First unmanned test flight of India’s Gaganyaan capsule likely slips to next year

Artist rendering of India’s Gaganyaan capsule
Though India’s space agency ISRO still insists it will attempt the first unmanned orbital test flight of its Gaganyaan capsule before the end of 2025, its chairman has also indicated this schedule might slip into early next year due to agency’s upcoming launch schedule.
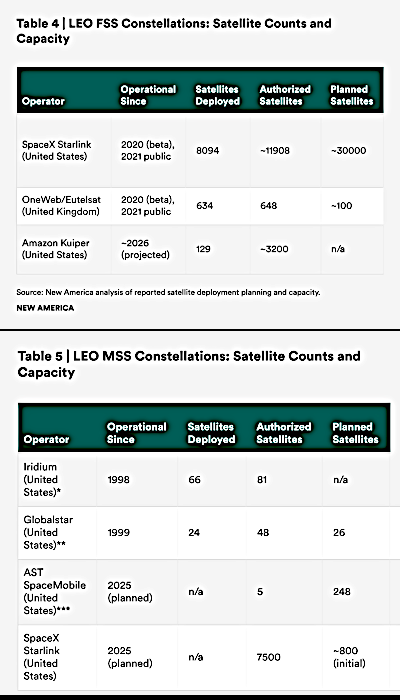
The problem is that it only has one launchpad for its largest rocket, LVM3 (recently nicknamed Bahubala) that Gaganyaan must use, and it has a contract with the American satellite company AST SpaceMoble to use Bahubala to launch one of its satellites next month. Furthermore, a Bahubala launch just occurred on that pad two days ago to launch a communications satellite for the Indian government. Thus, to do both the AST and Gaganyaan launches by the end of this year would mean it would have to do three launches from that pad in less than two months, something ISRO has never done.
ISRO plans to do at least three unmanned test flights of Gaganyaan before it attempts a manned orbital mission in 2027. If the first mission is slips into 2026, next year will be a very active one for ISRO, more active than that agency has been since it shut down during COVID.
Based on the present schedule, it appears that ISRO will set a pace of about one Bahubala launch every two months to complete this schedule, with the first Gaganyaan launch occurring around February 2026, and the next two Gaganyaan test launches in summer and fall. That would set the stage for the manned mission in early 2027.

Artist rendering of India’s Gaganyaan capsule
Though India’s space agency ISRO still insists it will attempt the first unmanned orbital test flight of its Gaganyaan capsule before the end of 2025, its chairman has also indicated this schedule might slip into early next year due to agency’s upcoming launch schedule.
The problem is that it only has one launchpad for its largest rocket, LVM3 (recently nicknamed Bahubala) that Gaganyaan must use, and it has a contract with the American satellite company AST SpaceMoble to use Bahubala to launch one of its satellites next month. Furthermore, a Bahubala launch just occurred on that pad two days ago to launch a communications satellite for the Indian government. Thus, to do both the AST and Gaganyaan launches by the end of this year would mean it would have to do three launches from that pad in less than two months, something ISRO has never done.
ISRO plans to do at least three unmanned test flights of Gaganyaan before it attempts a manned orbital mission in 2027. If the first mission is slips into 2026, next year will be a very active one for ISRO, more active than that agency has been since it shut down during COVID.
Based on the present schedule, it appears that ISRO will set a pace of about one Bahubala launch every two months to complete this schedule, with the first Gaganyaan launch occurring around February 2026, and the next two Gaganyaan test launches in summer and fall. That would set the stage for the manned mission in early 2027.