Circular feature on Mars?
Click for full resolution image.
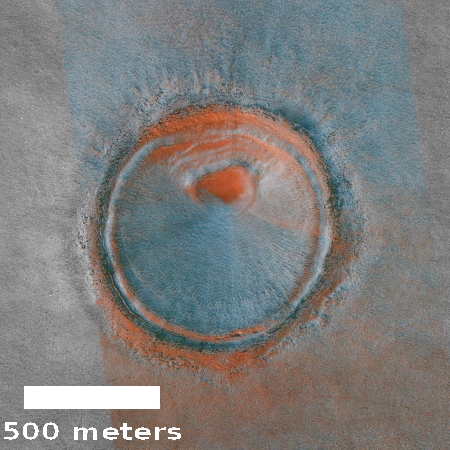
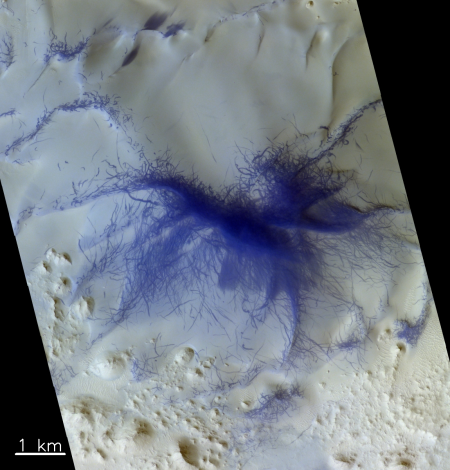
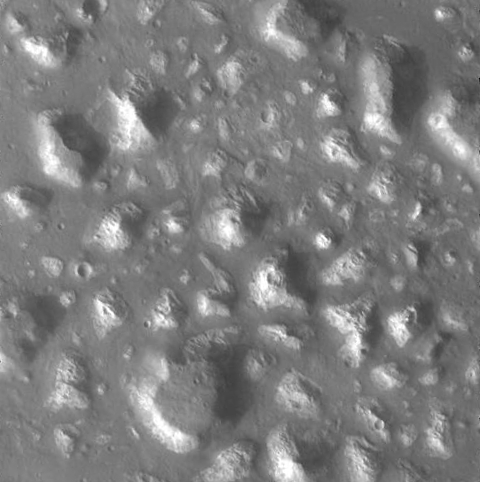
Today’s cool image is cool for two reasons. First and foremost, the image, found in the archive of the high resolution camera of Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), is titled “Circular Feature.” On the right is the full image, reduced to post here. I have searched it high and low, at low resolution as well as full resolution, and can find nothing, nothing at all, that invokes a circular feature to me.
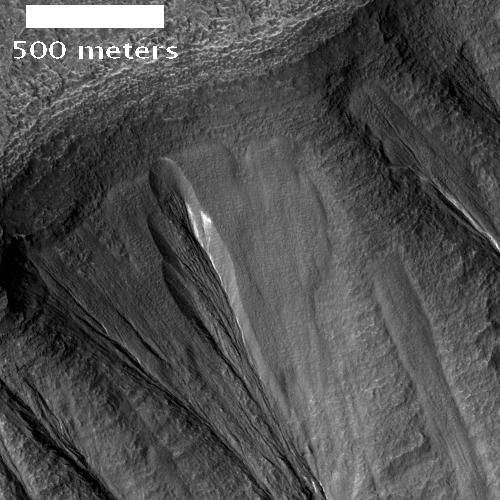
This strange terrain is located very close to the southern icecap. If anything, the knobs and features that fill this image remind me of brain terrain, partly obscured by a layer of partly melted snow or frost. Nothing however seems circular in the slightest.
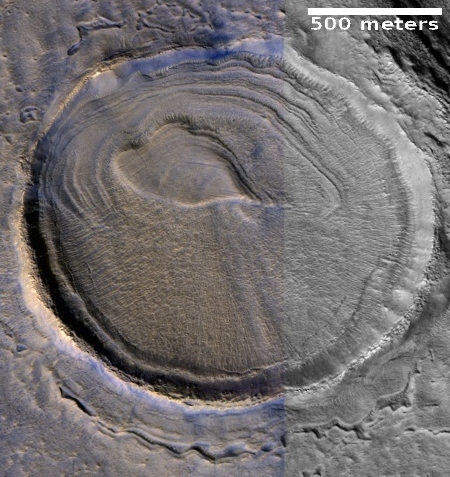
The second reason this image is cool is that it is very representative of its very large surrounding region. For what appears to be several hundred miles in all directions this is all that one can see, in a variety of MRO images, here, here, here, here, here, and here, to show only a few. Ever so often a craterlike feature pops out, like in the last example, but generally the surface continues in this undulating bland manner, endlessly. The only changing aspect is the dark streaks that cut across, likely dust devil tracks made over a long period of time.
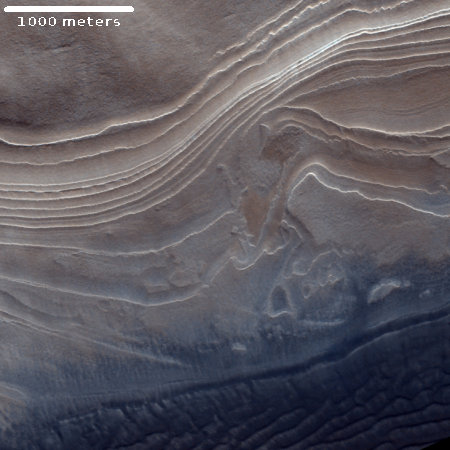
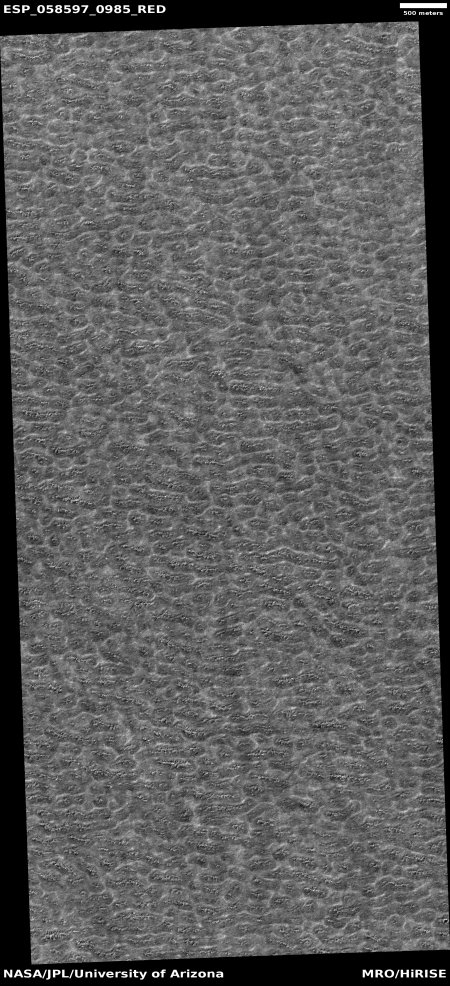
Below the fold is a section of the full resolution image, at full resolution. It doesn’t really matter where I took the crop, as anywhere in the full image everything looks pretty much the same. The only slow change that I can perceive is that the surface seems to be descending to the north, with the lighter areas implying the existence of terraces.
Take a look, and try to figure out for yourself what is going on here.
» Read more

Click for full resolution image.
Today’s cool image is cool for two reasons. First and foremost, the image, found in the archive of the high resolution camera of Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), is titled “Circular Feature.” On the right is the full image, reduced to post here. I have searched it high and low, at low resolution as well as full resolution, and can find nothing, nothing at all, that invokes a circular feature to me.
This strange terrain is located very close to the southern icecap. If anything, the knobs and features that fill this image remind me of brain terrain, partly obscured by a layer of partly melted snow or frost. Nothing however seems circular in the slightest.
The second reason this image is cool is that it is very representative of its very large surrounding region. For what appears to be several hundred miles in all directions this is all that one can see, in a variety of MRO images, here, here, here, here, here, and here, to show only a few. Ever so often a craterlike feature pops out, like in the last example, but generally the surface continues in this undulating bland manner, endlessly. The only changing aspect is the dark streaks that cut across, likely dust devil tracks made over a long period of time.
Below the fold is a section of the full resolution image, at full resolution. It doesn’t really matter where I took the crop, as anywhere in the full image everything looks pretty much the same. The only slow change that I can perceive is that the surface seems to be descending to the north, with the lighter areas implying the existence of terraces.
Take a look, and try to figure out for yourself what is going on here.
» Read more