SpaceX launches two astronauts to ISS, setting new annual launch record for the U.S.
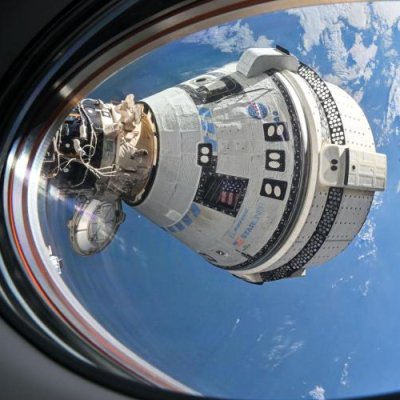
SpaceX this morning launched two astronauts to ISS in the fourth flight of the Freedom Dragon capsule, the Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral.
The first stage completed its second flight, landing back at Cape Canaveral. Freedom will dock with ISS tomorrow.
While most news stories will focus on the rescue aspect of this mission, its crew reduced by two so that the two astronauts launched in June on Boeing’s Starliner capsule can come home on it in February, the real news story is that with this launch the United States set a new record for the number of launches in a single year. With this launch the U.S. has completed 111 successful launches in 2024, exceeding the record set last year’s of 110 launches. And this record was achieved in less than three quarters of the year. At this rate is it very likely the U.S. will double the record of 70 set in 1966 that lasted until 2022.
China meanwhile completed its own launch late yesterday, its Long March 2D rocket placing what China’s state-run press described as “its first reusable and returnable test satellite,” designed to do orbital operations and experiments, return to Earth with those materials, and then later relaunch again. This is very similar to the commercial capsules that the startup Varda is flying and using to produce pharmaceuticals for sale.
The rocket lifted off from China’s Jiquan spaceport in northwest China. No word where its lower stages, using toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
95 SpaceX
44 China
11 Russia
11 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 111 to 67, while SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world, including American companies, 95 to 83.
SpaceX this morning launched two astronauts to ISS in the fourth flight of the Freedom Dragon capsule, the Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral.
The first stage completed its second flight, landing back at Cape Canaveral. Freedom will dock with ISS tomorrow.
While most news stories will focus on the rescue aspect of this mission, its crew reduced by two so that the two astronauts launched in June on Boeing’s Starliner capsule can come home on it in February, the real news story is that with this launch the United States set a new record for the number of launches in a single year. With this launch the U.S. has completed 111 successful launches in 2024, exceeding the record set last year’s of 110 launches. And this record was achieved in less than three quarters of the year. At this rate is it very likely the U.S. will double the record of 70 set in 1966 that lasted until 2022.
China meanwhile completed its own launch late yesterday, its Long March 2D rocket placing what China’s state-run press described as “its first reusable and returnable test satellite,” designed to do orbital operations and experiments, return to Earth with those materials, and then later relaunch again. This is very similar to the commercial capsules that the startup Varda is flying and using to produce pharmaceuticals for sale.
The rocket lifted off from China’s Jiquan spaceport in northwest China. No word where its lower stages, using toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
95 SpaceX
44 China
11 Russia
11 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 111 to 67, while SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world, including American companies, 95 to 83.