Dubai-based AI/3D printing company successfully test fires an aerospike engine
The Dubai-based startup LEAP71, focused on using AI software to quickly develop rocket engine designs it can then 3D print, has successfully test fired a prototype aerospike engine on December 18, 2024 during a static fire test campaign conducted in the United Kingdom.
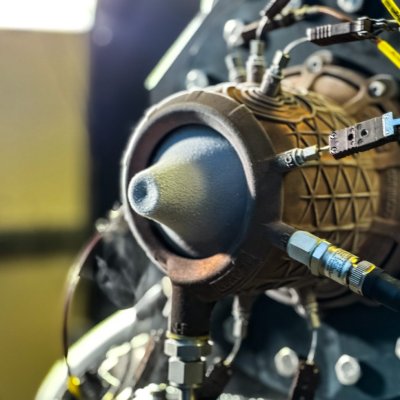
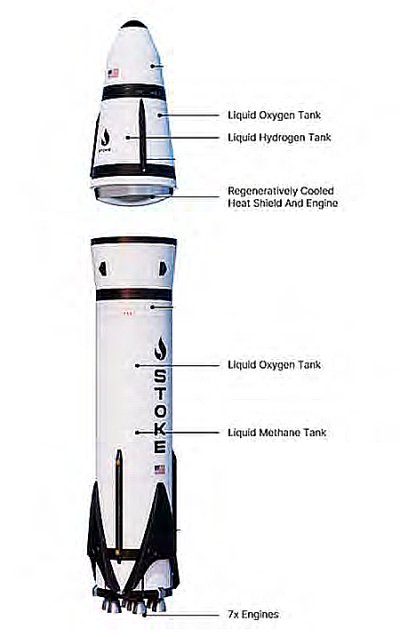
Aerospikes are more compact and significantly more efficient across various atmospheric pressures, including the vacuum of space. They forego the conventional bell-shaped nozzle by placing a spike in the center of a toroidal combustion chamber [as shown in the photo to the right]. Since it is surrounded by 3,500ºC hot exhaust gas, cooling the spike is an enormous challenge.
Josefine Lissner, CEO and Co-Founder of LEAP 71, stated: “We were able to extend Noyron’s physics to deal with the unique complexity of this engine type. The spike is cooled by intricate cooling channels flooded by cryogenic oxygen, whereas the outside of the chamber is cooled by the kerosene fuel. I am very encouraged by the results of this test, as virtually everything on the engine was novel and untested. It’s a great validation of our physics-driven approach to computational AI.”
The spike in the center acts as one wall of the nozzle, and the changing pressure of the atmosphere acting as the other side of the nozzle, allowing the nozzle size to change as the rocket rises, thus making its thrust as efficient as possible.
This test was apparently with a small scale prototype, not a full scale engine. LEAP71 engineers are going to have to go though a lot more iterations using their AI software and 3D printing to get to a version usable on a rocket. The company claims that development will go far faster this way. That this company did its testing in the UK but is based in Dubai suggests its capital comes from that Middle Eastern country, which is trying to develop a space industry of its own, but it is mainly relying on British designers — at this point — to get things done.
It will have to do so quickly, since another startup, German-based Polaris Spaceplanes, in November 2024 actually completed the first test flight ever of a prototype using an aerospike engine.
After decades of speculation about the advantages of an aerospike engine but no successful flights, we now have a race between two companies to be the first to fly one, and the effort is going on in Europe.
The Dubai-based startup LEAP71, focused on using AI software to quickly develop rocket engine designs it can then 3D print, has successfully test fired a prototype aerospike engine on December 18, 2024 during a static fire test campaign conducted in the United Kingdom.
Aerospikes are more compact and significantly more efficient across various atmospheric pressures, including the vacuum of space. They forego the conventional bell-shaped nozzle by placing a spike in the center of a toroidal combustion chamber [as shown in the photo to the right]. Since it is surrounded by 3,500ºC hot exhaust gas, cooling the spike is an enormous challenge.
Josefine Lissner, CEO and Co-Founder of LEAP 71, stated: “We were able to extend Noyron’s physics to deal with the unique complexity of this engine type. The spike is cooled by intricate cooling channels flooded by cryogenic oxygen, whereas the outside of the chamber is cooled by the kerosene fuel. I am very encouraged by the results of this test, as virtually everything on the engine was novel and untested. It’s a great validation of our physics-driven approach to computational AI.”
The spike in the center acts as one wall of the nozzle, and the changing pressure of the atmosphere acting as the other side of the nozzle, allowing the nozzle size to change as the rocket rises, thus making its thrust as efficient as possible.
This test was apparently with a small scale prototype, not a full scale engine. LEAP71 engineers are going to have to go though a lot more iterations using their AI software and 3D printing to get to a version usable on a rocket. The company claims that development will go far faster this way. That this company did its testing in the UK but is based in Dubai suggests its capital comes from that Middle Eastern country, which is trying to develop a space industry of its own, but it is mainly relying on British designers — at this point — to get things done.
It will have to do so quickly, since another startup, German-based Polaris Spaceplanes, in November 2024 actually completed the first test flight ever of a prototype using an aerospike engine.
After decades of speculation about the advantages of an aerospike engine but no successful flights, we now have a race between two companies to be the first to fly one, and the effort is going on in Europe.