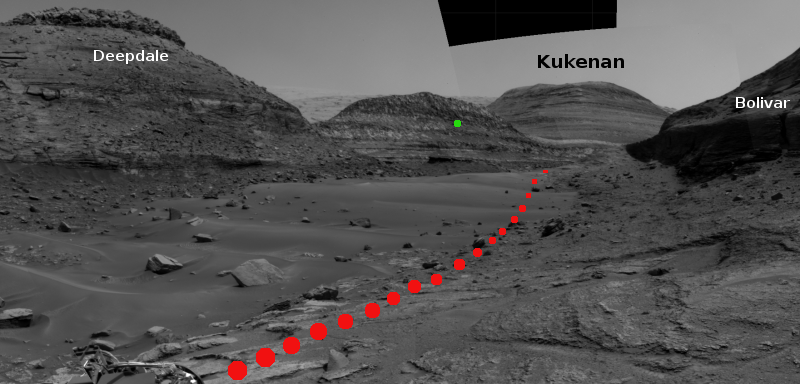
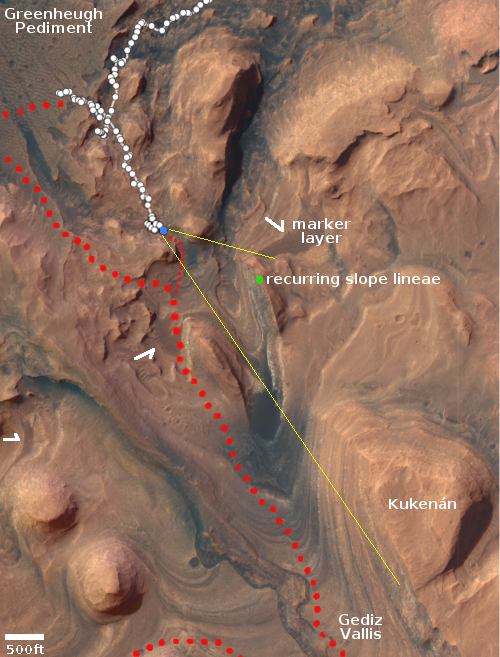
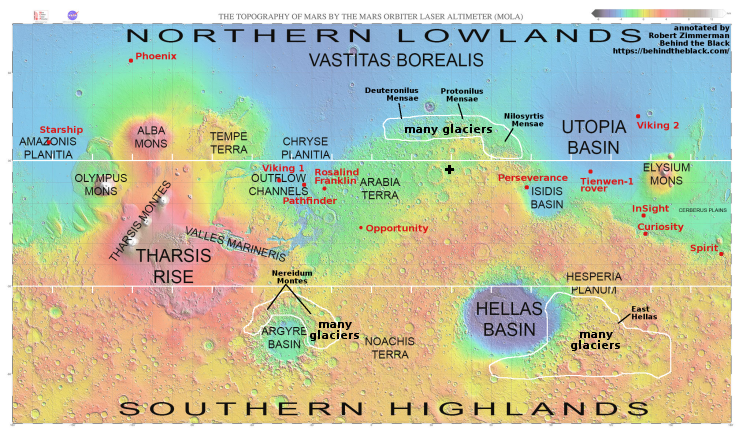
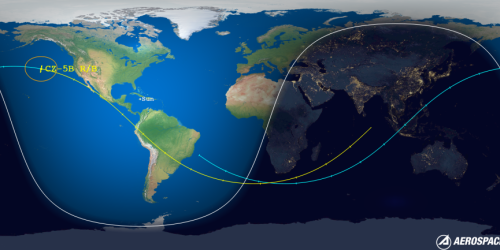
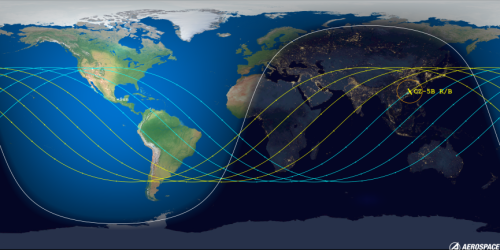
It is unknown how much information China will release much about this launch. Stay tuned.
I will only believe Blue Origin has delivered a flightworthy engine to ULA when ULA actually begins installing that engine on a Vulcan rocket. Until then, I view everything Blue Origin posts on Twitter on this subject to be nothing more than empty air.
Today I am beginning a new mid-day feature on Behind the Black, thanks to the effort of reader Jay, who has recently been acting as a stringer by sending me new stories he finds on Twitter. I don’t do Twitter, so his help has been very much appreciated.
Most of these Twitter stories however do not merit a full post. Most are usually just interesting images, or PR updates from companies and space agencies announcing future events. Up to now I check them out, and then file them away. I decided we might as well post them each day, all at once, in a single post. Jay has agreed to gladly help make this happen.
So, let’s begin:
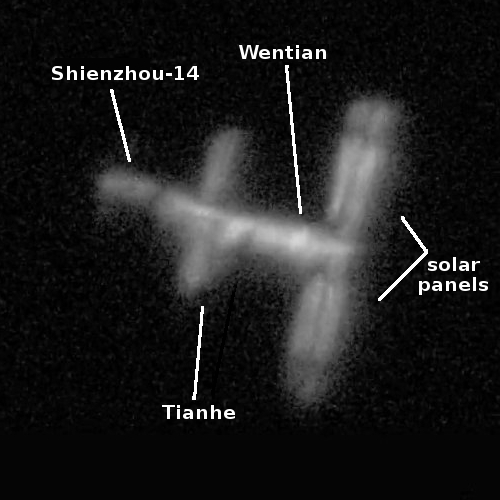
It is unknown how much information China will release much about this launch. Stay tuned.
I will only believe Blue Origin has delivered a flightworthy engine to ULA when ULA actually begins installing that engine on a Vulcan rocket. Until then, I view everything Blue Origin posts on Twitter on this subject to be nothing more than empty air.