First flight of government-built hopper to test vertical landings delayed two years
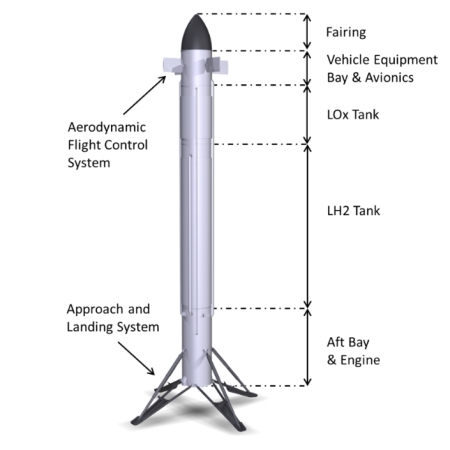
Callisto’s basic design
This story about a first stage government-built Grasshopper-type rocket designed to demonstrate and test vertical landing has instead become a perfect demonstration of why governments should not design, build, and own anything.
It appears the first test flight of the Callisto test rocket, first proposed in 2015 and being built by a joint partnership of the German (DLR), French (CNES), and Japanese (JAXA) space agencies, has now slipped from 2024 to 2026.
Earlier this month, CNES deployed a refreshed website. Prior to that deployment, the agency’s Callisto project page had stated that the rocket’s first flight would occur in 2024. The new Callisto project page has a more detailed timeline, stating that the detailed design phase will be completed by the end of 2024. Vehicle integration in Japan is then expected in 2025, followed by a first launch from the Guiana Space Centre between 2025 and 2026. This revision outlines an approximate two-year slip in the project’s timeline. [emphasis mine]
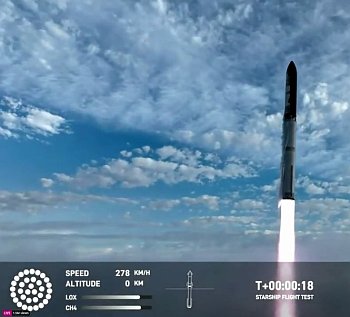
These three agencies took almost a decade to simply conceive and design the project. Apparently they not yet even built anything. This despite a budget of slightly less than $100 million carved out of the entire budget for creating the Ariane-6 expendable. Compare that with SpaceX, which conceived its Grasshopper vertical test prototype in 2011, began flying that year, and resulted in an actual Falcon 9 first stage landing in 2015.
Will Callisto ever fly? Maybe, but don’t expect it to produce a rocket that is financially competitive with SpaceX. Instead, expect these three government agencies to subsidize its cost in order to make its price competitive on the open market. More likely Callisto will fly a few times, but will likely result in no new orbital rocket. Instead it will be superseded by the private rocket startups worldwide that are now building actual orbital rockets and will likely make them reuseable before Callisto even leaves the ground.

Callisto’s basic design
This story about a first stage government-built Grasshopper-type rocket designed to demonstrate and test vertical landing has instead become a perfect demonstration of why governments should not design, build, and own anything.
It appears the first test flight of the Callisto test rocket, first proposed in 2015 and being built by a joint partnership of the German (DLR), French (CNES), and Japanese (JAXA) space agencies, has now slipped from 2024 to 2026.
Earlier this month, CNES deployed a refreshed website. Prior to that deployment, the agency’s Callisto project page had stated that the rocket’s first flight would occur in 2024. The new Callisto project page has a more detailed timeline, stating that the detailed design phase will be completed by the end of 2024. Vehicle integration in Japan is then expected in 2025, followed by a first launch from the Guiana Space Centre between 2025 and 2026. This revision outlines an approximate two-year slip in the project’s timeline. [emphasis mine]
These three agencies took almost a decade to simply conceive and design the project. Apparently they not yet even built anything. This despite a budget of slightly less than $100 million carved out of the entire budget for creating the Ariane-6 expendable. Compare that with SpaceX, which conceived its Grasshopper vertical test prototype in 2011, began flying that year, and resulted in an actual Falcon 9 first stage landing in 2015.
Will Callisto ever fly? Maybe, but don’t expect it to produce a rocket that is financially competitive with SpaceX. Instead, expect these three government agencies to subsidize its cost in order to make its price competitive on the open market. More likely Callisto will fly a few times, but will likely result in no new orbital rocket. Instead it will be superseded by the private rocket startups worldwide that are now building actual orbital rockets and will likely make them reuseable before Callisto even leaves the ground.