Rocket Lab experiences a tank failure during Neutron pressure test

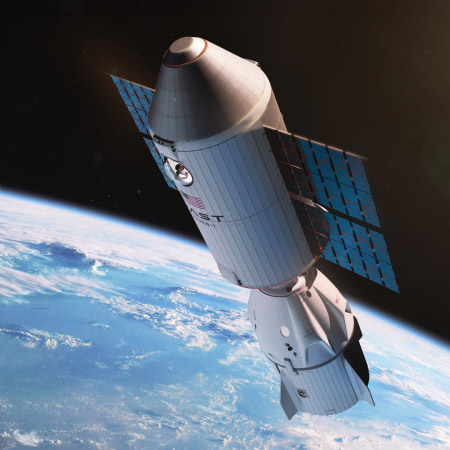
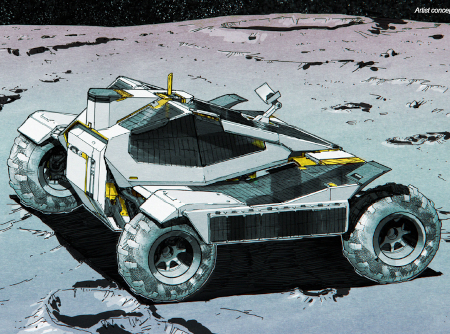
Artist’s rendering of Neutron’s first stage fairings opening
to deploy the payload with the second stage engine.
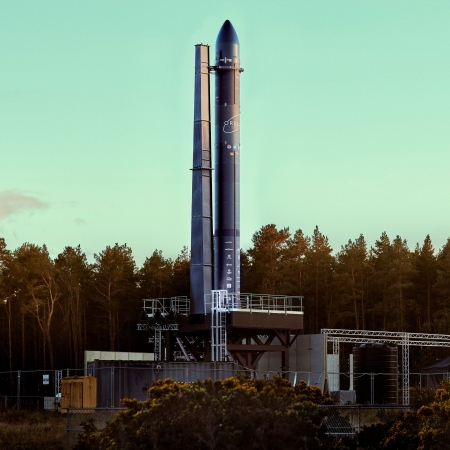
According to an update posted yesterday, during a pressure test of a first stage tank for Rocket Lab’s new Neutron rocket, the tank ruptured.
As the company pushes Neutron to the limits and beyond to qualify its systems and structures for launch, qualification testing of the Stage 1 tank overnight resulted in a rupture during a hydrostatic pressure trial. Testing failures are not uncommon during qualification testing. We intentionally test structures to their limits to validate structural integrity and safety margins to ensure the robust requirements for a successful launch can be comfortably met.
There was no significant damage to the test structure or facilities, the next Stage 1 tank is already in production, and Neutron’s development campaign continues while the team assesses today’s test outcome.
The team is reviewing the Stage 1 test data, which will determine the extent of the impact to Neutron’s launch schedule.
The company was aiming to do Neutron’s first launch in the first quarter of this year. Though the press release is vague on this point, its language suggests the rupture did not occur at the expected maximum pressure, but took place sooner, at a lower pressure level. If the tank failed at maximum pressure, then there would be no need to reconsider the launch schedule. A failure at lower pressures would require changes in tank design, and thus a launch delay.
The company says it will provide an update in February, which further suggests a launch in the first quarter is now unlikely.

Artist’s rendering of Neutron’s first stage fairings opening
to deploy the payload with the second stage engine.
According to an update posted yesterday, during a pressure test of a first stage tank for Rocket Lab’s new Neutron rocket, the tank ruptured.
As the company pushes Neutron to the limits and beyond to qualify its systems and structures for launch, qualification testing of the Stage 1 tank overnight resulted in a rupture during a hydrostatic pressure trial. Testing failures are not uncommon during qualification testing. We intentionally test structures to their limits to validate structural integrity and safety margins to ensure the robust requirements for a successful launch can be comfortably met.
There was no significant damage to the test structure or facilities, the next Stage 1 tank is already in production, and Neutron’s development campaign continues while the team assesses today’s test outcome.
The team is reviewing the Stage 1 test data, which will determine the extent of the impact to Neutron’s launch schedule.
The company was aiming to do Neutron’s first launch in the first quarter of this year. Though the press release is vague on this point, its language suggests the rupture did not occur at the expected maximum pressure, but took place sooner, at a lower pressure level. If the tank failed at maximum pressure, then there would be no need to reconsider the launch schedule. A failure at lower pressures would require changes in tank design, and thus a launch delay.
The company says it will provide an update in February, which further suggests a launch in the first quarter is now unlikely.