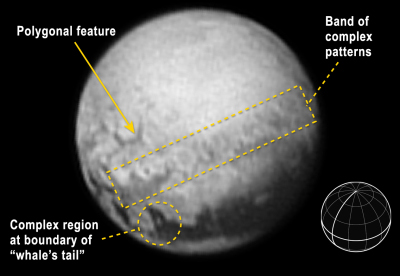
Pluto and Charon in false color
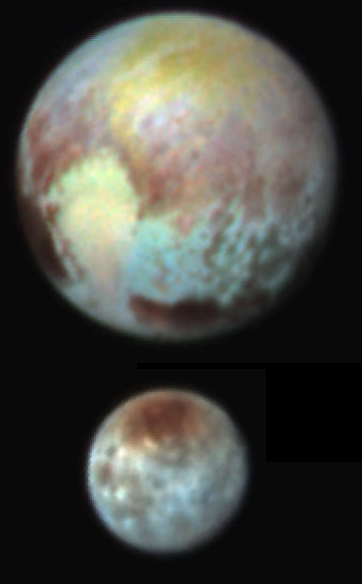
While waiting for word about how New Horizons has fared during its close fly-by of Pluto, the science team today released the false color images on the right of both Pluto and Charon to illustrate the complicated surface geology of both planetary bodies.
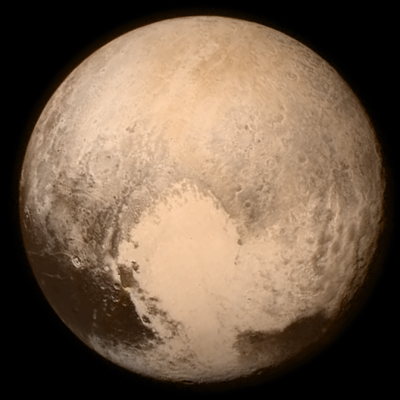
The new color images reveal that the “heart” of Pluto actually consists of two remarkably different-colored regions. In the false-color image, the heart consists of a western lobe shaped like an ice cream cone that appears peach color in this image. A mottled area on the right (east) side looks bluish. A mid-latitude band appears in shades ranging from pale blue through red. Even within the northern polar cap, in the upper part of the image, various shades of yellow-orange indicate subtle compositional differences. This image was obtained using three of the color filters of the Ralph instrument on July 13 at 3:38 am EDT and received on the ground on at 12:25 pm.
The surface of Charon is viewed using the same exaggerated color. The red on the dark northern polar cap of Charon is attributed to hydrocarbon and other molecules, a class of chemical compounds called tholins. The mottled colors at lower latitudes point to the diversity of terrains on Charon. This image was obtained using three of the color filters of the Ralph instrument on July 13 at 3:38 am EDT and received on the ground on at 12:25 pm.
Word on the spacecraft’s status will arrive at around 9 pm (eastern) tonight. Images and data will then follow, assuming all is well.
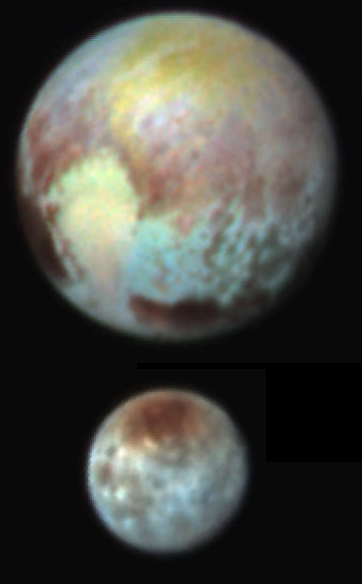
While waiting for word about how New Horizons has fared during its close fly-by of Pluto, the science team today released the false color images on the right of both Pluto and Charon to illustrate the complicated surface geology of both planetary bodies.
The new color images reveal that the “heart” of Pluto actually consists of two remarkably different-colored regions. In the false-color image, the heart consists of a western lobe shaped like an ice cream cone that appears peach color in this image. A mottled area on the right (east) side looks bluish. A mid-latitude band appears in shades ranging from pale blue through red. Even within the northern polar cap, in the upper part of the image, various shades of yellow-orange indicate subtle compositional differences. This image was obtained using three of the color filters of the Ralph instrument on July 13 at 3:38 am EDT and received on the ground on at 12:25 pm.
The surface of Charon is viewed using the same exaggerated color. The red on the dark northern polar cap of Charon is attributed to hydrocarbon and other molecules, a class of chemical compounds called tholins. The mottled colors at lower latitudes point to the diversity of terrains on Charon. This image was obtained using three of the color filters of the Ralph instrument on July 13 at 3:38 am EDT and received on the ground on at 12:25 pm.
Word on the spacecraft’s status will arrive at around 9 pm (eastern) tonight. Images and data will then follow, assuming all is well.