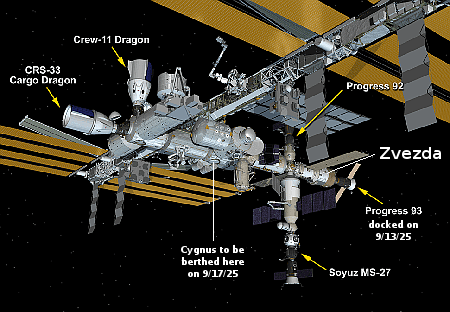
NASA cancels Sierra Space’s contract for Dream Chaser cargo missions to ISS

Tenacity grounded in a warehouse, with the
Shooting Star small cargo capsule attached to
its aft port.
NASA today announced it has modified its fixed-price cargo contract with Sierra Space, canceling the planned seven cargo missions as well as a demo docking mission, replacing this with one test flight that will simply go into orbit and then return to Earth.
After a thorough evaluation, NASA and Sierra Space have mutually agreed to modify the contract as the company determined Dream Chaser development is best served by a free flight demonstration, targeted in late 2026. Sierra Space will continue providing insight to NASA into the development of Dream Chaser, including through the flight demonstration. NASA will provide minimal support through the remainder of the development and the flight demonstration. As part of the modification, NASA is no longer obligated for a specific number of resupply missions, however, the agency may order Dream Chaser resupply flights to the space station from Sierra Space following a successful free flight as part of its current contract.
The first launch of Tenacity, the only Dream Chaser so far constructed, has been repeatedly delayed for the past two years, with no explanation from either the company or NASA. Those delays started in 2023 as engineers began the final ground testing before launch, so though we do not know what the issue is it is likely that testing found something fundamentally wrong with the spacecraft that Sierra could not afford to fix.
According to Sierra’s own press release, the company will target a late 2026 launch for that free flyer mission. The company still hopes that mission will make further flights possible, either purchased by NASA or by others wishing to use Tenacity for in-orbit manufacturing, something it first proposed last year.
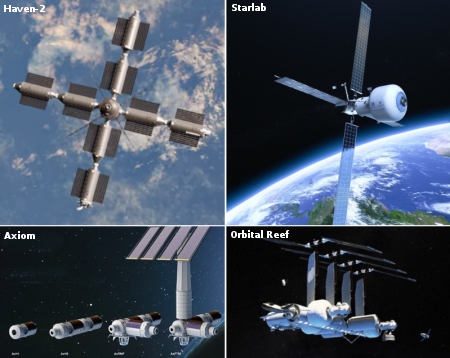
In the past two years, Sierra has shifted its focus away from commercial manned space and more towards winning military defense contracts. Part of that decision might have come from the problems with Dream Chaser. The decision might have also been fueled by the company’s generally unsatisfactory experience working with Blue Origin on their proposed Orbital Reef space station. While Sierra committed cash to develop and test its LIFE inflatable module, including a full scale prototype, Blue Origin appeared to do nothing at all. As early as September 2023 there were rumors the partnership was falling apart.

Tenacity grounded in a warehouse, with the
Shooting Star small cargo capsule attached to
its aft port.
NASA today announced it has modified its fixed-price cargo contract with Sierra Space, canceling the planned seven cargo missions as well as a demo docking mission, replacing this with one test flight that will simply go into orbit and then return to Earth.
After a thorough evaluation, NASA and Sierra Space have mutually agreed to modify the contract as the company determined Dream Chaser development is best served by a free flight demonstration, targeted in late 2026. Sierra Space will continue providing insight to NASA into the development of Dream Chaser, including through the flight demonstration. NASA will provide minimal support through the remainder of the development and the flight demonstration. As part of the modification, NASA is no longer obligated for a specific number of resupply missions, however, the agency may order Dream Chaser resupply flights to the space station from Sierra Space following a successful free flight as part of its current contract.
The first launch of Tenacity, the only Dream Chaser so far constructed, has been repeatedly delayed for the past two years, with no explanation from either the company or NASA. Those delays started in 2023 as engineers began the final ground testing before launch, so though we do not know what the issue is it is likely that testing found something fundamentally wrong with the spacecraft that Sierra could not afford to fix.
According to Sierra’s own press release, the company will target a late 2026 launch for that free flyer mission. The company still hopes that mission will make further flights possible, either purchased by NASA or by others wishing to use Tenacity for in-orbit manufacturing, something it first proposed last year.
In the past two years, Sierra has shifted its focus away from commercial manned space and more towards winning military defense contracts. Part of that decision might have come from the problems with Dream Chaser. The decision might have also been fueled by the company’s generally unsatisfactory experience working with Blue Origin on their proposed Orbital Reef space station. While Sierra committed cash to develop and test its LIFE inflatable module, including a full scale prototype, Blue Origin appeared to do nothing at all. As early as September 2023 there were rumors the partnership was falling apart.