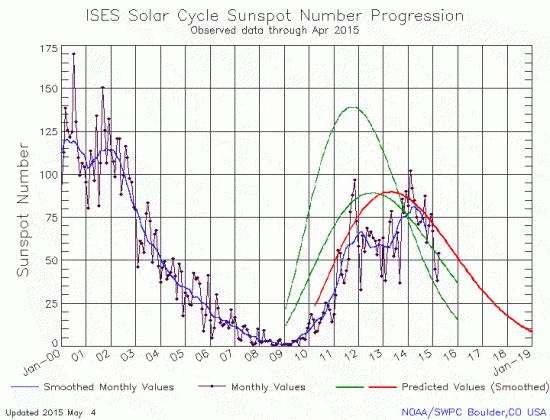
The uncertainty of science: Using new data gathered by the 10-meter Keck telescope in Hawaii, astronomers have found that the outer stars of elliptical galaxies exhibit the same behavior as the outer stars of spirals, suggesting once again the existence of dark matter.
One of the most important scientific discoveries of the 20th century was that the spectacular spiral galaxies, such as our own Milky Way, rotate much faster than expected, powered by [the] extra gravitational force of invisible “dark matter” as it is now called. Since this discovery 40 years ago, we have learned that this mysterious substance, which is probably an exotic elementary particle, makes up about 85 percent of the mass in the Universe, leaving only 15 percent to be the ordinary stuff encountered in our everyday lives. Dark matter is central to our understanding of how galaxies form and evolve – and is ultimately one of the reasons for the existence of life on Earth – yet we know almost nothing about it.
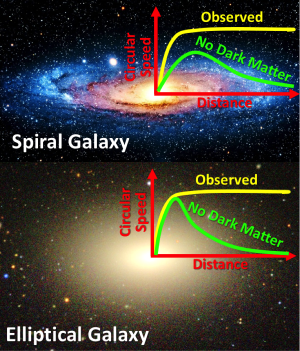
“The surprising finding of our study was that elliptical galaxies maintain a remarkably constant circular speed out to large distances from their centers, in the same way that spiral galaxies are already known to do,” said Cappellari. “This means that in these very different types of galaxies, stars and dark matter conspire to redistribute themselves to produce this effect, with stars dominating in the inner regions of the galaxies, and a gradual shift in the outer regions to dark matter dominance.”
What is most fascinating about this press release, however, is that it also noted that dark matter is only one explanation for the data, and that the failure of Newtonian physics at large distances, instead of dark matter, might also provide an explanation.
However, the [solution] does not come out naturally from models of dark matter, and some disturbing fine-tuning is required to explain the observations. For this reason, the [problem] even led some authors to suggest that, rather than being due to dark matter, it may be due to Newton’s law of gravity becoming progressively less accurate at large distances. Remarkably, decades after it was proposed, this alternative theory (without dark matter) still cannot be conclusively ruled out.
Physicists call this other theory MOND, for modified Newtonian dynamics. It is not a very popular theory, however, and is almost always ignored, even though it appears to work as well as dark matter to explain the motion of stars in galaxies. Instead, most scientists favor dark matter.
For this press release to mention it as suggests the new data favors it over dark matter, which would make this a significant discovery.